Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Many patients with controlled rheumatoid arthritis (RA) continue to report high levels of disease activity (PGA), as well as other disturbing patient-related outcomes (PROs), such as depression and anxiety. Aiming to improve PGA and PROs in a pragmatic pilot study, Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), an eight-week non-pharmacological approach, was offered to patients with controlled RA but elevated negative PROs.
Methods: Patients in clinical remission on stable treatment at their regular visit were referred to research assistants to determine their interest in the study. Recruitment strategies (Table 1) were based either on elevated Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression scale (CES-D) scores or on a differenre ≥2/10 (Delta) between PGA and Physician General Assessment (EGA). Patients were evaluated 1-4 weeks before MBSR and 6 and 12 months after MBSR’s end. Scores were compared between baseline and 6 and 12 months. Differences within and between groups were calculated with linear mixed regression models for continuous outcomes or with generalized estimating equation for dichotomic outcomes. Some participants were interviewed about their experience after the 6-month assessment to complete a qualitative evaluation.
Results: Out of 325 tagged patients, 224 were identified as candidates by rheumatologists, 67 were proposed MBSR, 39 (58%) agreed to participate, 31 took part to 1 of 4 MBSR groups provided over 18 months, and 28 (42%) completed both the baseline and the 6- and/or 12-month evaluation (Table 2). Timing (day vs evening), frequency of the group meetings, distance from home, severe depression, extremes of age and comorbidities were examples of barriers to participation.
Results showed a significant improvement from baseline to 12 months post-MBSR for depression (CES-D; estimate (95% CI)=(-9.21 (-13.96 to -4.41), p=0.004), anxiety (GAD-7; -3.18 (-5.15 to -1.22), p=0.004), emotional coping (-5.18 (-7.82 to -2.53), p=0.004), sleep (-2.06 (-3.12 to -0.99), p=0.004) and function (M-HAQ; -0.28 (-0.43 to -0.12), p=0.009) (Table 3). At baseline, PGA was significantly correlated with function (r=0.54) but not depression (r=0.18) or anxiety (r=0.19). At 6 months, PGA showed a higher correlation with function (r=0.72) and became significantly correlated with depression (r=0.60) and anxiety (r=0.44). Emotional coping strategy was the only one significantly modified by MBSR; this maladaptive approach to illness is critical to quality of life. Qualitative interviews at 6 months in 10 patients indicated persistent subjective patient benefits including integration of MBSR techniques and effective coping strategies into daily life.
Conclusion: Offering MBSR to RA patients with high negative PROs is both feasible and helpful. MBSR had lasting benefits on outcomes that are important to patients, particularly anxiety, depression, and function. MBSR helped empower patients to practice self-management and enabled them to use fewer emotional coping strategies. MBSR did not appear to improve PGA, despite PGA correlations with function, depression, and anxiety at 6 months. The reasons for this apparent PGA disconnect require further studies.
