Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) are at an increased risk of sarcopenia and muscle involvement. This study aims to describe the ultrasound findings of muscle mass, quality, and stiffness in SSc patients and their correlation with the handgrip test (HG), a validated tool for assessing muscle strength, and disease-related characteristics.
Methods: This cross-sectional multicentric study included consecutive SSc patients and healthy controls (HCs). Using ultrasound, bilateral quadriceps muscle (QM) thickness was measured by summing the thickness of the rectus femoris muscle and vastus intermedius muscle. Muscle quality was evaluated by assessing muscle echogenicity both semi-quantitatively with a modified Heckmatt scale (mHS) and using grey-scale histogram analysis (GSA) via ImageJ software. Rectus femoris muscle stiffness was measured using Shear-Wave elastosonography (SWE). In SSc patients, the correlations between the ultrasound findings and HG, as well as clinical disease characteristics, were explored.
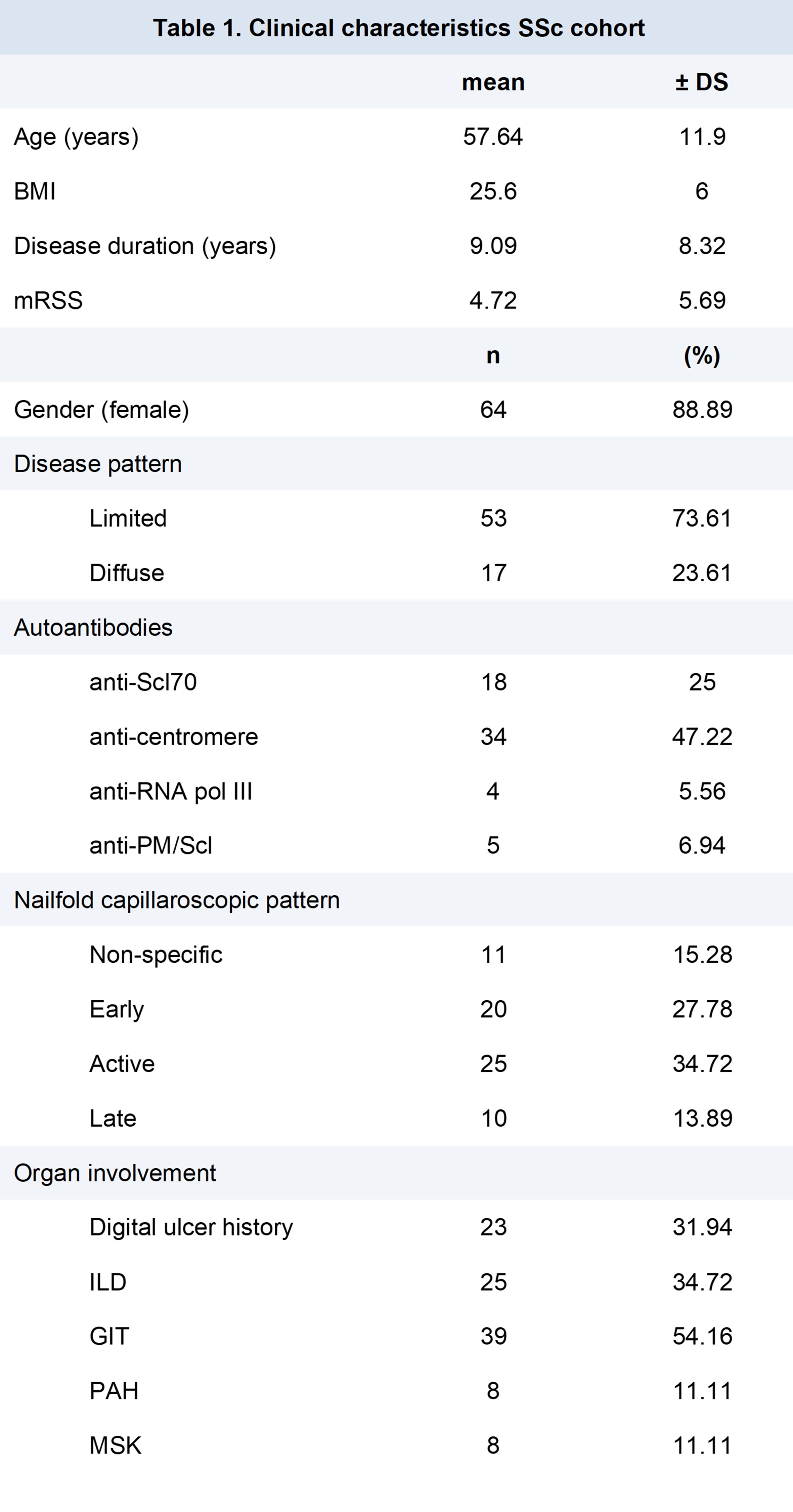
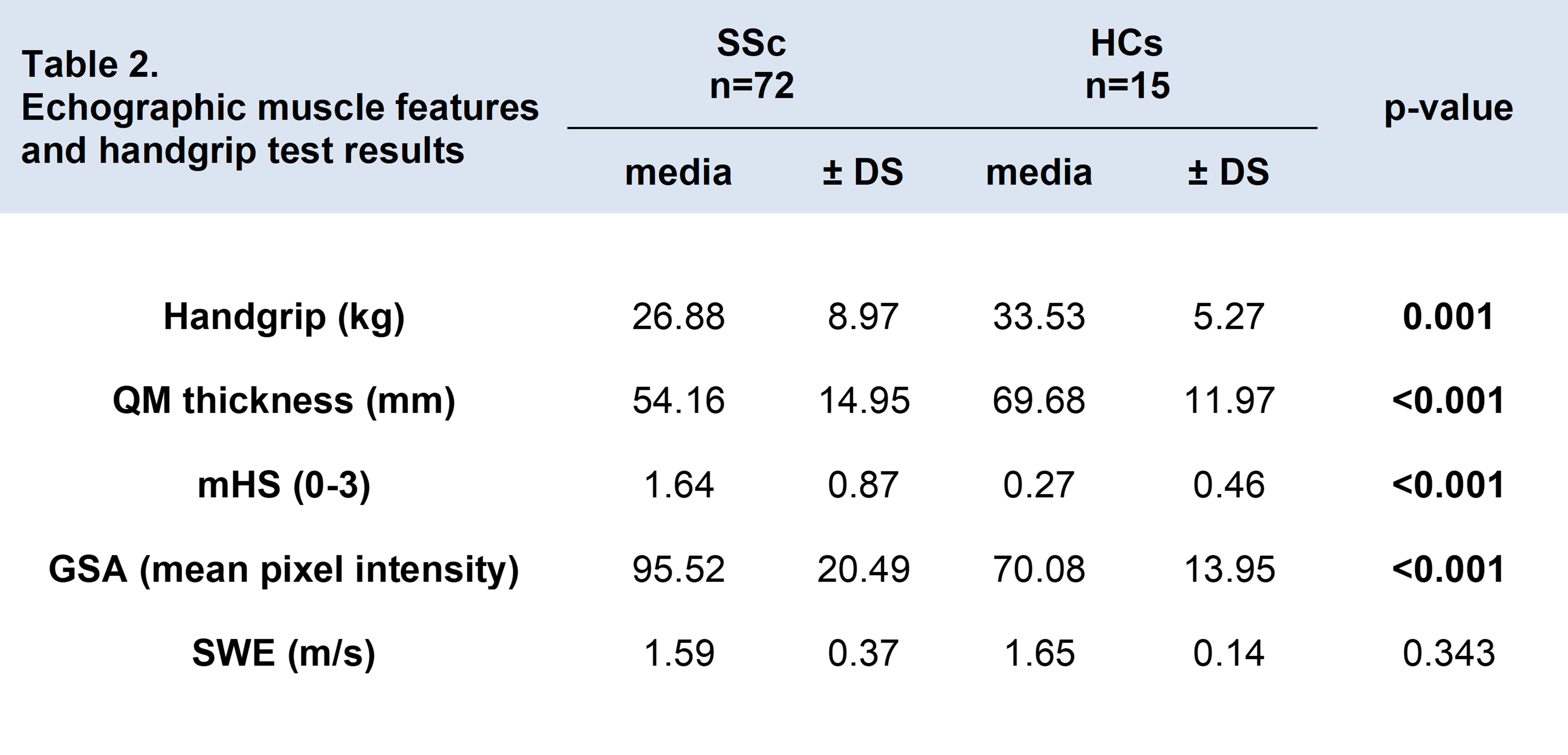
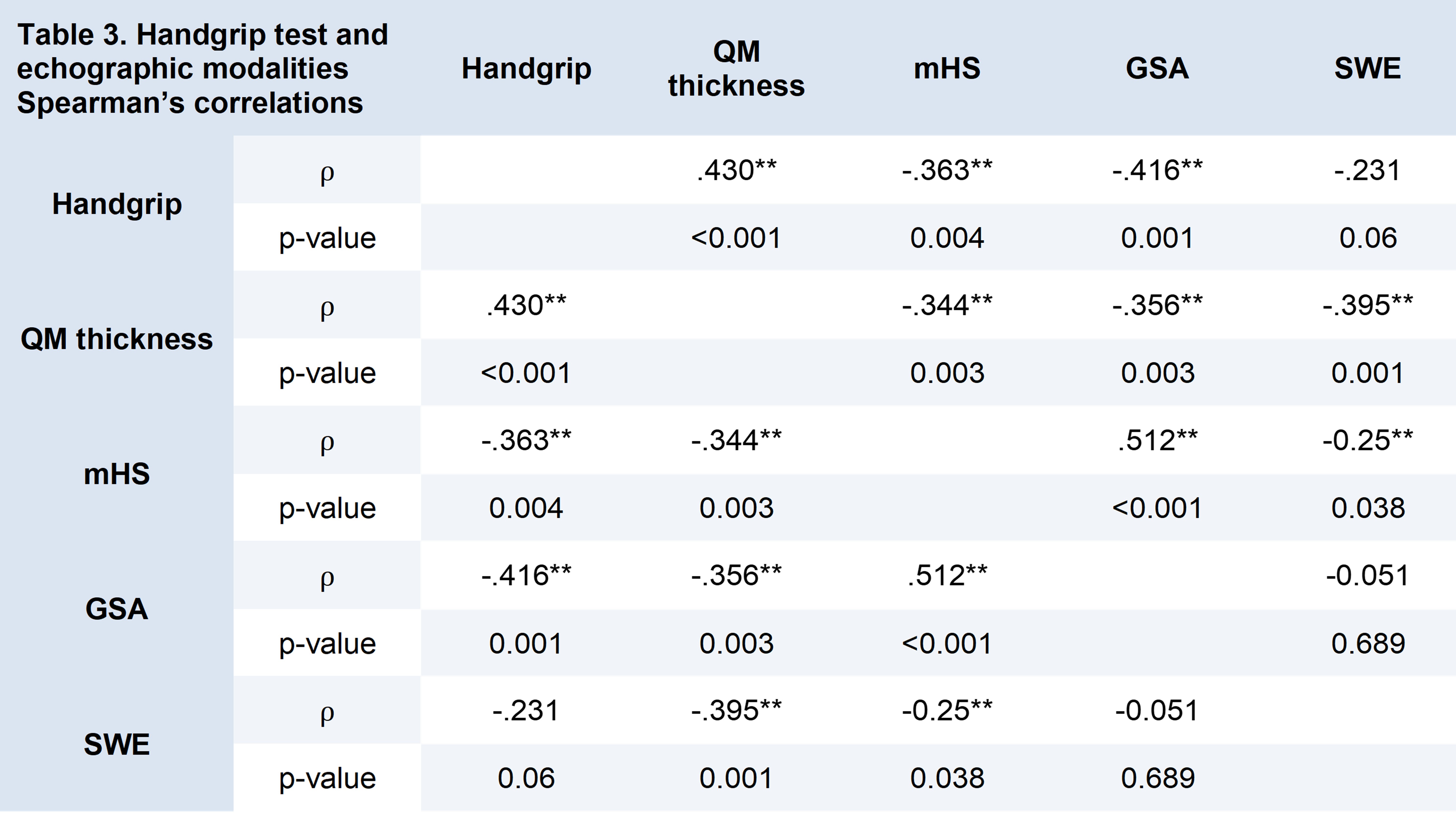
