Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0691–0721) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immunoglobulin A Vasculitis (IgAV) is a B-cell-mediated inflammatory disease. NF-kappa B (NF-kB) plays a key role in autoimmunity and inflammation1. In this regard, the development of B-cells is described as dependent on the activation of NF-kB2. In addition, NFKB1 (gene encoding NF-kB) is described as a shared risk locus for several immune-mediated diseases3. Specifically, NFKB1 is crucial in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy4,5, a disease that shares molecular mechanisms with IgAV. Accordingly, we aimed to determine whether NFKB1 and NFKBIA (gene encoding the NF-kB Inhibitor Alpha) represent novel genetic risk factors for IgAV.
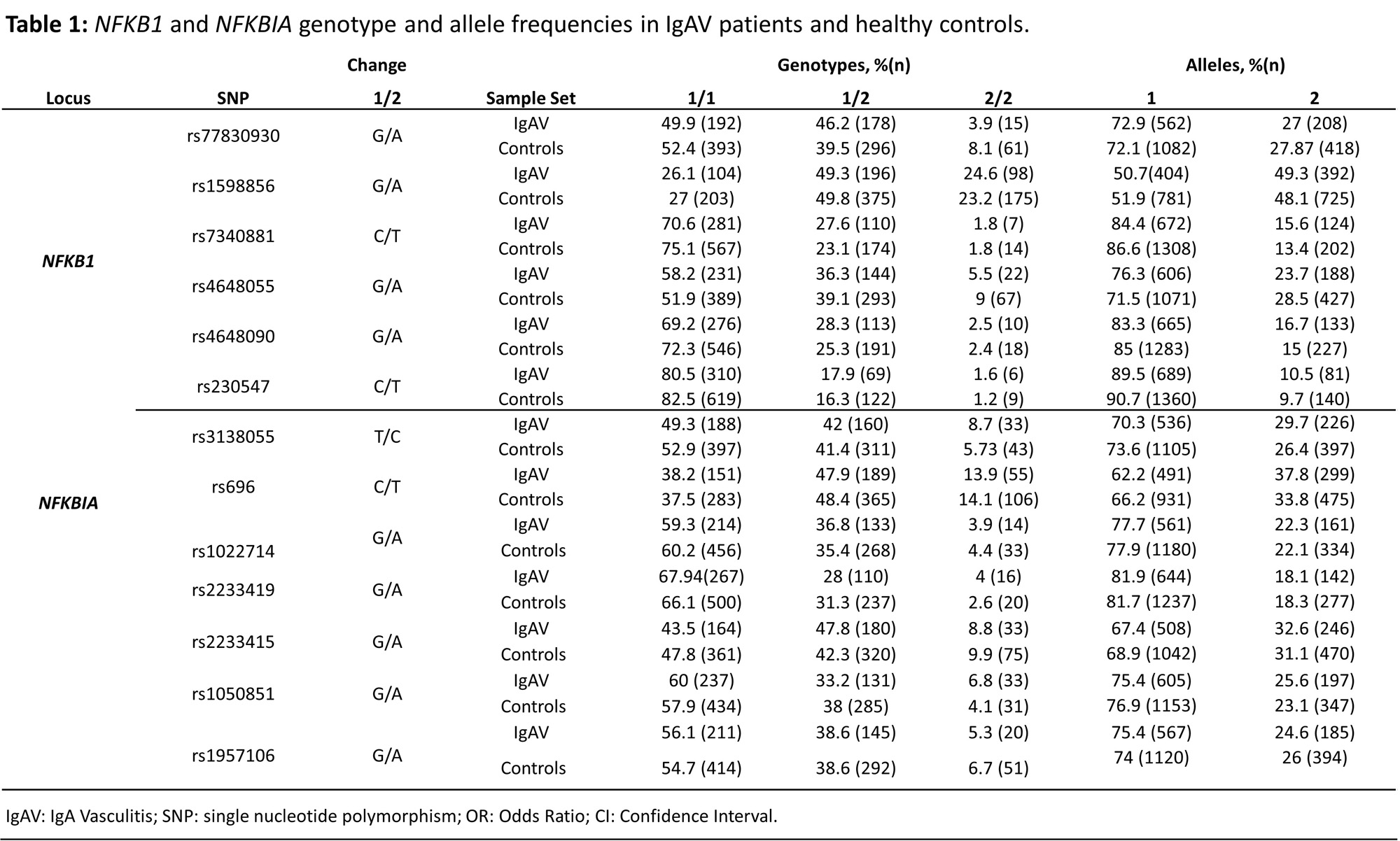
Methods: 410 patients with IgAV, the largest series of Caucasian patients with IgAV ever assessed for genetic studies, and 764 healthy ethnically matched controls, were recruited for this study. Six tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within NFKB1 (rs77830930, rs1598856, rs7340881, rs4648055, rs4648090 and rs230547) and 7 NFKBIA tag SNPs (rs3138055, rs696, rs1022714, rs2233419, rs2233415, rs1050851 and rs1957106) were genotyped using TaqMan Probes. P-values were corrected with the FDR method for multiple testing.
