Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: RA, Spondyloarthritis, & OA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although DMARDs are essential for early aggressive control of RA to reduce symptoms and disability, medication adherence is variable. Beliefs about the necessity of medications and safety concerns predict adherence and are modifiable. Little is known about perceptions of RA medications in patients who are newly diagnosed. We examined associations among RA medication necessity beliefs and concerns, sociodemographics, RA characteristics, symptom levels and function in new RA patients around the time of diagnosis and starting medications.
Methods: Baseline data were analyzed from participants in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) who enrolled between 2017-2020 and completed the Beliefs about Medicine Questionnaire (BMQ) and PROMIS-29. All met ACR1987 or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria and had active RA at enrollment. BMQ Necessity (N) and Concerns (C) scores were classified as high (≥20) or low (< 20) and categorized into: Accepting (↑N ↓C); Ambivalent (↑N↑C); Sceptical (↓N↑C); and 4) Indifferent (↓N↓C). Groups were compared using ANOVA and chi-square tests.
Results: The 362 patients were mostly white (83%) women (66%) with a mean (SD) age of 56 (15), symptom duration of 6 (3) months, and 32% were obese (BMI≥30). More than half (56%) were DMARD-naive or minimally exposed. Mean N and C scores were similar between men and women; 54% were classified as Indifferent, 31% Accepting, 9% Ambivalent, and 6% Sceptical (Table 1). As compared to those classified as Accepting, more Indifferent participants smoked, had a healthy weight, lower TJCs, and trend for lower CDAI (Table 1). Groups were similar by sociodemographics, symptom duration, and DMARD/steroid use, except fewer Indifferent patients received MTX.
Most (67-100%) worried about the long-term effects of their medications (Table 2). Indifferent patients had statistically and meaningfully lower patient global, depression, anxiety, fatigue and pain interference, and higher function and participation scores (Table 3).
Conclusion: Most new RA patients worried about the long-term safety of their RA medications. Many had low medication necessity beliefs and concerns, and only 31% had high necessity beliefs and low concerns around diagnosis. Lifestyle and lower CDAI, TJCs, symptoms and functional impacts were associated with RA medication indifference. Exploring medication beliefs in newly diagnosed RA patients may help identify information gaps and provide opportunities to address concerns, potentially improving adoption and persistence over time.
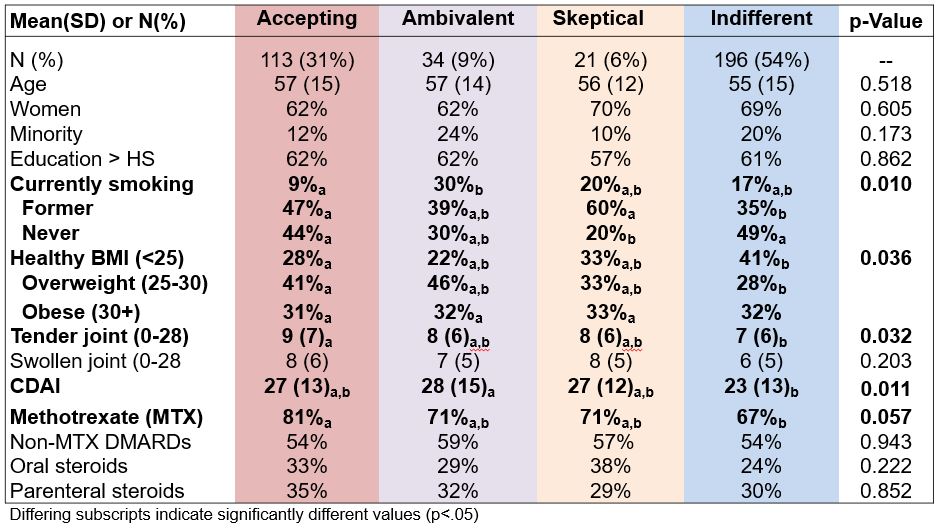 Table 1. Patient characteristics at baseline by profiles.
Table 1. Patient characteristics at baseline by profiles.
