Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Microvascular damage is part of the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis and is associated with internal organ involvement. Nintedanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of SSc-ILD. The SENSCIS trial was a placebo-controlled trial of nintedanib in patients with SSc-ILD. We assessed absolute changes in nailfold videocapillaroscopy (NVC) measures in a sub-study of the SENSCIS trial.
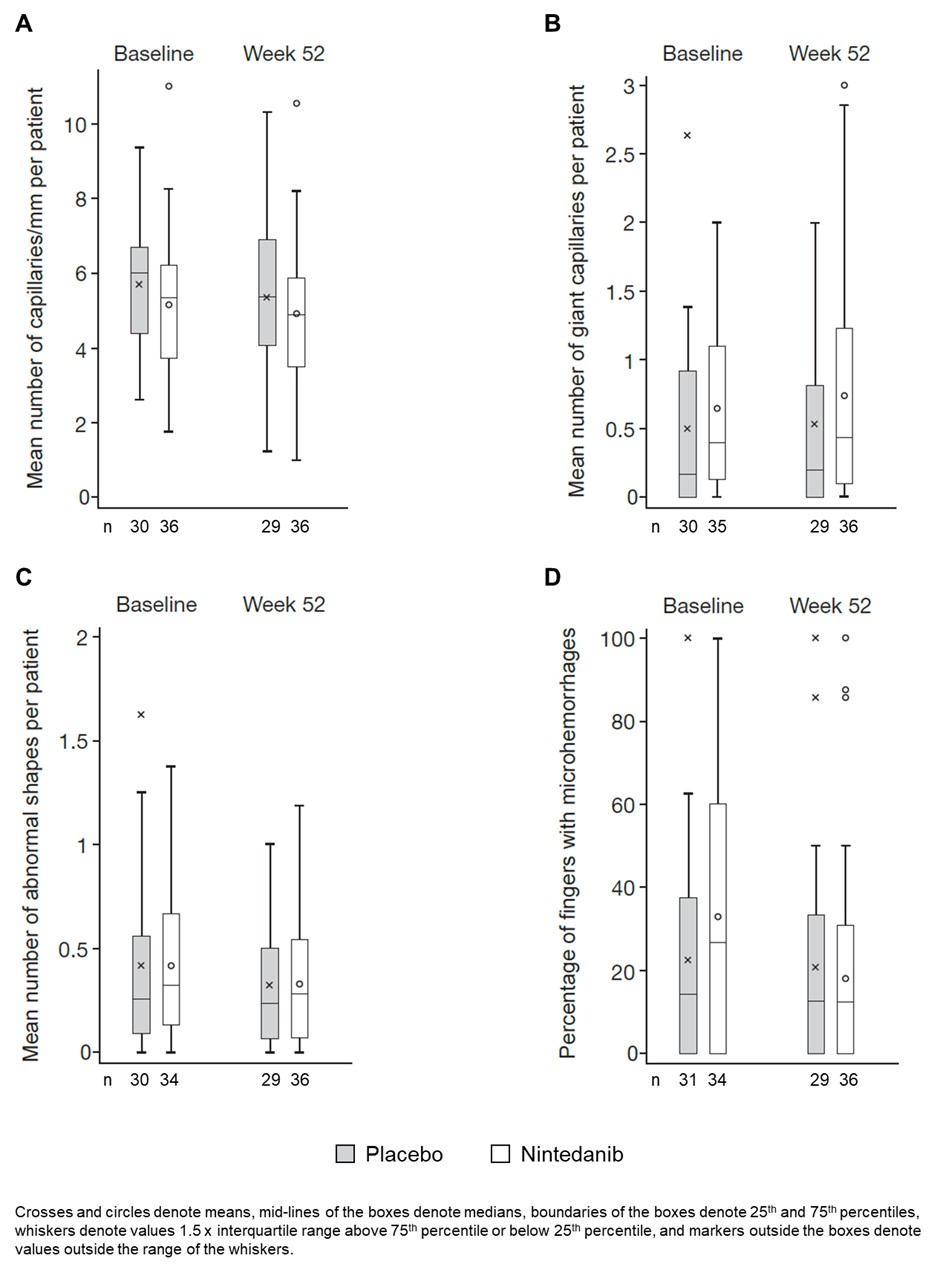
Methods: The SENSCIS trial enrolled patients with SSc with first non-Raynaud symptom in the prior ≤7 years and an extent of fibrotic ILD on high-resolution computed tomography ≥10%. Patients were randomized to receive nintedanib or placebo. In a sub-study, NVC was performed at baseline and weeks 12, 24, 36 and 52 [Smith et al. Autoimmun Rev 2020;19:102458]. Images from all 8 fingers were assessed by a central reader. Data were summarized by patient for mean capillary density (number of capillaries/mm), mean number of giant capillaries, mean number of abnormal shapes, and the percentage of fingers with microhemorrhages. These data are presented descriptively as the mean (SD) across patients.
Results: Of 576 patients in the SENSCIS trial, 120 participated in the NVC sub-study. At baseline, among the patients in the sub-study, mean (SD) age was 53.2 (11.9) years, 73.3% were female, median time since first non-Raynaud symptomwas 3.4 years, 50.0% had diffuse cutaneous SSc, mean (SD) modified Rodnan skin score was 11.4 (8.8), 59.2% were taking mycophenolate. Mean (SD) capillary density was 5.4 (1.8) capillaries/mm. The mean (SD) number of giant capillaries was 0.6 (0.6) and the mean (SD) number of abnormal shapes was 0.4 (0.4). The mean (SD) percentage of fingers with microhemorrhages was 28.0 (30.4). There were no notable changes in mean capillary density, the mean number of giant capillaries, the mean number of abnormal shapes, or the percentage of fingers with microhemorrhages over 52 weeks in either the placebo or nintedanib groups (Figure).
Conclusion: In a sub-study of the SENSCIS trial in patients with SSc-ILD, NVC showed no notable changes in the mean number of microvascular abnormalities over 52 weeks in either the placebo or nintedanib groups. These analyses were limited by the small number of patients providing data at baseline and week 52. Further evaluation is needed to assess whether there were differences in capillaroscopic characteristics in patients whose disease did or did not progress, as has been observed in previous studies [Avouac et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;47:86-94; Vanahecke et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022:61:4384-96].
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smith V, Denton C, Herrick A, Ittrich C, Alves M, Cutolo M. Nailfold Capillaroscopy in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD) Treated with Nintedanib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nailfold-capillaroscopy-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-treated-with-nintedanib/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nailfold-capillaroscopy-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-treated-with-nintedanib/