Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: SjD disease (SjD) is typically diagnosed by the presence of an anti-SSA antibody or focal lymphocytic sialadenitis in salivary gland tissue. Among SjD patients who are anti-SSA antibody negative (SSA-), a salivary gland biopsy is required for diagnosis. Our objective was to identify novel autoantibodies as a non-invasive means to diagnose SSA- SjD.
Methods: Using sera from SSA- SjD (n=8) and age- sex-matched healthy controls (n=8), IgG binding to a high density whole human peptidome array was quantified. The highest bound peptides from the array, as defined by MixTwice method, were internally validated by ELISA using sera from the same subjects. Based on results from internal validation, 12 peptides were selected for ELISA external validation using sera from the following age-, sex-, and race-matched groups from the SICCA biorepository: SSA- SjD subjects (meet 2016 ACR/EULAR criteria for SjD; n=76), sicca controls (sicca with negative ANA, rheumatoid factor, SSA, and focus score < 1; n=75), and autoimmune controls (positive ANA (≥1:320), rheumatoid factor, or SSA, but fail to meet 2016 ACR/EULAR criteria for SjD; n=38). ELISA results were compared using parametric testing for sample sizes ≥15 and likelihood ratio chi-square for categorical variables. We performed adaptive shrinkage with Lasso regression to select peptides for a random forest model to predict SSA- SjD.
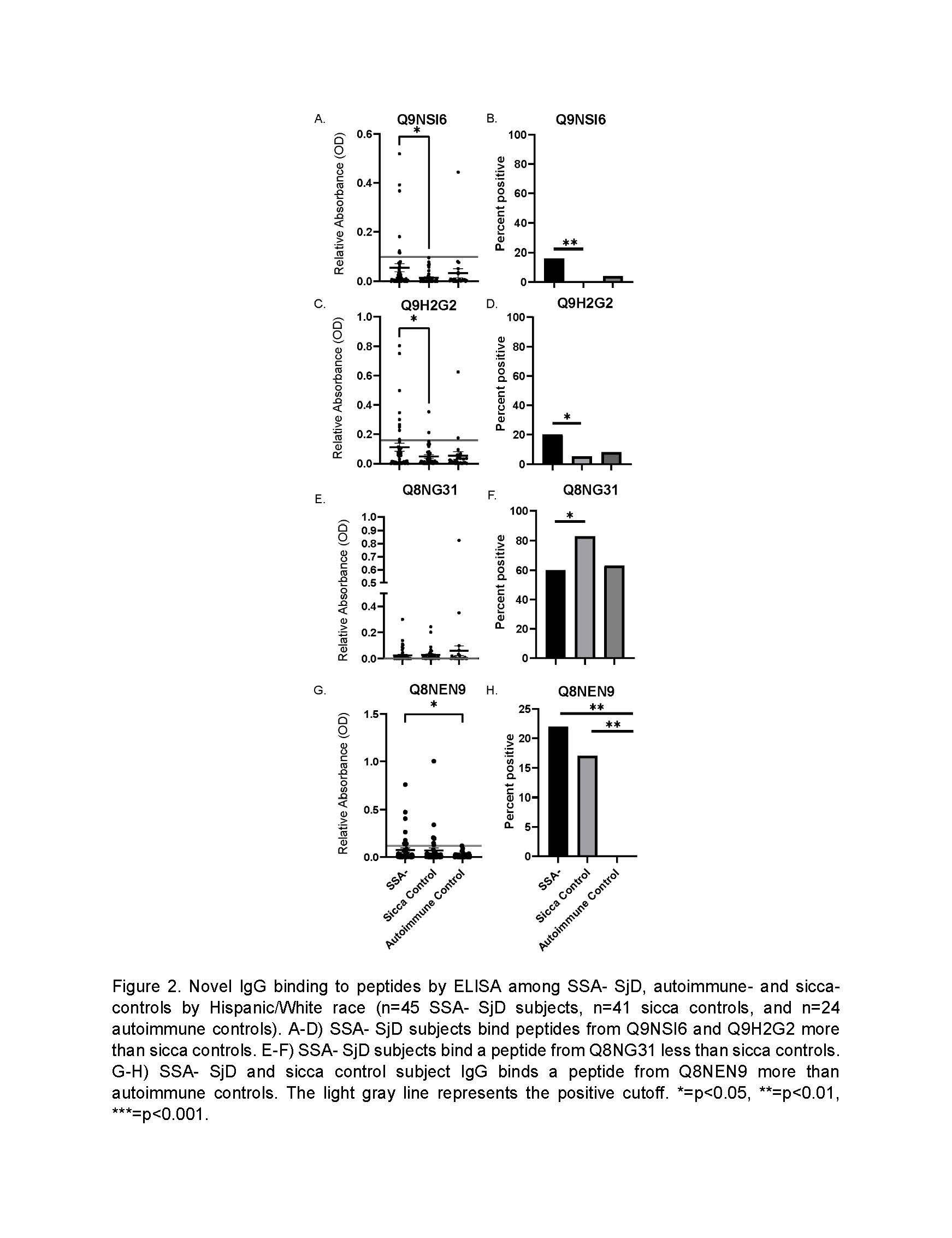
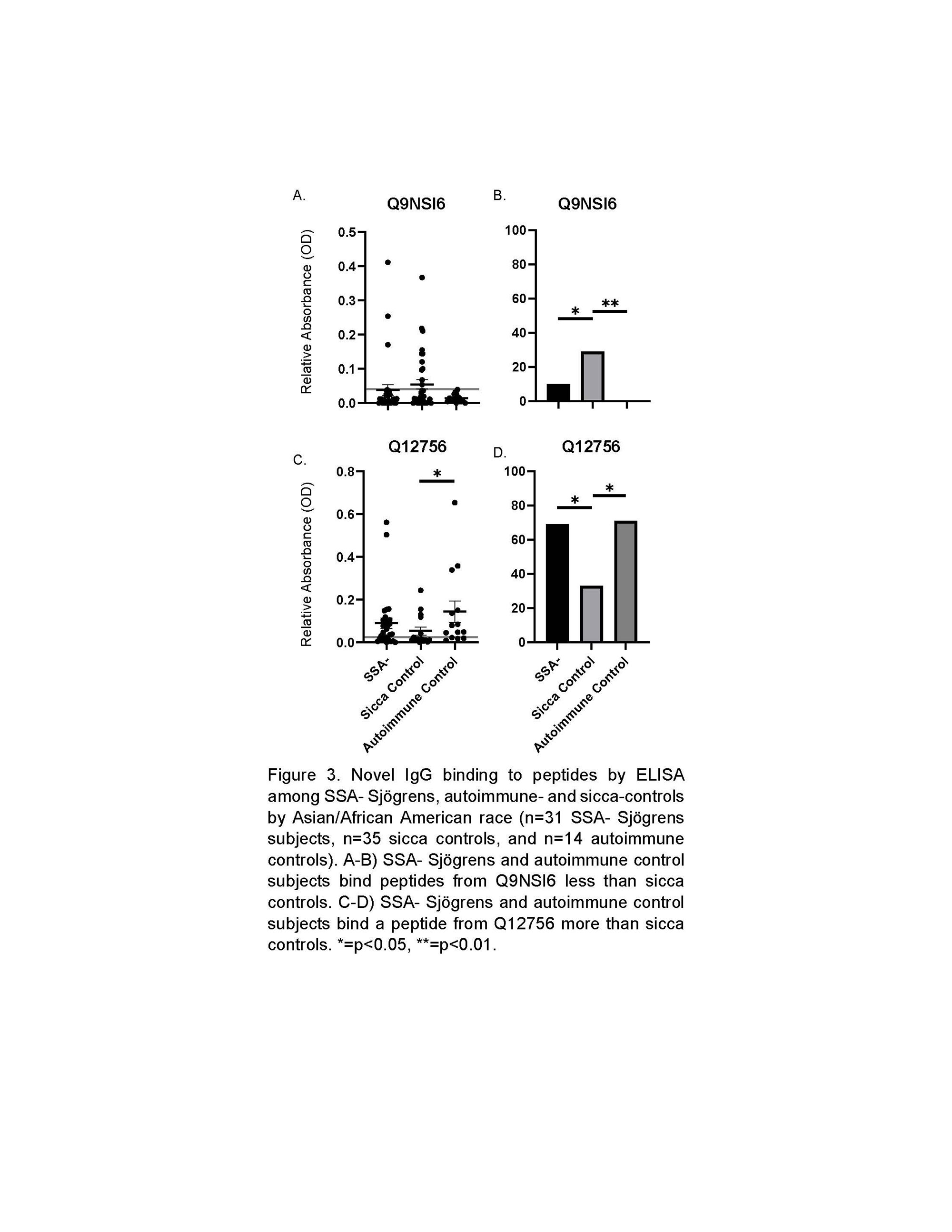
Results: IgG against a peptide from Q8NEN9 (PDZ domain-containing protein 8) was greater in SSA- SjD and sicca controls than autoimmune controls (p< 0.001 and 0.02, respectively; Figure 1). IgG against Q9NSI6 (Bromodomain and WD repeat-containing protein 1) and Q9H2G2 (STE-like serine/threonine-protein