Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatment I: Preventative and Novel Treatments (1674–1679)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:15PM-1:30PM
Background/Purpose: A substantial number of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) experience treatment failure, incomplete response, or intolerance to TNFis (TNFi-IR). Neuroimmune modulation using an implantable neurostimulator device to electrically stimulate the left cervical vagus nerve is an emerging therapeutic approach for such patients. We present a TNFi-IR subgroup analysis from the RESET-RA study (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04539964).
Methods: RESET-RA is a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled study that enrolled 242 patients at 41 sites in the U.S. with moderate to severe RA, and an inadequate response or intolerance to at least 1 prior biological or targeted-synthetic DMARD. All patients were implanted with an integrated neurostimulator device and randomized 1:1 to receive either active stimulation (treatment) or sham. The primary endpoint of ACR20 response was assessed at 3 months. After 3 months, all patients crossed over to receive active stimulation during an open-label follow-up period, with results reported through 12 months. A subgroup analysis for patients only having prior exposure to TNFi therapies was performed to assess efficacy outcomes, including ACR20/50/70 response, improvement in disease activity, and adjunctive drug use in combination with stimulation.
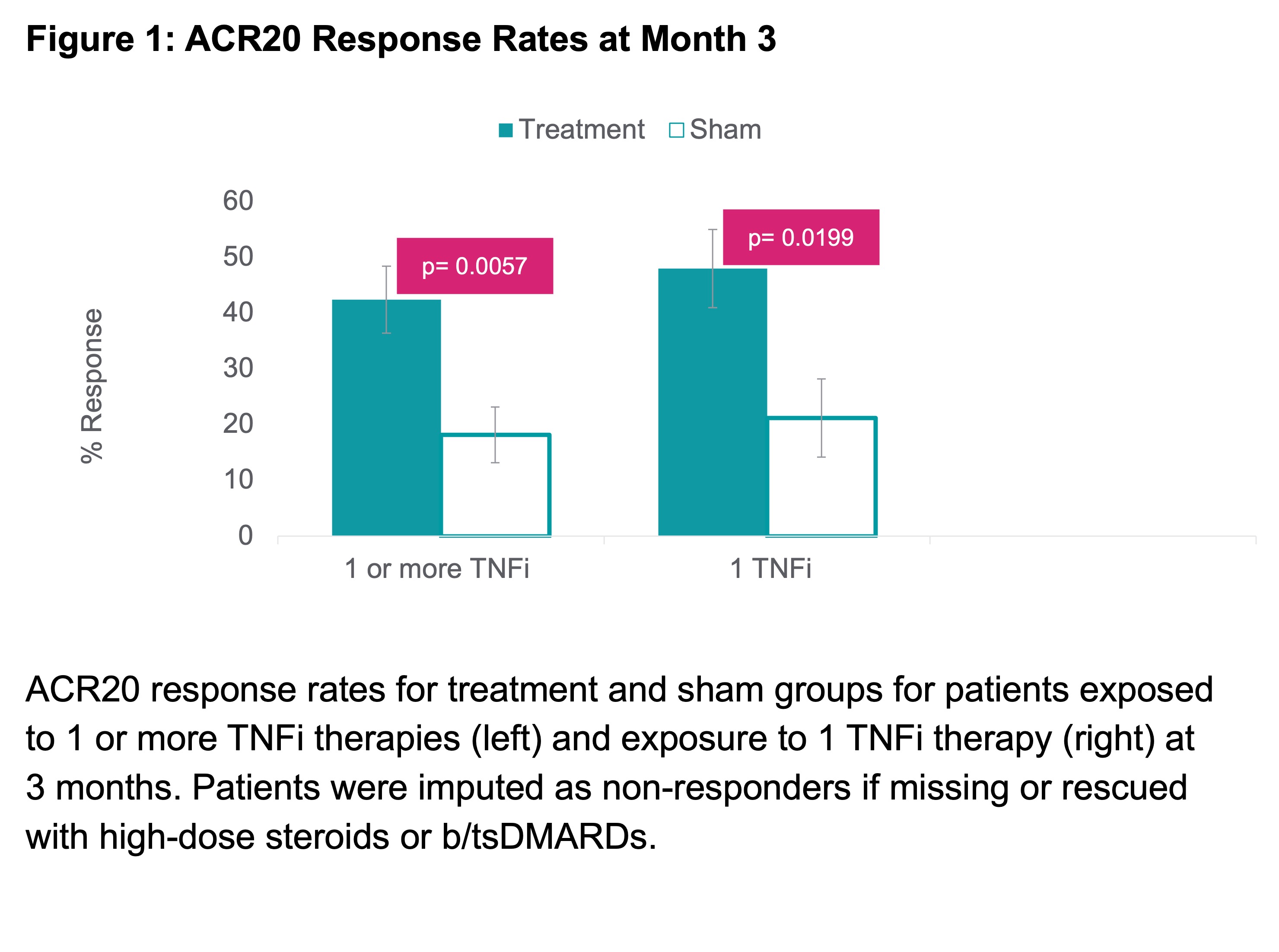
Results: 124 patients (67 treatment; 57 sham) had exposure solely to TNFi therapies prior to enrolling. 83 (67%) had inadequate response or intolerance to 1 prior TNFi, 31 (25%) to 2 prior TNFis, and 10 (8%) to ≥3 prior TNFis. Baseline characteristics were well-balanced with mean age 55.5 years, 85.5% female, RA duration 11.7 years, 14.4 tender joints, 9.9 swollen joints (28 joint count), 5.3 DAS28-CRP, and 36.5 CDAI. ACR20 response at 3 months showed a statistically significant difference between treatment 42.4% (28/66) vs. sham 18.2% (10/55) (p=0.0057). ACR20 response at 3 months for patients with prior exposure to just 1 TNFi was even higher, with treatment 48.0% and sham 21.2% (p=0.0199) (Figure 1). ACR responses improved further through 12 months (Table 1). Other endpoints such as mean change in tender and swollen joint counts, DAS28-CRP and CDAI LDA/remission rates also favored the treatment group at 3 months and further improved through 12 months (Figure 2). Augmentation of therapy with a b/tsDMARD in combination with stimulation was allowed without restriction following the 3-month, controlled portion of participation. Therapy augmentation with a b/tsDMARD occurred in 7%, 11%, and 13% of all patients at months 6, 9, and 12, respectively. For treatment patients only receiving stimulation (i.e., non-augmented), ACR20/50/70 response rates at 12 months were 60%, 38% and 16% respectively, with 52% and 49% achieving LDA or remission per DAS28-CRP and CDAI scores, respectively.
Conclusion: In a population of RA patients previously treated with only TNFi therapies, neuroimmune modulation using an implantable device to stimulate the left vagus nerve had statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in efficacy at 3 months, with durable improvements through 12 months. Neuroimmune modulation provides a differentiated, non-pharmaceutical treatment option for RA in patients with inadequate response to TNFi therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Valenzuela G, Box J, Crowley A, June J, Wickersham P, Peterson J, Thakor M, Kim S, Shah T, Chernoff D, Tesser J. Neuroimmune modulation in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to TNF inhibitors (TNFi) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neuroimmune-modulation-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-an-inadequate-response-to-tnf-inhibitors-tnfi/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neuroimmune-modulation-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-an-inadequate-response-to-tnf-inhibitors-tnfi/

.jpg)
.jpg)