Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science (1897–1900)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:15AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with gout have an increased risk of mortality. Current ACR guidelines for the treatment of gout recommend a treat-to-target approach with titration of urate lowering therapy (ULT) based on serum urate (SU) concentrations. However, it remains to be determined whether this treat-to-target approach improves long-term outcomes in gout. Therefore, the goal of this study was to examine whether ULT administration and SU values concordant with a treat-to-target approach are associated with all-cause mortality.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study, identifying patients with gout using national Veteran’s Health Administrative (VHA) data from 1/1999-9/2015 based on the presence of ≥2 ICD-9 codes for gout (274.X) (Helget LN et al. Arthritis Care Res 2020). Patients’ gout treatment status was categorized in a time-varying manner as either “well-treated” or “sub-optimally treated” during each 365 days of follow-up. Gout patients were considered “well-treated” if during the preceding 365-day period had: 1) ≥2 fills of ≥90 days duration for ULT and 2) a mean SU < 6 mg/dL, using VHA pharmacy and laboratory data. Gout patients who did not meet these criteria were classified as “sub-optimally treated”. Patients were followed from the index date (date fulfilling gout algorithm) until death (identified through linkage with the National Death Index) or censoring due to end of study period (12/2015). We assessed the association of time-varying gout treatment status with all-cause mortality using multivariable Cox regression models adjusting for demographics and comorbidities obtained from VHA administrative data.
Results: We identified 506,981 gout patients in the VHA during our study period. Patients were predominantly male (99%) and had a mean (SD) age of 66.6 (11.6) years. During follow-up, 61.3% received at least one ULT prescription and >78% had at least one SU measurement. Over 3,004,816 patient-years of follow-up, there were 176,591 deaths. Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated reduced survival in gout patients who were “sub-optimally treated” (log-rank p-value < 0.0001) (Figure 1). In unadjusted models, patients with gout who were “sub-optimally treated” had a 24% higher risk of all-cause mortality (aHR 1.24 [95% CI 1.23-1.26]). These results were not changed following multivariable adjustment (Table 1).
Conclusion: Using data from the largest integrated health system in the U.S., we found that patients with gout receiving suboptimal gout management based on ULT administration and SU measurements demonstrated an approximately 22% higher rate of all-cause mortality. These findings illustrate the long-term consequences of suboptimal treatment and support current ACR guidelines recommending a treat-to-target approach in the management of chronic gout. Additional research is needed to better understand factors mediating the relationship between optimal management and survival, as this information will be essential in informing future strategies aimed at improving long-term outcomes in gout.
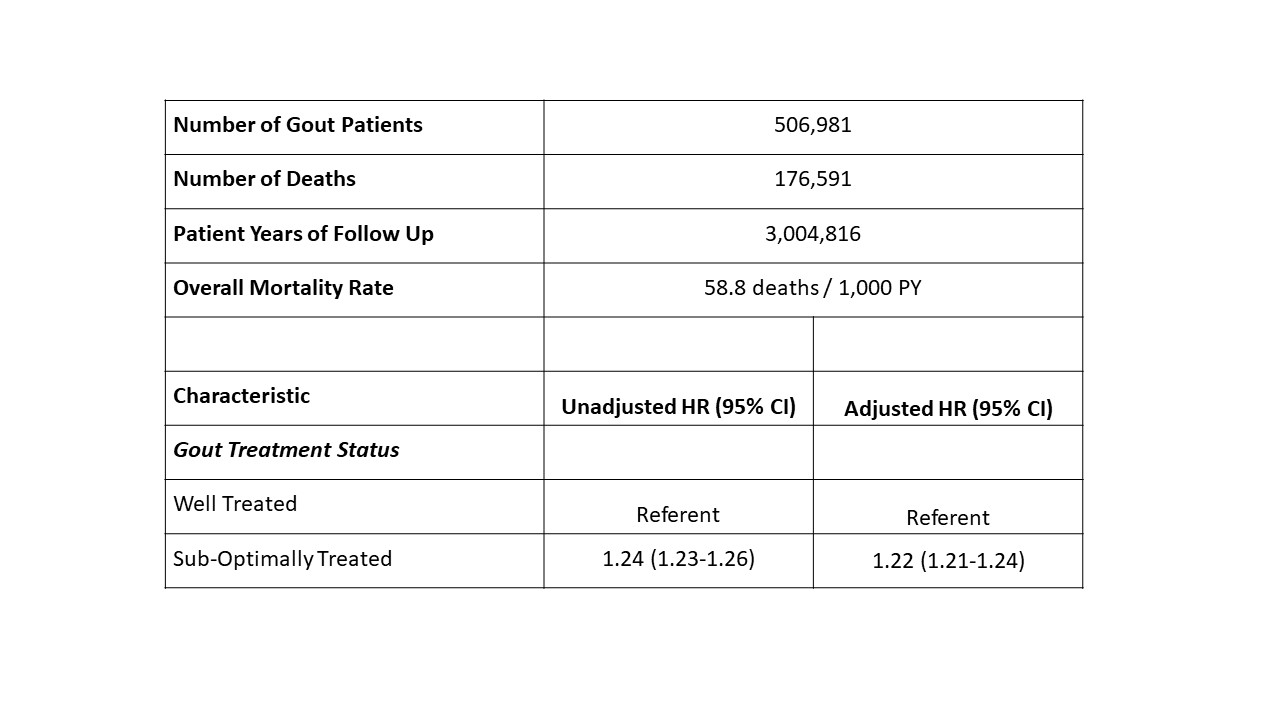 Table 1. Study patients, follow-up, mortality rate and risk of death associated with treatment status
Table 1. Study patients, follow-up, mortality rate and risk of death associated with treatment status
 Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier survival estimates demonstrating increased all-cause mortality among sub-optimally treated gout patients (red line) compared to well-treated patients with gout (blue line); log-rank test p-value < 0.0001.
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier survival estimates demonstrating increased all-cause mortality among sub-optimally treated gout patients (red line) compared to well-treated patients with gout (blue line); log-rank test p-value < 0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Helget L, England B, Roul P, Sayles H, Petro A, Neogi T, Mikuls T. Mortality in Patients with Sub-Optimally Treated Gout in the Veteran’s Health Administration: A National Retrospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-in-patients-with-sub-optimally-treated-gout-in-the-veterans-health-administration-a-national-retrospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mortality-in-patients-with-sub-optimally-treated-gout-in-the-veterans-health-administration-a-national-retrospective-cohort-study/
