Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1365–1382) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s disease (SjD) is typically diagnosed by the presence of an anti-SSA antibody or focal lymphocytic sialadenitis in salivary gland tissue. Among SjD patients who are anti-SSA antibody negative (SSA-), a salivary gland biopsy is required for diagnosis. Our objective was to identify novel autoantibodies to non-invasively diagnose SSA- SjD.
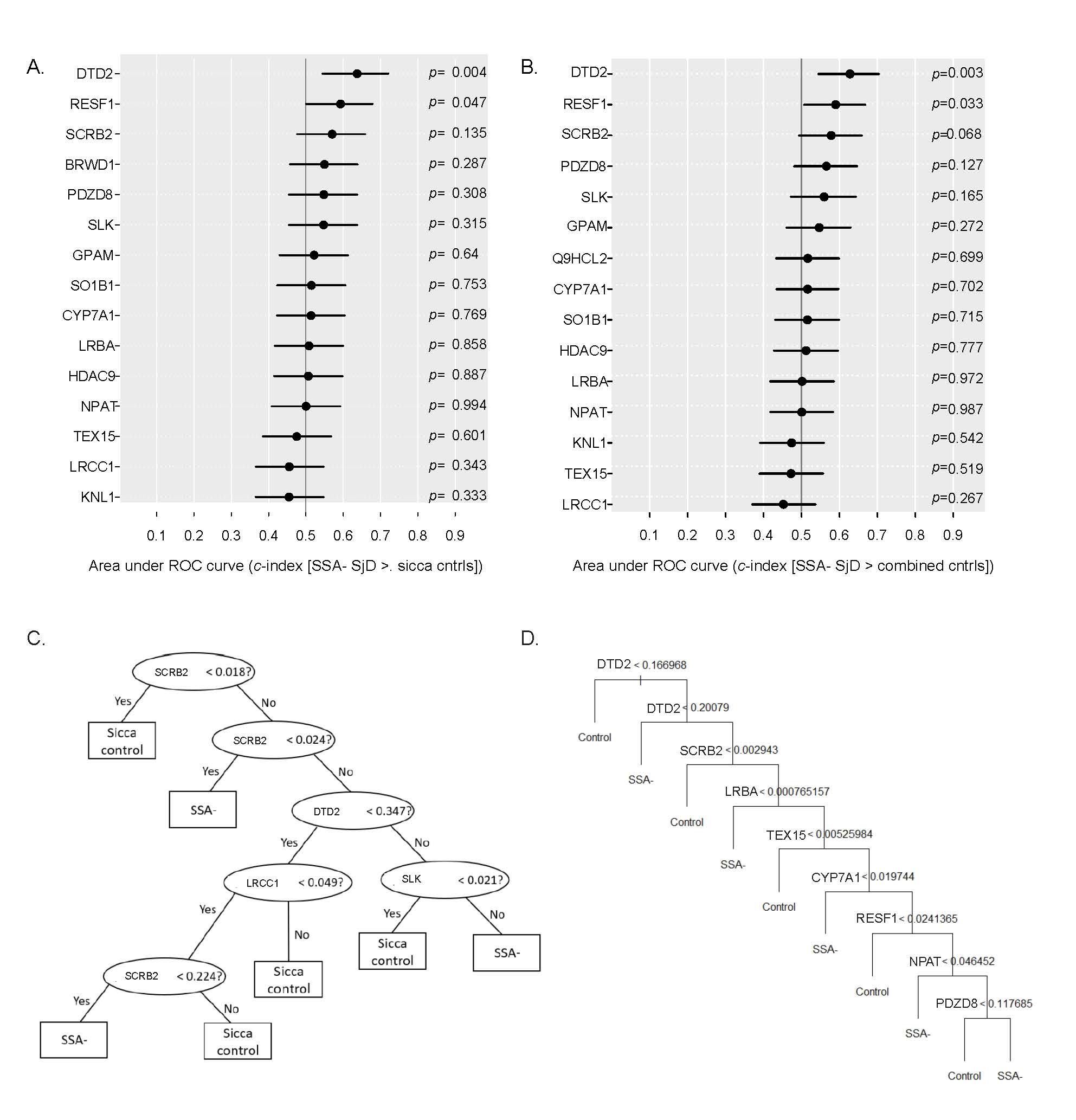
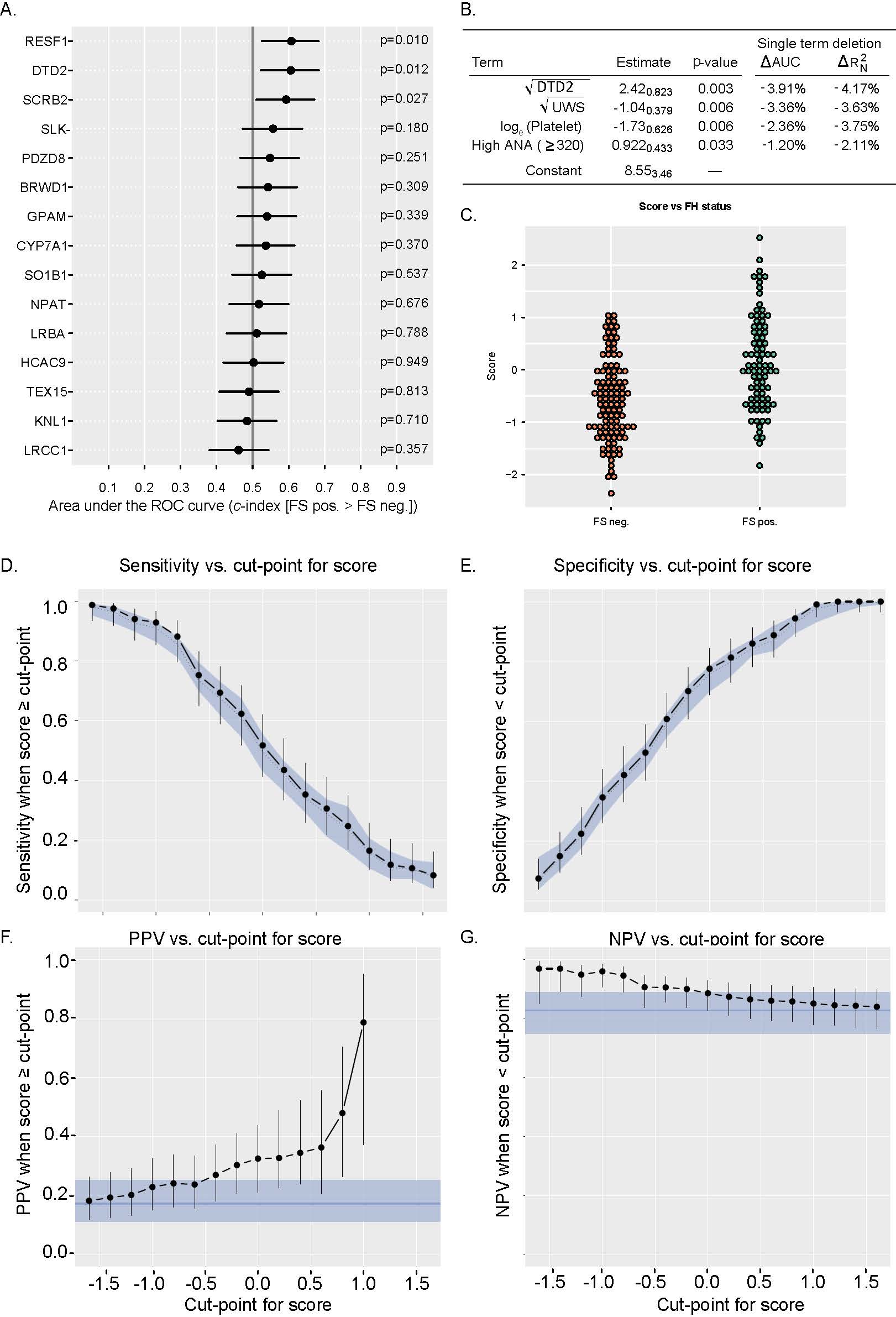
Methods: IgG binding to a high density whole human peptidome array was quantified using sera from SSA- SjD (n=8) cases and age- and sex-matched healthy controls (n=8). The highest bound peptides from the array were confirmed by ELISA. Fifteen peptides were selected for external validation by ELISA using an independent cohort of subjects that were age-, sex-, and race-matched from the SICCA biorepository: SSA- SjD subjects (met 2016 ACR/EULAR criteria for SjD; n=76), sicca controls (sicca with negative ANA, rheumatoid factor, SSA, and focus score < 1; n=75), and autoimmune controls (positive ANA [≥1:320], rheumatoid factor, or SSA, but failed to meet 2016 ACR/EULAR criteria for SjD; n=41). Among all subjects, 85/192 (44.3%) had a positive focus score (FS ≥1). Peptide abundance was compared between groups using area under the ROC curve (c-index; AUC). Binary decision trees using R trees package were used to generate models predictive of SjD vs. controls. Adaptive Lasso was used for variable selection for binary logistic regression models.
Results: IgG against a peptide from DTD2 (D-aminoacyl-tRNA deacylase 2) and RESF1 (retroelement silencing factor 1) was bound more in SSA- SjD than in sicca controls (p=.004; p=0.045; Fig 1a) and more in SSA- SjD than in combined controls (sicca and autoimmune) (p=0.003, p=0.03; Fig 1b). The top performing classification tree model discriminating SjD vs. sicca