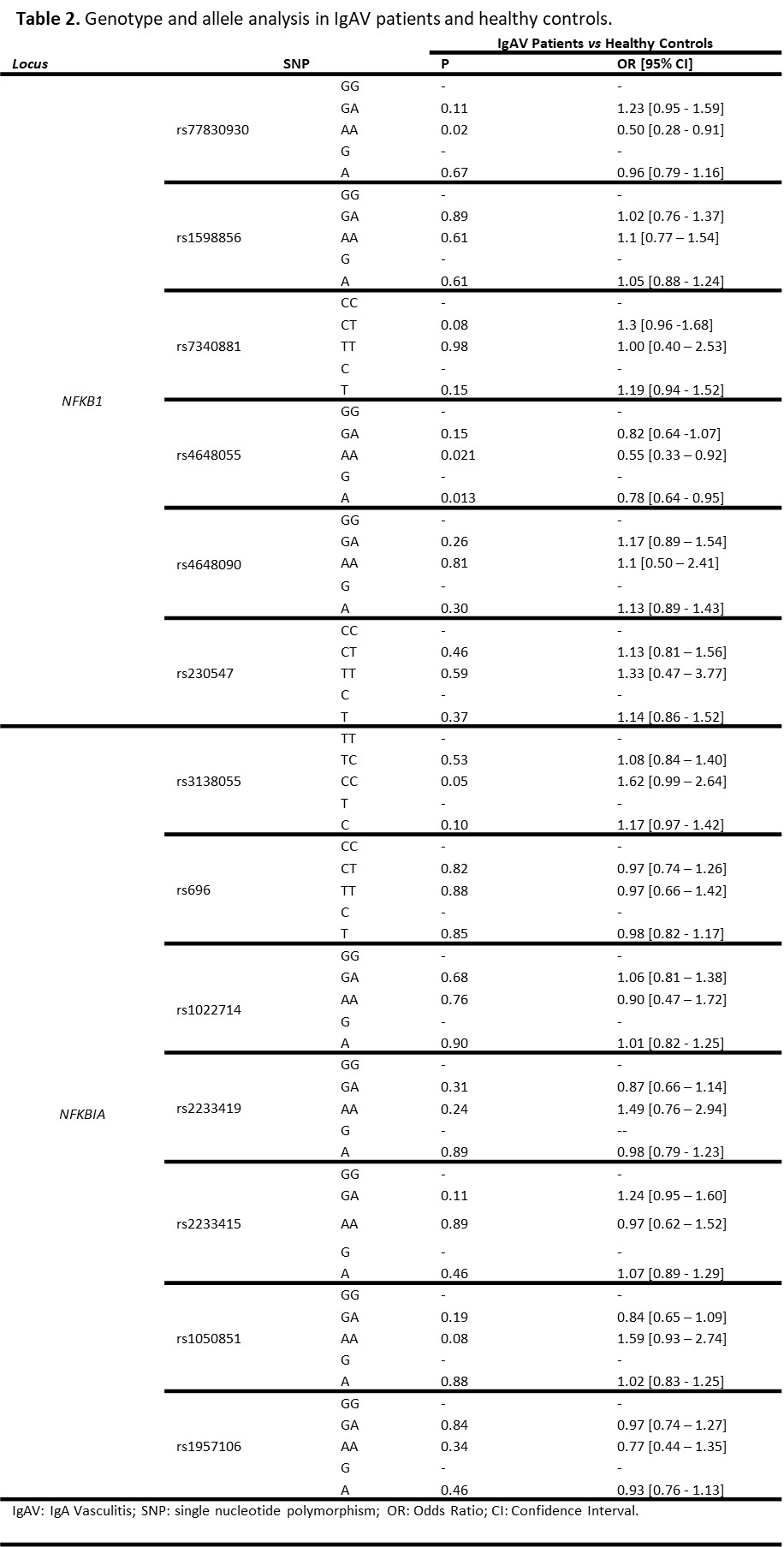
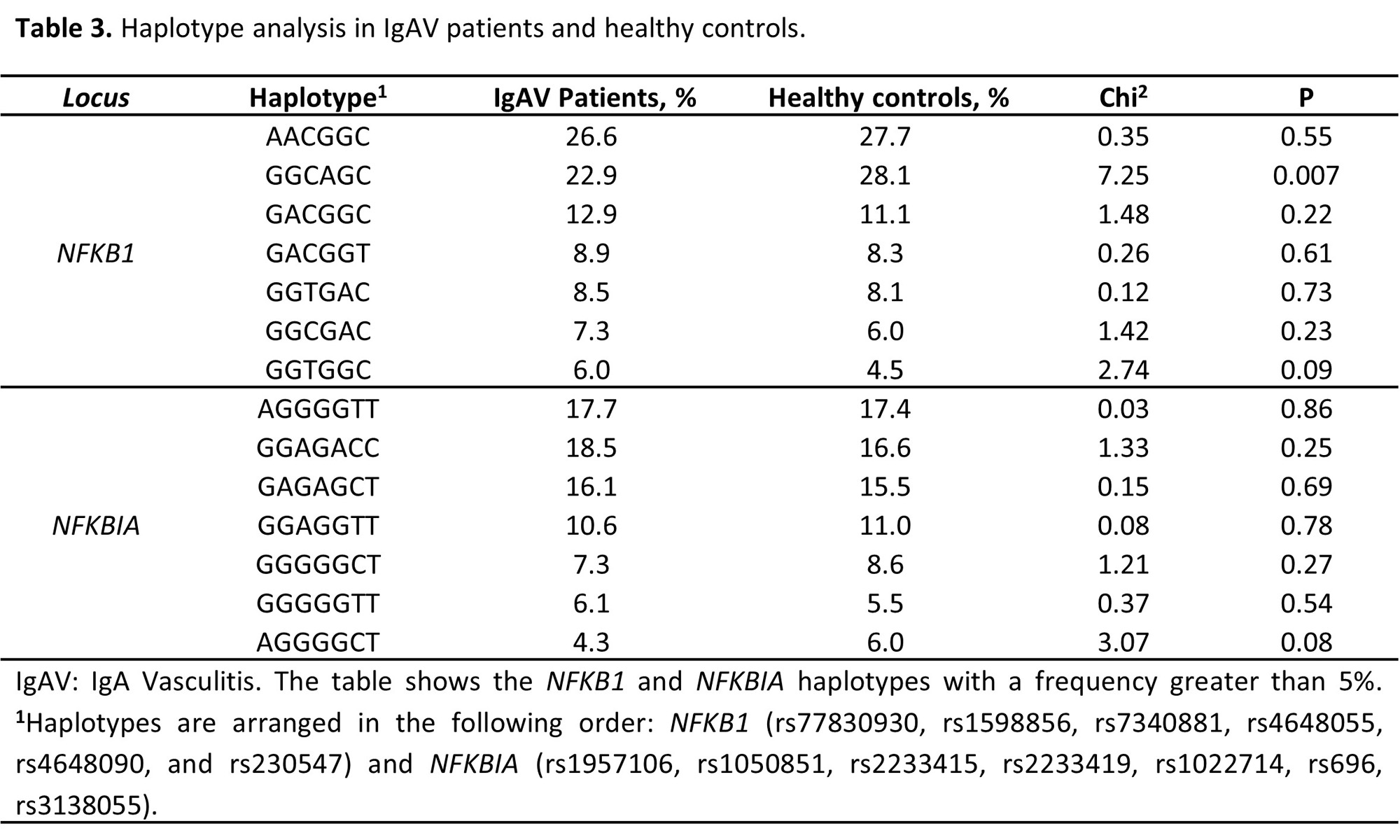
Results: A statistically significant decrease of NFKB1 rs4648055 A allele was disclosed in patients with IgAV when compared to controls (p=0.013 OR=0.78 [0.64 – 0.95], Tables 1 and 2). Additionally, a statistically significant decrease in the NFKB1 GGCAGC haplotype was observed in IgAV patients compared to controls (p=0.007, Table 3). These results were not significant after FDR correction. No other statistically significant results were found in NFKB1 and NFKBIA genotype, allele, or haplotype frequencies between patients with IgAV and controls (Tables 1-3), nor when IgAV patients were stratified according to the age at disease onset or the presence/absence of gastrointestinal or renal manifestations (data not shown).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that NFKB1 and NFKBIA do not seem to be involved in the pathogenesis of IgAV.
References:[1] N Engl J Med 1997;336:1066-71; [2] Nat Immunol 2003;4:274-9; [3] Hum Mol Genet 2004;13:35-45; [4] Front Immunol 2019;10:815.; [5] Cell Biosci 2015;5:63.
