Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1100–1123) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is an inflammatory arthritis that results in severe joint inflammation, pain, disability, and lower quality of life (QoL). Determining minimal clinically important differences (MCIDs) for QoL metrics is essential for effectively evaluating gout patient QoL and the impact of therapy. Here, we determine and examine potential predictors of MCID for Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)-Disability Index (DI), -Pain, and -Health using data from adult uncontrolled gout patients treated with pegloticase during the MIRROR Randomized Controlled Trial(RCT)1.
Methods: MIRROR RCT participants received ≤52 weeks of pegloticase+methotrexate (MTX) orpegloticase+placebo (PBO) co-therapy1.The change from baseline in HAQ scores were obtained at prespecified time points, including Weeks 24 and 52. HAQ scores range from 0-3 for DI, 0-100 for Pain, and 0-100 for Health, with a higher score indicating worse QoL. MCIDs were calculated using two distribution-(0.5 standard deviation[SD], standard error of the mean)and two anchor-based (change difference, receiver operator curve) approaches, with physician global assessment(PhGA), serum urate response, and number of gout flares considered as anchors. Time-to-MCID was evaluated by treatment group using Kaplan-Meier curves. A logistic model and a multicollinearity test including seven covariates were used to assess baseline factors that potentially influenced reaching MCID.
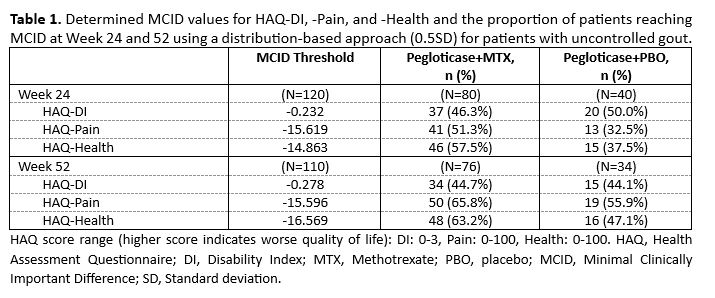
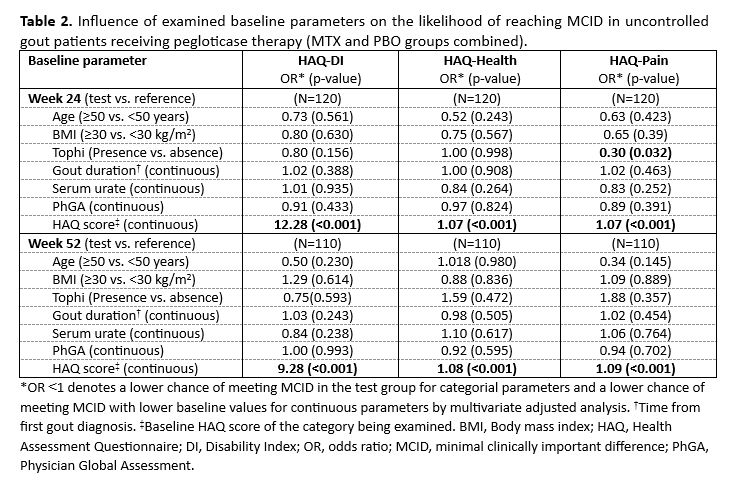
Results: A total of 80 and 76 patients in the MTX group and 40 and 34 patients in the PBO group had Week 24 and 52 HAQ data, respectively. Across analysis methods, MCID values were similar. Herein, results for the0.5SDapproach are presented. MCID thresholds for all HAQ measures were established, with notable differences in the proportion of MTX and PBO patients achieving -Health and -Pain MCID at Week 24 and 52 (Table 1). Time-to-MCID for HAQ-DI and -Pain did not differ between treatment groups but was shorter for -Health in the MTX group through Week 52 (median: 20 vs. 24 weeks).Worse baseline QoL was a significant predictor of reaching MCID during therapy for all HAQ measures(Table 2). Additionally, patients with tophi at baseline were significantly less likely to reach MCID for HAQ-Pain at Week 24, but not Week 52.
Conclusion: For the first time, MCID values for HAQ-DI, -Pain, and -Health scores in an uncontrolled gout population were established. Pegloticase administered as monotherapy or with MTX co-therapy resulted in 33-66%ofpatients achieving MCID in all HAQ measures. Both treatment groups had similar median times-to-MCID ,further supporting the effect of pegloticase on QoL measures. Few assessed parameters were predictive of achieving HAQ MCIDs, but worse baseline QoL was associated with an increased likelihood of reaching all HAQ MCIDs at Week 24 and 52 and the presence of tophi at baseline was associated with a decreased likelihood of reaching HAQ-Pain MCID at Week 24. Further exploration is needed on how tophi influence levels of and changes in patient pain. These analyses are of importance for assessing potential QoL benefits during pegloticase and other urate-lowering therapies in both the clinical trial and practice settings.
1Botson, J. K. et al. Arthritis Rheumatol2023;75:293-304.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
LaMoreaux B, McKibbon C, Obermeyer K, Padnick-Silver L, Smith G, Wang J, Patel H. Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) of Quality of Life Assessments in Patients with Uncontrolled Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/minimal-clinically-important-difference-mcid-of-quality-of-life-assessments-in-patients-with-uncontrolled-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/minimal-clinically-important-difference-mcid-of-quality-of-life-assessments-in-patients-with-uncontrolled-gout/