kinase) was higher in SSA- SjD than sicca controls among White/Hispanic subjects (p=0.02 and p=0.03, respectively; Figure 2). After defining positive cutoffs, Q9NSI6 and Q9H2G2 were positive more in SSA- SjD than sicca controls (16% vs. 0 [p=0.0002] and 20% vs. 5% [p=0.03], respectively) in White/Hispanic subjects. We also found IgG bound Q8NG31 (Kinetochore scaffold 1) less in SSA- SjD than sicca controls (60% vs. 89% positive, respectively; p=0.02). IgG from SjD and sicca control subjects binds a Q8NEN9 peptide more than autoimmune controls. We included eight peptides in our random forest model and achieved an area under the receiver operator curve of 0.97 to predict SSA- SjD among White/Hispanic subjects. Among Asian/African American subjects, IgG binding to peptides from Q9NSI6 and Q12756 (Kinesin-like protein KIF1A) differed between SSA- SjD, autoimmune, and sicca controls (Figure 3).
Conclusion: We present novel autoantibodies unique to SSA- SjD compared to autoimmune- and sicca-controls. These antibodies have good predictive value amongst Whites/Hispanic subjects for SjD. Future directions include performing further modeling in validation cohorts and discerning associations between autoantibodies and SjD characteristics.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parker M, Zheng Z, Parker Q, Vande Loo A, Newton M, Shelef M, McCoy S. Novel Autoantibodies Identified in Seronegative Sjögren’s Disease Using Innovative Whole Peptidome Array Technology [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-autoantibodies-identified-in-seronegative-sjogrens-disease-using-innovative-whole-peptidome-array-technology/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-autoantibodies-identified-in-seronegative-sjogrens-disease-using-innovative-whole-peptidome-array-technology/