Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Etiology and Pathogenesis (0795–0800)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-1:15PM
Background/Purpose: To characterize molecular profiles of RA patients through multi-omics integration and evaluate their associations with disease status and therapeutic response to csDMARDs, TNF inhibitors (TNFi), and JAK inhibitors (JAKi).
Methods: Transcriptomic profiling was performed on PBMCs from established RA patients (n=206; 177 starting TNFi or JAKi), early RA (n=53; 30 initiating csDMARDs), and healthy donors (HD, n=42) using RNA-seq (Illumina). Serum levels of 92 inflammatory proteins were measured via Proximity Extension Assay (Olink). Therapeutic responses were assessed at six months according to EULAR criteria. Multivariate and machine learning approaches identified molecular subgroups and predictive biomarkers.
Results: Unsupervised clustering of PBMC transcriptomes identified three patient groups with distinct gene module involving innate and adaptive immune responses, inflammation, and cellular metabolism, most notably in cluster 1 (CL1) (Figure 1A). Circulating proteomic profiles supported these findings; 38 proteins were differentially expressed, highlighting a strong inflammatory signature in CL1 (Figure 1B & 1C). These molecular features correlated significantly with disease activity (DAS28, SDAI), autoantibodies, and cardiovascular risk, with CL1 patients exhibiting higher activity, autoantibody titres, and systemic inflammation.Established RA showed a greater number of differentially expressed genes and proteins compared to early RA, indicating increasing immune complexity. Stronger correlations between molecular alterations and clinical outcomes in established RA underscored progressive molecular deregulation.Machine learning models achieved an AUC over 0.8 in predicting response, featuring specific transcriptomic signatures: i) csDMARDs: high metabolic gene expression and low oxidative stress genes; ii) TNFi: high inflammatory and low cytotoxicity gene expression. Iii) JAKi: elevated interferon-related and decreased mitochondrial gene expression.Clinically applicable predictive models, combining proteomic and clinical data demonstrated high accuracy: i) csDMARDs: five dysregulated inflammatory proteins, elevated monocyte count, and high SDAI; ii) TNFi: nine proteins and high disease activity scores; iii) JAKi: four proteins, high lymphocyte count, and tender joint count. Baseline inflammatory burden predicts response to csDMARDs and TNFi, while lymphocytic activity is more predictive for JAKi response.
Conclusion: Molecular profiles allow stratification of RA patients based on disease stage and clinical features. Progression involves increased molecular complexity, and treatment responses correlate with specific pre-treatment signatures. These findings highlight the potential of integrative omics to inform personalized therapy in RA.Acknowledgments:Supported by EU/EFPIA IMI-JU 3TR, ISCIII (PI24/00959, CD21/00187, RICOR-24/0007/0019), co-financed by European Union, and MINECO (RYC2021-033828-I/PID2022-141500OA-I00).
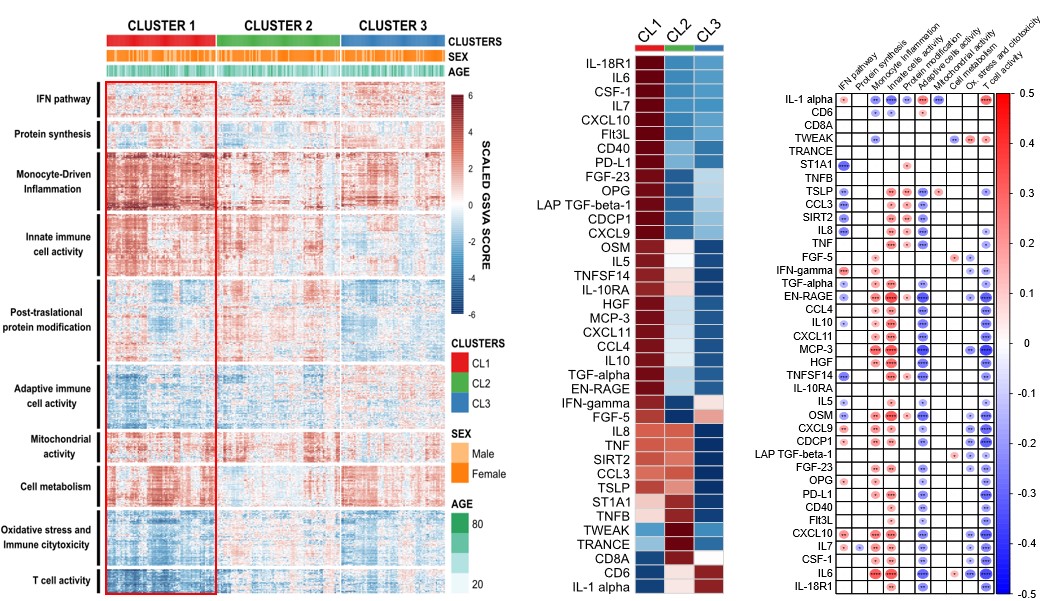 Figure 1. (A) Unsupervised clustering of PBMC transcriptomes with functional annotation of associated gene modules. (B) Differential expression profile of circulating inflammatory proteins across patient subgroups. (C) Correlation between altered inflammatory proteins and PBMC transcriptomic modules.
Figure 1. (A) Unsupervised clustering of PBMC transcriptomes with functional annotation of associated gene modules. (B) Differential expression profile of circulating inflammatory proteins across patient subgroups. (C) Correlation between altered inflammatory proteins and PBMC transcriptomic modules.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sanchez-Pareja I, Toro D, Pérez Sánchez C, muñoz-Barrera L, Cerdó T, Moreno-Caño E, Corrales S, Formanti Alonso L, Ortega-Castro R, Calvo J, Ladehesa L, Aranda-Valera C, Abalos-Aguilera M, Merlo-Ruiz C, AGUIRRE ZAMORANO M, Alarcon-Riquelme M, Escudero Contreras A, López pedrera C. Molecular Stratification of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients by Multi-Omics Integration Reveals Disease Status and Predictors of Therapeutic Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/molecular-stratification-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-by-multi-omics-integration-reveals-disease-status-and-predictors-of-therapeutic-response/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/molecular-stratification-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-by-multi-omics-integration-reveals-disease-status-and-predictors-of-therapeutic-response/