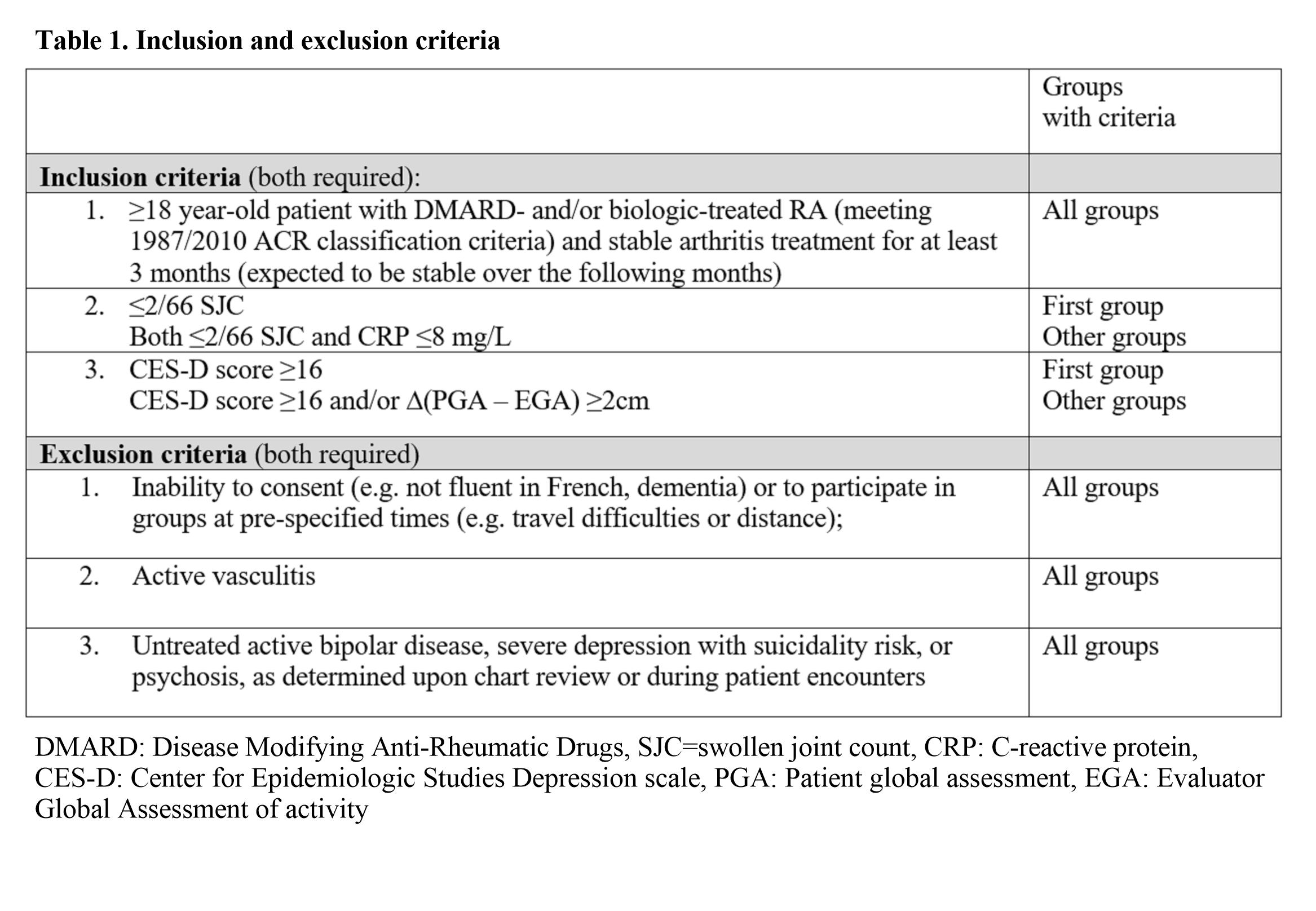 Table 1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Table 1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
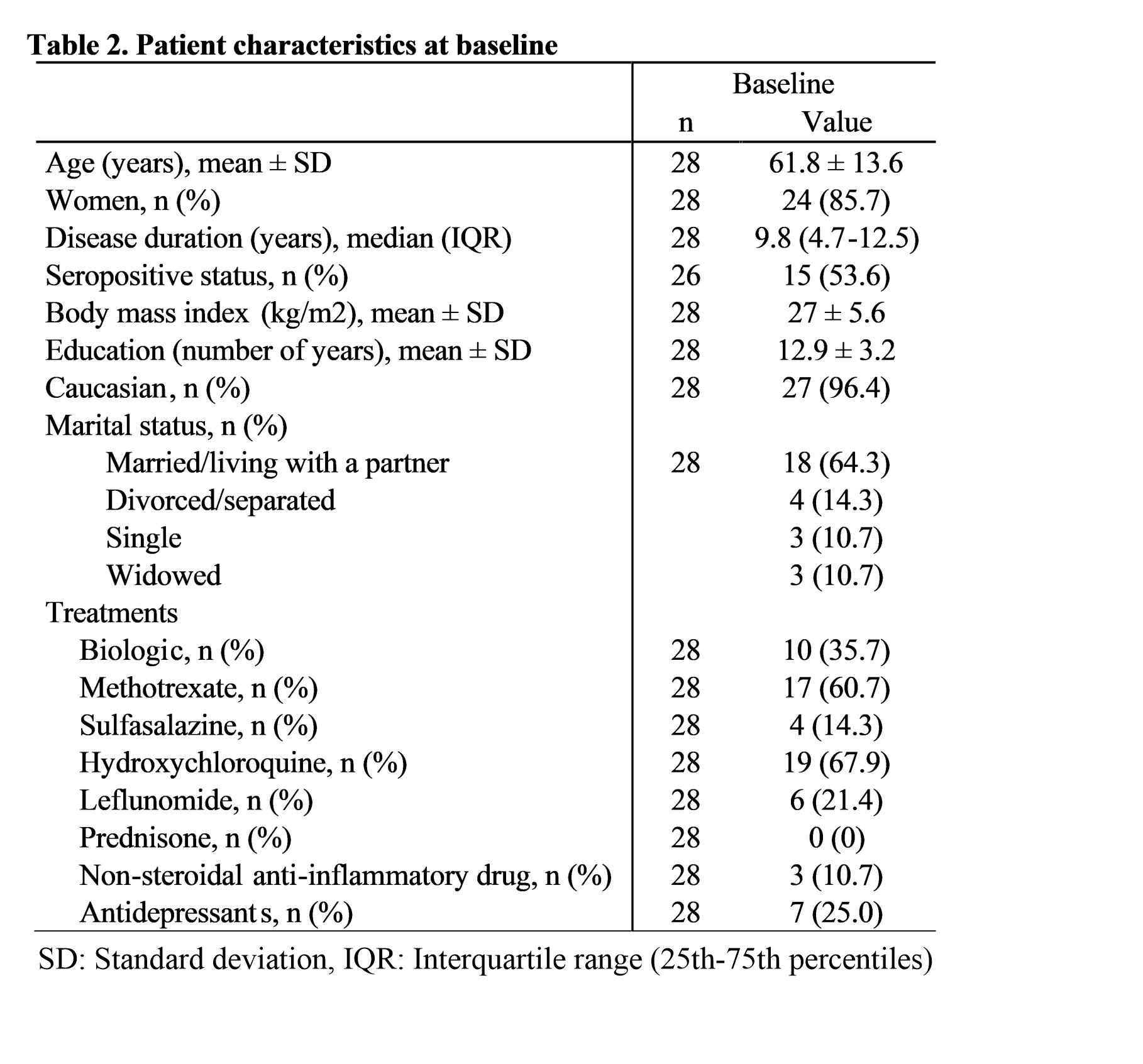 Table 2. Patient characteristics at baseline
Table 2. Patient characteristics at baseline
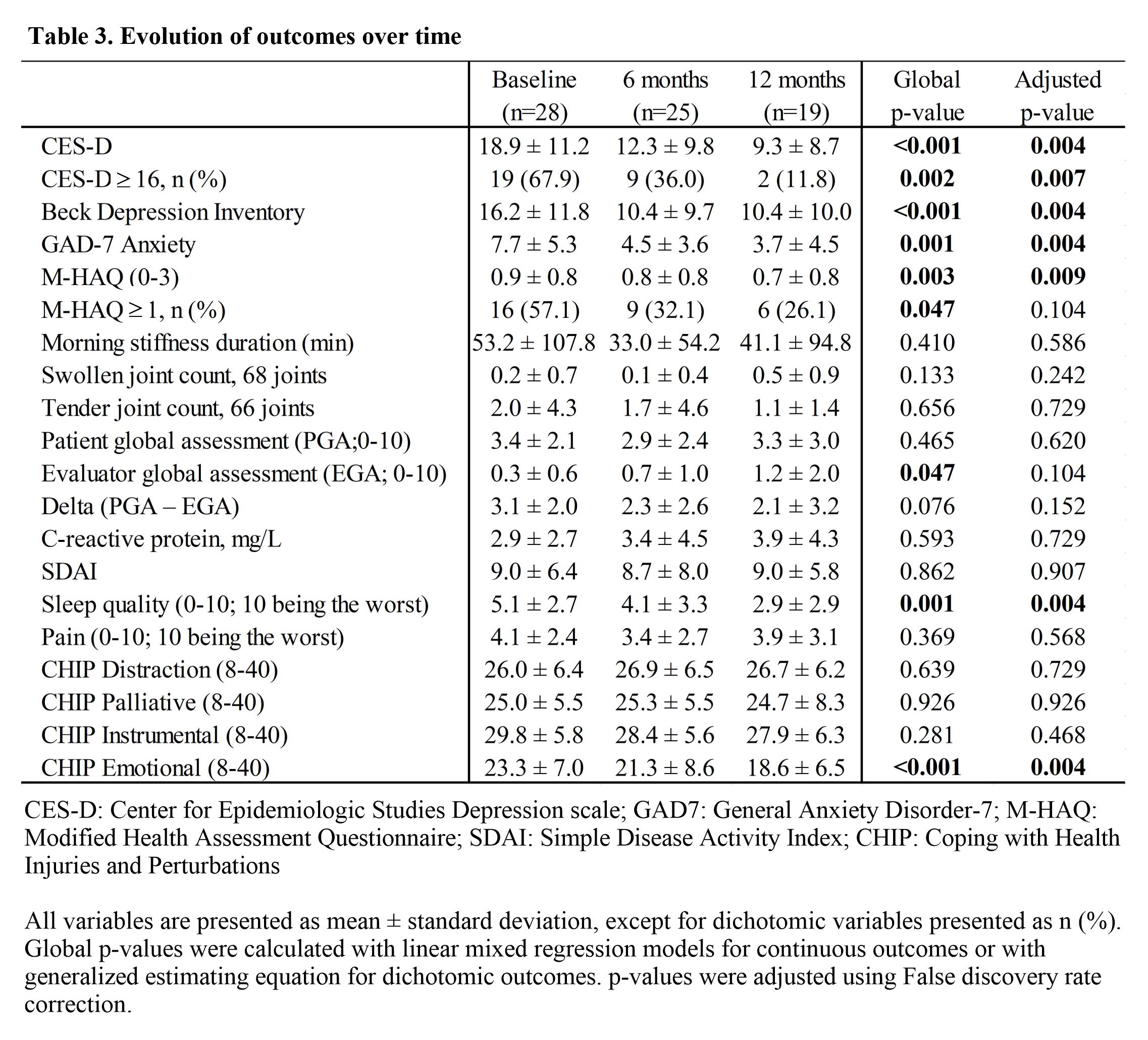 Table 3. Evolution of outcomes over time
Table 3. Evolution of outcomes over time
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beaulieu M, Gaboury I, Dobkin P, Carrier N, Gervais F, Gendron F, Roberge P, DAGENAIS P, Roux S, Boire G. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) to Improve Patient-Related Outcomes (PROs) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Clinical Remission but Elevated Negative PROs: A Pragmatic Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mindfulness-based-stress-reduction-mbsr-to-improve-patient-related-outcomes-pros-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-clinical-remission-but-elevated-negative-pros-a-pragmatic-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mindfulness-based-stress-reduction-mbsr-to-improve-patient-related-outcomes-pros-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-clinical-remission-but-elevated-negative-pros-a-pragmatic-pilot-study/
