Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is one of the main causes of death in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients [1]. Early diagnosis of RA-ILD+ is critical to avoid irreversible lung damage in these patients [1], but no definitive serum biomarkers are available to identify this disease. Lung fibrosis development in RA is accompanied by a dysbalanced tissue remodeling process controlled by various proteolytic enzymes. The matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of zinc- and calcium-dependent endopeptidases that can degrade all major connective tissue matrices and are regulated by their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) [2]. These proteins have previously been involved in the development of several autoimmune diseases (AD) and lung complications, including ILD [2-4]. However, it is unclear which MMPs and TIMPs may be involved in extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in RA-ILD+.
Accordingly, this study aimed to investigate whether certain MMPs and TIMPs could be potential biomarkers reflecting the lung fibrotic process specifically in RA patients.
Methods: Peripheral venous blood was collected from 49 RA-ILD+ patients and three comparative groups: 25 RA-ILD– patients, 53 patients with other AD-ILD+, and 39 idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patients. Serum levels of MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-9, MMP-10, MMP-12, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 were measured by using a chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay and analyzed in the Fujirebio Lumipulse G600 II instrument.
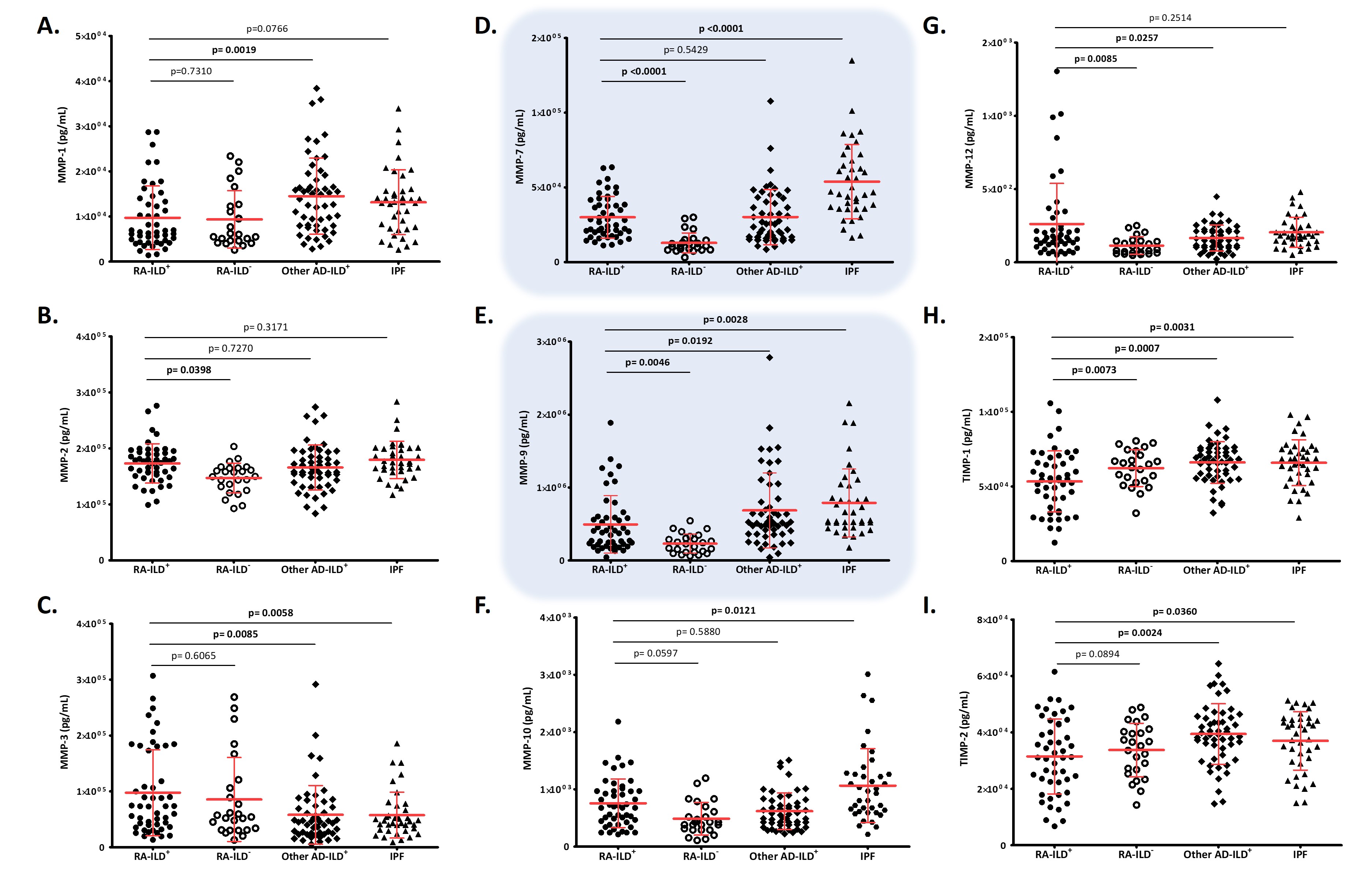
Results: Firstly, RA-ILD+ patients presented increased levels of MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, and MMP-12 in relation to RA-ILD– patients (p=0.0398, p< 0.0001, p=0.0046 and p=0.0085, respectively; Figure 1B, 1D, 1E, 1G). For TIMP-1, RA-ILD+ patients showed lower levels than RA-ILD– patients (p=0.0073; Figure 1H).
Secondly, a decreased of MMP-1, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 serum levels were found in patients with RA-ILD+ compared to those with other AD-ILD+ (p=0.0019, p=0.0192, p=0.0007 and p=0.0024, respectively; Figure 1A, 1E, 1H, 1I). Regarding MMP-3 and MMP-12, patients with RA-ILD+ exhibited higher levels than those with other AD-ILD+ (p=0.0085 and p=0.00257, respectively; Figure 1C, 1G).
Thirdly, the MMP-7, MMP-9, MMP-10, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 levels were decreased in patients with RA-ILD+ in relation to those with IPF (p< 0.0001, p=0.0028, p=0.0121, p=0.0031 and p=0.0360; respectively, Figure 1D, 1E, 1F, 1H, 1I). About MMP-3, patients with RA-ILD+ showed increased levels compared with IPF patients (p=0.0058, Figure 1C).
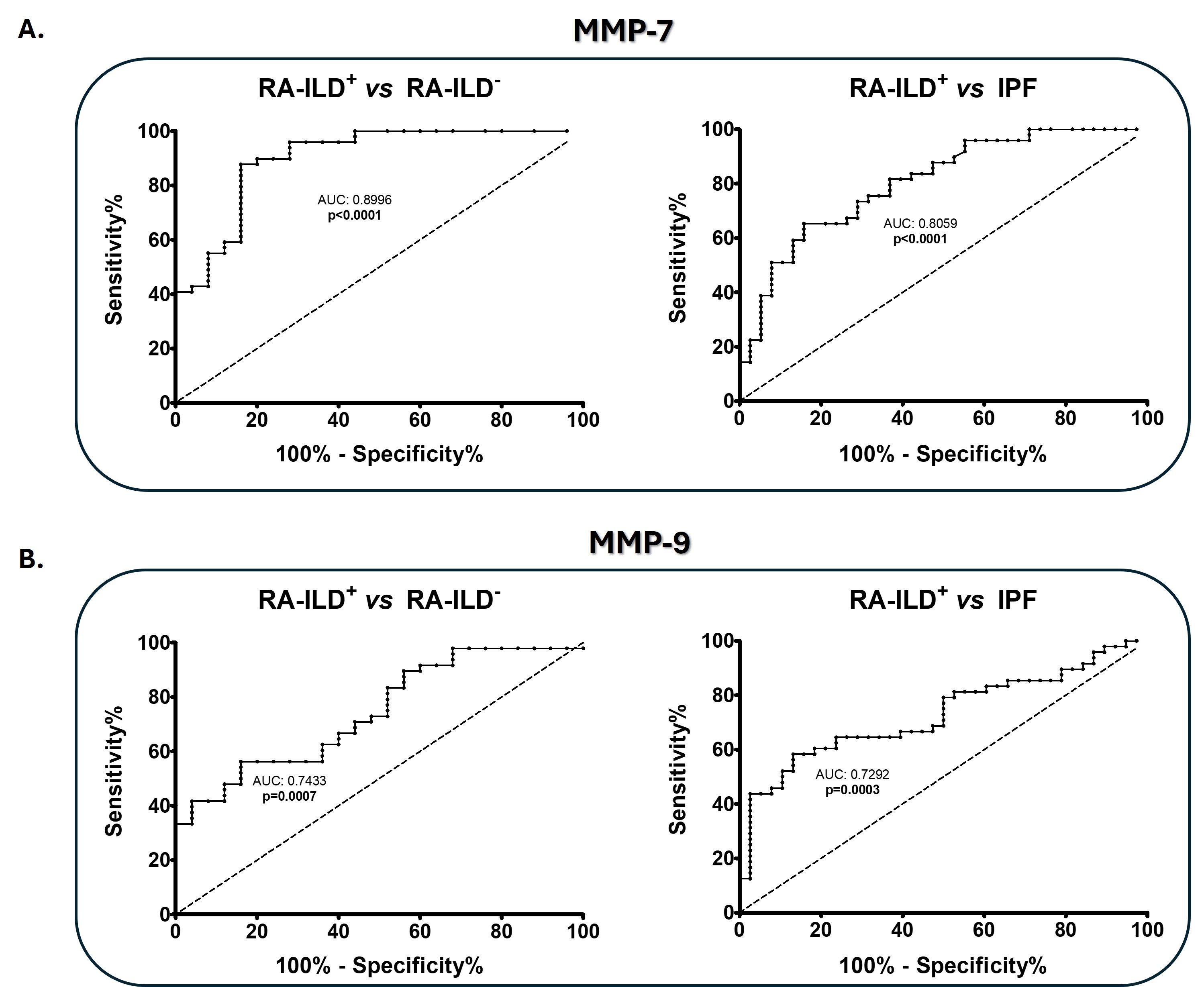
