Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Inflammatory Arthritis – RA, SpA, & Gout (0560–0593)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) has a poor long-term prognosis, including premature mortality. Longitudinal monitoring of patients in clinical and clinical trial settings includes the routine measurement of forced vital capacity (FVC) from pulmonary function tests (PFT). However, the availability of PFT data in real-world datasets is highly variable, limiting examination of this key outcome in long-term observational studies. Natural Language Processing (NLP), an artificial intelligence method, has been used to transform unstructured text from the electronic health record (EHR) to structured clinical data. We aimed to develop a NLP program to capture FVC values from EHR notes.
Methods: We identified patients in the Veterans Health Administration (VA) with RA-ILD between 2000 and 2020 by ICD-9/10 codes for RA and ILD, based on previously validated RA-ILD algorithms. We developed a NLP program to capture FVC values from all available notes from the EHR using MS SQLServer, based on a program for FEV1 values (Akgun et al. PLoS ONE, 2020). We identified FVC string patterns and extracted numeric values in proximity to these strings. Subsequently, we performed several processing steps to account for variability in note type and structure, related PFT output (e.g. FEV1/FVC ratio), and values copied across multiple notes. Dates were assigned to FVC values by cross referencing EHR note dates with the most recent date accompanying CPT codes for PFTs. FVC values derived by the NLP program were compared to observed FVC values recorded directly from PFT equipment and available as structured data in the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW). These represent a subset of all PFTs completed in the VA due to PFT compatibility.
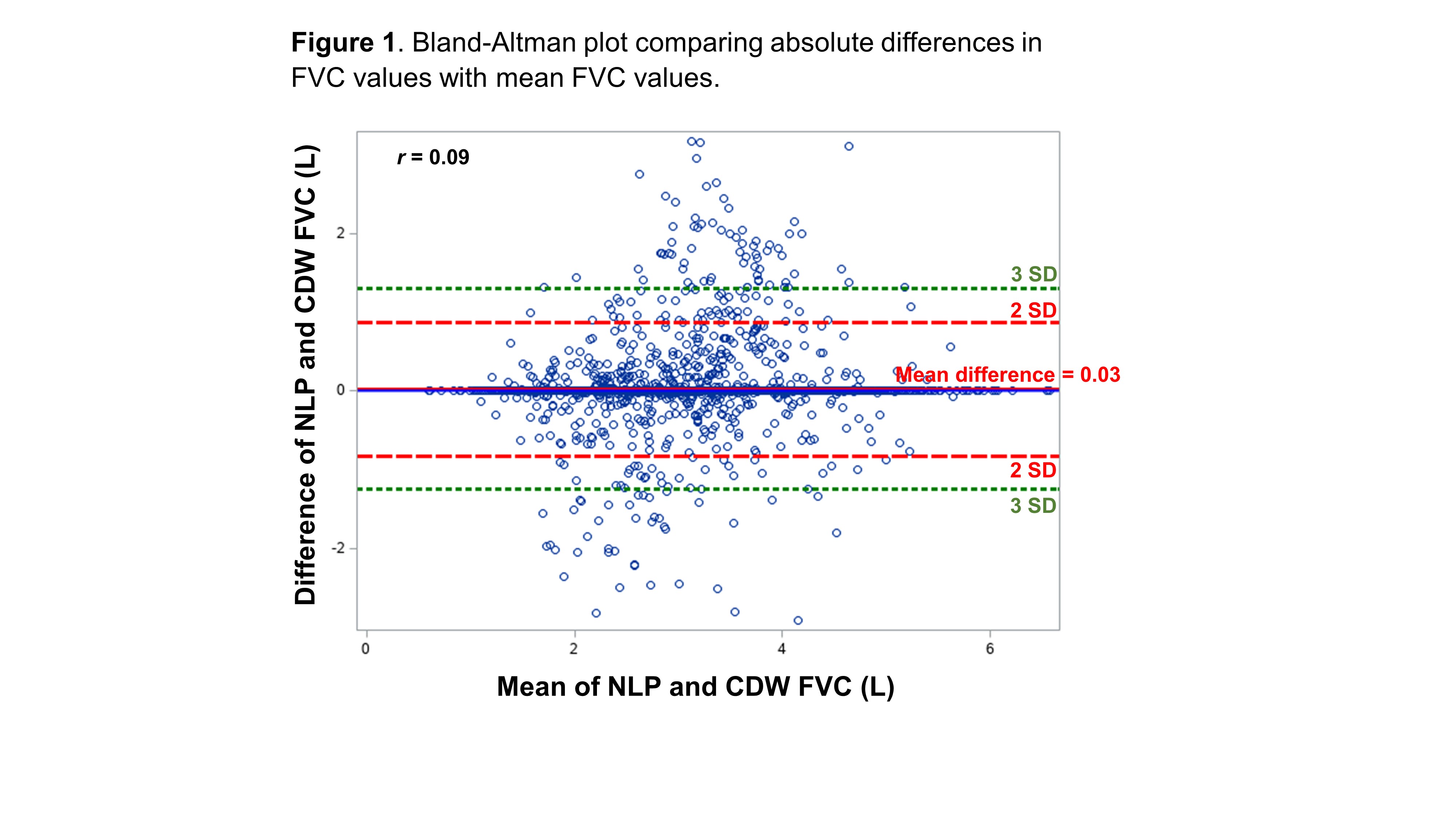
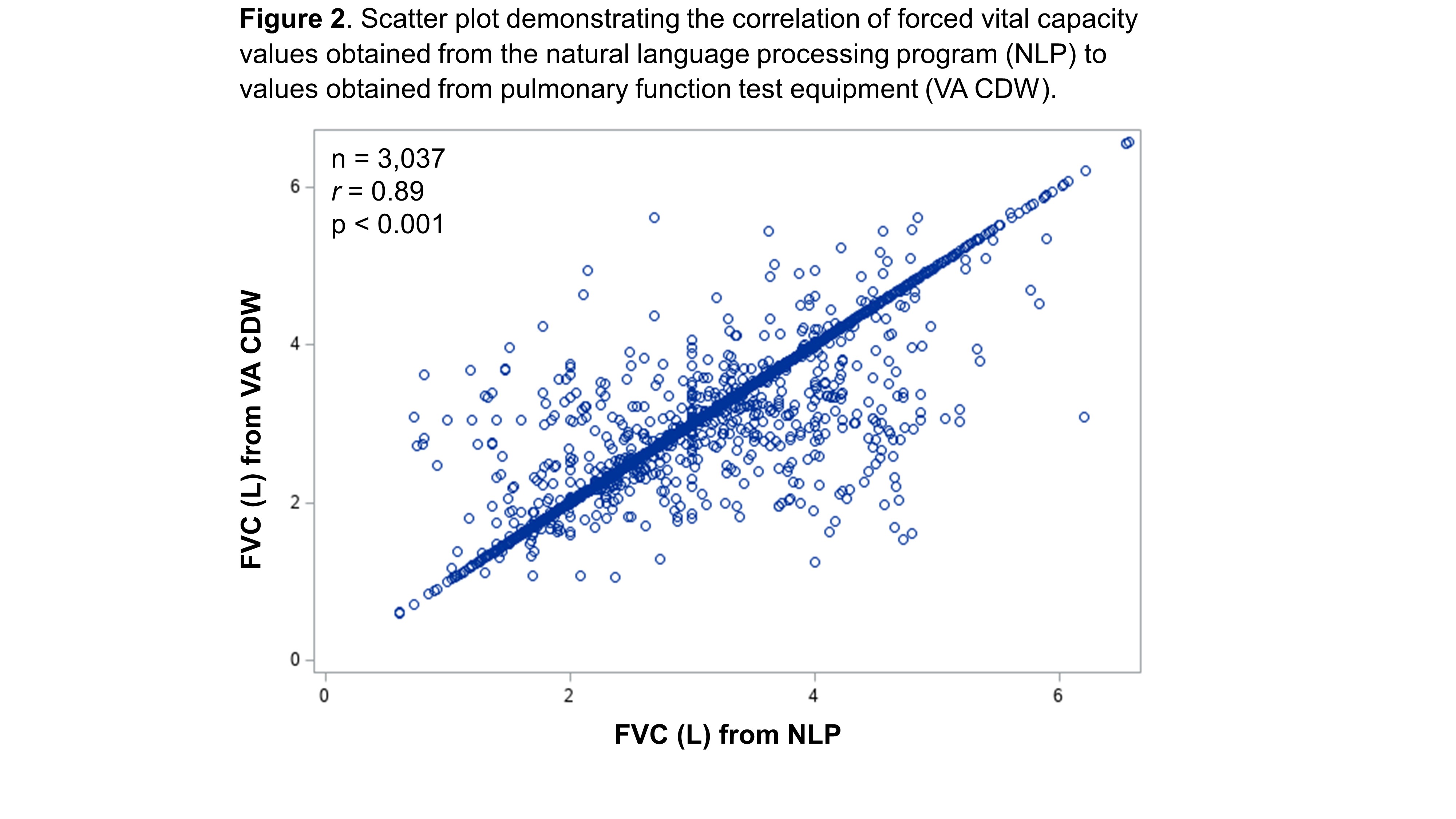
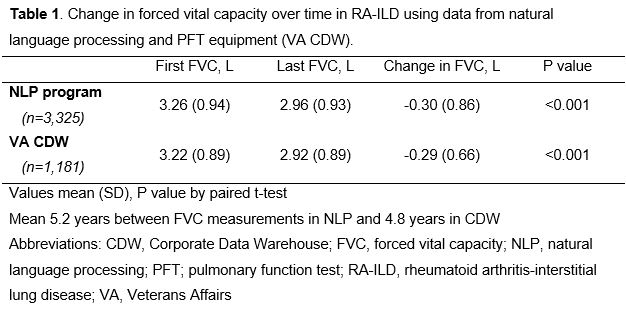
Results: We developed and tested the NLP program in a cohort of 7,485 patients with RA-ILD. In the VA CDW, there were 6,002 FVC values for 1,843 unique patients. The NLP program increased the yield of FVC values by >2.6-fold, extracting 15,983 FVC values for 4,849 patients. Among 3,037 date matched FVC values from NLP and CDW, mean (SD) FVC was 3.0 (0.9) L from both sources, and 80% of NLP values were within 0.1L of CDW values. The mean difference in FVC between NLP and CDW values was 0.03L with no systematic bias in NLP derived FVC values seen on Bland-Altman plot (Figure 1). NLP and CDW FVC values strongly correlated (Figure 2, r=0.89, p< 0.001). A total of 3,325 RA-ILD patients had at least two FVC values captured by NLP. Comparing the first and last FVC values, there was a mean decline in FVC of -0.30 (SD 0.86) L over a mean follow-up of 5.2 (SD 4.6) years (p< 0.001 by paired t-test) (Table 1). Similar changes in FVC (mean -0.29 [SD 0.66] L) were observed using CDW data, but this data source captured fewer RA-ILD patients (n=1,181).
Conclusion: NLP of EHR notes substantially increases the capture of longitudinal FVC values among patients with RA-ILD. These values are highly accurate compared to the gold standard of direct output from PFT equipment which may not always be available in structured format. Use of this NLP program can facilitate clinical and epidemiologic research studies in RA-ILD by capturing longitudinal changes among one of the most critical outcomes measures in RA-ILD.
Abbreviations: CDW, Corporate Data Warehouse; FVC, forced vital capacity; NLP, natural language processing; SD, standard deviation
Abbreviations: CDW, Corporate Data Warehouse; FVC, forced vital capacity; NLP, natural language processing
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Roul P, Yang Y, Hershberger D, Mikuls T, Rojas J, Curtis J, Baker J, Sauer B, England B. Natural Language Processing of Electronic Health Record Notes Captures Forced Vital Capacity in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/natural-language-processing-of-electronic-health-record-notes-captures-forced-vital-capacity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/natural-language-processing-of-electronic-health-record-notes-captures-forced-vital-capacity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/