control included peptides from proteins SCRB2, DTD2, LRCC1, and SLK (65% accurate on validation set; Fig 1c). The top performing tree (55% accuracy upon validation) to discriminate between SjD and sicca controls involved peptides from proteins DTD2, SCRB2, CYP7A1, LRCC1, and KNL1. The top performing (62% accuracy upon validation) to discriminate between SjD and combined controls included peptides from proteins DTD2, RESF1, SCRB2, LRBA, TEX15, CYP7A1, NPAT, and PDZD8 (Fig 1d). Next, we defined if we could predict a positive FS. IgG against peptides from proteins RESF1, DTD2, and SCRB2 were bound more in patients with FS positive vs. negative (p=.010; p=0.012; p=0.027; Figure 2a). We incorporated peptide binding into a regression model with clinical variables including platelet count, SSB, ANA≥1:320, rheumatoid factor, and unstimulated whole salivary flow. Our dependent variable was FS (positive vs. negative). The final model showed good discrimination between FS positive vs. negative (Fig 2b-c). The AUC for this model is 71.6% (95% CI 63.9-78.2%) and allows flexibility to optimize for specificity, sensitivity, and positive and negative predictive value (Fig 2d-g).
Conclusion: We present novel autoantibodies inSSA- SjD compared to autoimmune- and sicca-controls that can be used to predict an abnormal FS on labial salivary gland biopsy with good predictive value.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parker M, Zheng Z, Lasarev M, Alexandridis R, Newton M, Shelef M, McCoy S. Novel Autoantibodies Might Circumvent the Need for Labial Biopsy in a Subset of Seronegative Sjögren’s Disease Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-autoantibodies-might-circumvent-the-need-for-labial-biopsy-in-a-subset-of-seronegative-sjogrens-disease-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-autoantibodies-might-circumvent-the-need-for-labial-biopsy-in-a-subset-of-seronegative-sjogrens-disease-patients/