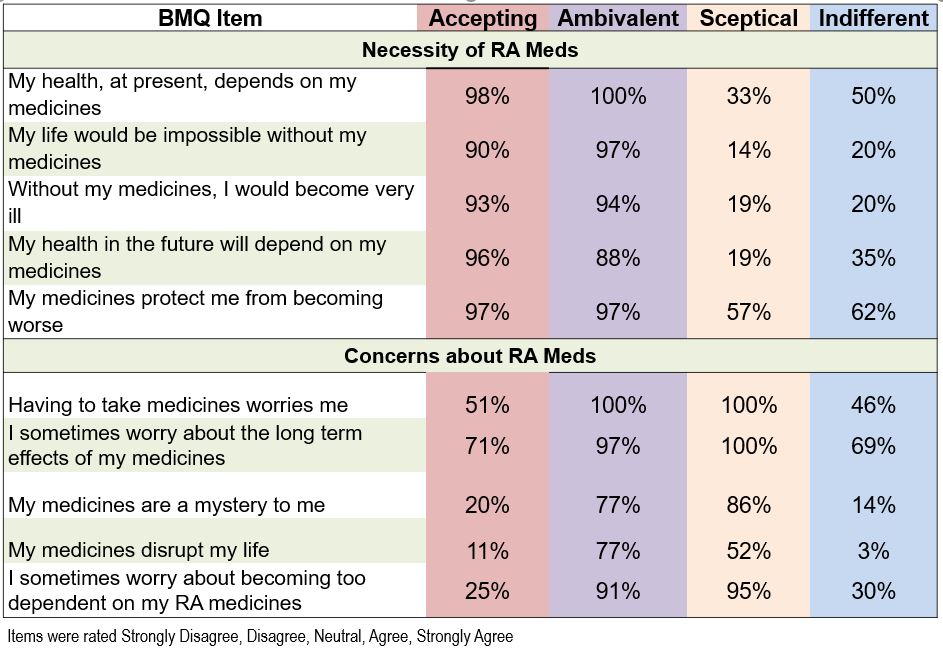 Table 2. Proportions of patients who agreed/strongly agreed with each item.
Table 2. Proportions of patients who agreed/strongly agreed with each item.
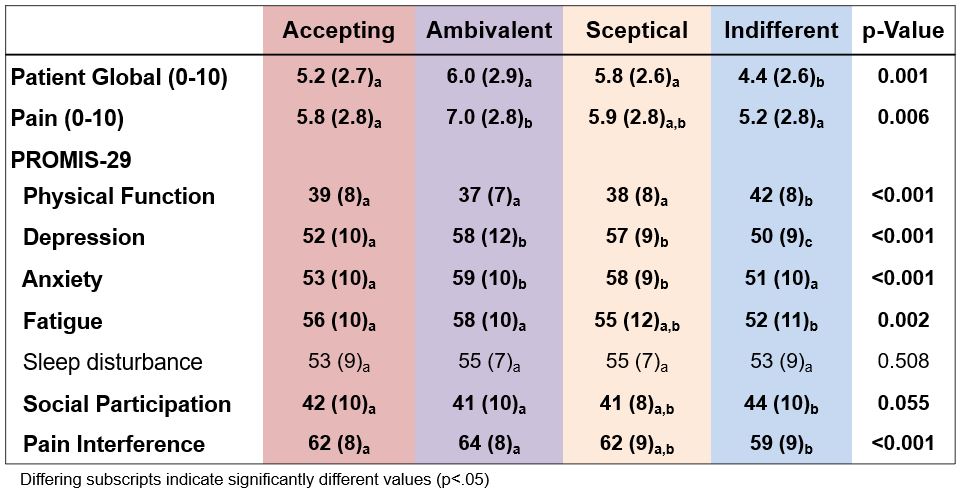 Table 3. Physical, emotional, and social function by BMQ attitudinal profiles.
Table 3. Physical, emotional, and social function by BMQ attitudinal profiles.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ta V, Schieir O, Valois M, Tin D, Hitchon C, Bessette L, Thorne C, Pope J, Boire G, Keystone E, Bykerk V, Bartlett S, (CATCH) Investigators C. More Than Half of Newly Diagnosed RA Patients Are Not Convinced of the Necessity of RA Medicines: Associations with RA Characteristics, Symptoms, and Function in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/more-than-half-of-newly-diagnosed-ra-patients-are-not-convinced-of-the-necessity-of-ra-medicines-associations-with-ra-characteristics-symptoms-and-function-in-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort-c/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/more-than-half-of-newly-diagnosed-ra-patients-are-not-convinced-of-the-necessity-of-ra-medicines-associations-with-ra-characteristics-symptoms-and-function-in-the-canadian-early-arthritis-cohort-c/