Interestingly, the ability of MMP-7 and MMP-9 levels to discriminate patients with RA-ILD+ from RA-ILD– and IPF was further confirmed by ROC curves (Figure 2A and 2B, respectively).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that MMPs and TIMPs play a relevant role in lung tissue remodeling in RA-ILD+. Interestingly, MMP-7 and 9 increase progressively with the presence and severity of lung involvement, standing out as promising blood biomarkers for the early and accurate diagnosis of RA-ILD+.
References: [1] Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021;17(5):485-497; [2] Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(6):1064-72; [3] PLoS Med. 2008;5(4):e93; [4] Front Pharmacol. 2022:13:805708.
Personal funds, JCB-L:FI22/00020(ISCIII-ESF); RL-M:CPII21/00004(ISCIII-ESF)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pulito-Cueto V, Atienza-Mateo B, Ocejo-Viñals g, Mora-Cuesta V, Iturbe-Fernández D, Batista-Liz J, Sebastián Mora-Gil M, Renuncio-García M, González López E, Cifrián J, Blanco-Alonso R, Lopez-mejias R. New Approach for Early and Accurate Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis-related Interstitial Lung Disease: Matrix Metalloproteinases 7 and 9 as Novel Blood Biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/new-approach-for-early-and-accurate-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-interstitial-lung-disease-matrix-metalloproteinases-7-and-9-as-novel-blood-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/new-approach-for-early-and-accurate-diagnosis-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-related-interstitial-lung-disease-matrix-metalloproteinases-7-and-9-as-novel-blood-biomarkers/