Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Nailfold capillaroscopy (NFC) has been suggested as a potential biomarker of disease severity in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Several studies report the association between capillary loss and disease severity however, the association of NFC abnormalities with novel severe organ involvement/progression in SSc has not been evaluated. We aim to evaluate the association of nailfold capillaroscopy (NFC) with novel major organ involvement/progression in SSc.
Methods: Follow-up data from patients with SSc registered between 2000 and 2022 were analysed. Patients underwent NFC at baseline. Novel severe organ involvement/progression was defined as new or progressive involvement of peripheral vasculature, lungs, heart, skin, gastrointestinal, kidney, musculoskeletal at 12 and 24 months of follow-up. The following NFC parameters were evaluated: capillary density, haemorrhages, enlarged and giant capillaries, avascular areas, organization of capillary architecture and scleroderma pattern (early/active/late). Logistic regression modelling was run to assess associations between NFC parameters and the occurrence of novel severe organ involvement and/or progression and risk factors.
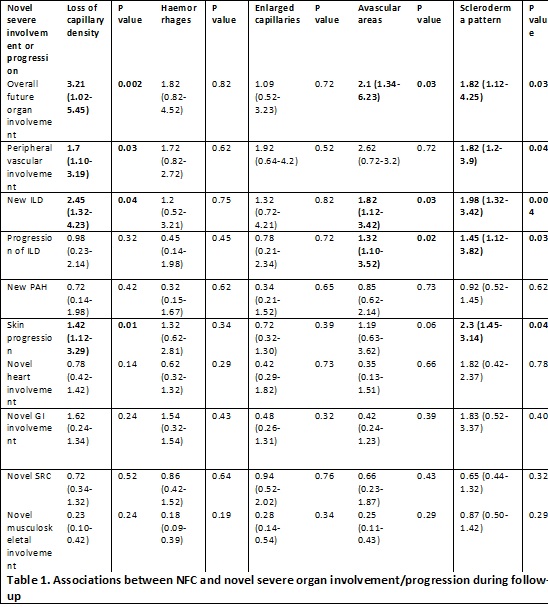
Results: 113 patients with SSc were included, 70 patients (61%) developed novel overall severe organ involvement/progression: 39 patients (56%) during the first 12 months and 31 patients (44%) from 12 to24 months of follow-up. 11% of patients developed novel peripheral vascular involvement, 21% developed novel interstitial lung disease (ILD), 11% had progression of known ILD, 6% had novel pulmonary hypertension, 11% had skin progression, 10% had novel heart involvement, 10% had novel gastrointestinal involvement, 6% had scleroderma renal crisis and 13% had novel musculoskeletal involvement. Table 1 summarizes the associations between NFC and novel severe organ involvement/progression during follow-up. Loss of capillary density was associated with overall severe organ involvement (p 0.002), peripheral vascular involvement (p 0.03), new ILD (p 0.04) and skin progression (p 0.01); avascular areas were associated with overall severe organ involvement (p 0.03), new ILD (p 0.03) and progression of ILD (p 0.02) and scleroderma pattern was associated with overall severe organ involvement (p 0.03), peripheral vascular involvement (OR p 0.04), new ILD (p 0.004), progression of ILD (p 0.03) and skin progression (p 0.04).
Conclusion: NFC may be a potential biomarker in SSc for predicting novel severe organ involvement and/or progression. Abnormal capillary density, avascular areas and scleroderma pattern are predictors of overall severe organ involvement, peripheral vascular involvement, novel and progression of ILD and skin progression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sieiro Santos C, Rego Salgueiro R, Moriano Morales C, Álvarez Castro C, Díez Álvarez E. Nailfold Capillaroscopy for Prediction of Novel Severe Organ Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nailfold-capillaroscopy-for-prediction-of-novel-severe-organ-involvement-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nailfold-capillaroscopy-for-prediction-of-novel-severe-organ-involvement-in-systemic-sclerosis/