Results: A total of 72 SSc patients were included. The main clinical characteristics of these patients have been reported in Table 1. When compared to HCs (n=15), SSc patients had significantly lower QM thickness (54.16±14.95 vs 69.68±11.97 mm; p< 0.001), suggesting lower muscle mass. SSc patients also had increased muscle echogenicity values, assessed with both mHS (1.64±0.87 vs 0.27±0.46 p< 0.001) and GSA (95.52±20.49 vs 70.08±13.95 mean pixel intensity; p< 0.001), indicating decreased muscle quality. No significant SWE values were observed between SSc patients and HCs (Table 2). Nine SSc patients (12.5%) met the criteria for “probable sarcopenia” based on EWGSOP2 guidelines for HG strength, while the remaining 63 were above the threshold for this classification. In SSc patients, HG was significantly associated with QM thickness (⍴=.43; p< 0.001), mHS (⍴=-.363; p=0.004), and GSA, (⍴=-.416; p=0.001), but not with SWE. QM thickness, mHS and GSA were significantly associated with each other, while SWE was associated only with QM thickness (⍴=-.395; p=0.001) and mHS (⍴=-.25; p=0.089) (Table 3). Gastrointestinal involvement was significantly associated with HG (⍴=-.302; p=0.015) and QM thickness (⍴=-.247; p=0.039) in SSc patients, while other organ involvements, disease duration, and disease pattern were not associated with any ultrasound measurement or HG values.
Conclusion: Ultrasound could be a valuable method for investigating changes in muscle mass, quality, and stiffness indicative of sarcopenia-related muscle involvement in SSc patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bixio R, Lommano M, Colak S, farah S, Pistillo F, Wakefield R, Salaffi F, Di Donato S, Viapiana O, De Angelis R, Rossini M, Cipolletta E, Filippucci E, Idolazzi L, Del Galdo F, Di Matteo A. Multimodal Ultrasound in the Assessment of Sarcopenia-related Muscle Involvement in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Multicentric Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multimodal-ultrasound-in-the-assessment-of-sarcopenia-related-muscle-involvement-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-multicentric-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/multimodal-ultrasound-in-the-assessment-of-sarcopenia-related-muscle-involvement-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-multicentric-study/