This research was funded by European Union FEDER funds and “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias” from “Instituto de Salud Carlos III” (ISCIII, Health Ministry, Spain), grant number PI18/00042 and PI21/00042. JCB-L is a recipient of a PFIS programme fellowship from the ISCIII, co-funded by the European Social Fund (“Investing in your future”), grant number FI22/00020. VP-C is supported by funds of “Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias” from ISCIII, grant number PI18/00042. MSM-G is supported by funds from IDIVAL, grant number TRANSVAL22/01. RL-M is a recipient of a Miguel Servet type II program fellowship from the ISCIII, co-funded by ESF (“Investing in your future”), grant number CPII21/00004.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Batista-Liz J, Pulito-Cueto V, Sebastián Mora-Gil M, Sevilla-Pérez B, Teresa Leonardo M, Ortego-Centeno N, Peñalba A, Narvaez J, martin penagos l, Rodrigo E, Belmar-Vega L, Gomez-Fernandez C, Caminal-Montero L, Collado P, Uriarte-Ecenarro M, Vicente Rabaneda E, Rubio E, León Luque M, Blanco-Madrigal J, Galindez-Agirregoikoa E, Castañeda S, Gonzalez-Gay M, Blanco R, López-Mejías R. NFKB1 and NFKBIA: Relevant Players in the Pathogenesis of IgA Vasculitis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nfkb1-and-nfkbia-relevant-players-in-the-pathogenesis-of-iga-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nfkb1-and-nfkbia-relevant-players-in-the-pathogenesis-of-iga-vasculitis/