Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Nailfold videocapillaroscopy (NVC) findings have been studied to differ in different subsets of myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSAs) associated inflammatory myopathies. Prior investigations observed a statistically significant reduced NVC score and greater capillary loss with presence of anti-transcriptional intermediary factor 1 gamma antibody (TIF). We aim to study differences in NVC findings amongst patients with TIF-associated dermatomyositis who developed cancer compared to patients who did not develop cancer in order to identify any prognostic NVC feature. This is the first study investigating this hypothesis to our knowledge.
Methods: Retrospective review of all patients with TIF dermatomyositis at Mayo Clinic from January 1st, 2010, till May 16th, 2024, was conducted. Adult patients >18 years of age were included and demographics, clinical features, serologies, date of diagnosis, laboratory data, last follow-up, response to treatment, NVC, and outcome were recorded. NVC was performed on all eight nailbeds using the 2nd-5th digits of both hands. Capillary morphology, density, organization, microhemorrhages, and ramifications of each nailbed were compared amongst TIF dermatomyositis with and without cancer. The study was approved by the Mayo Clinic Institutional Review Board.
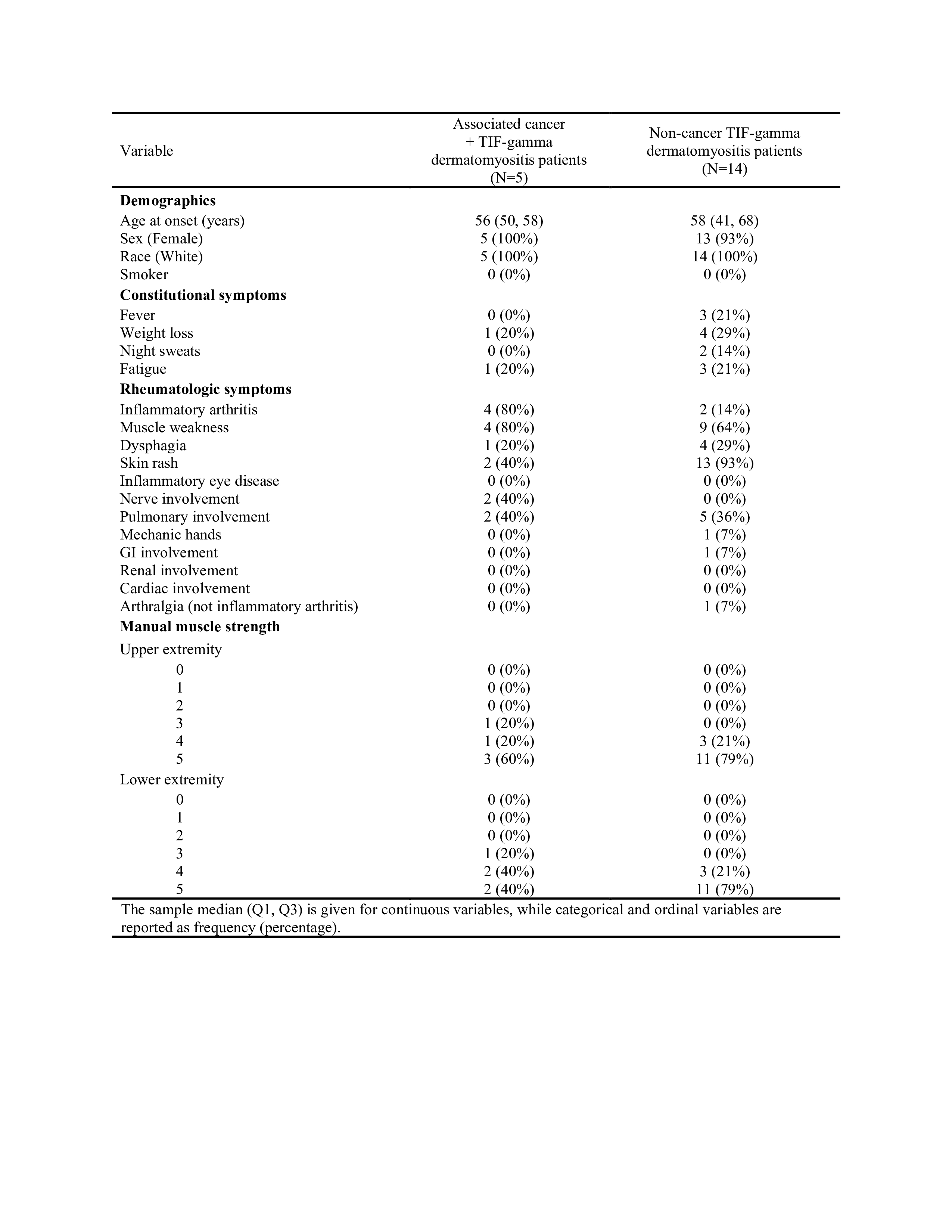
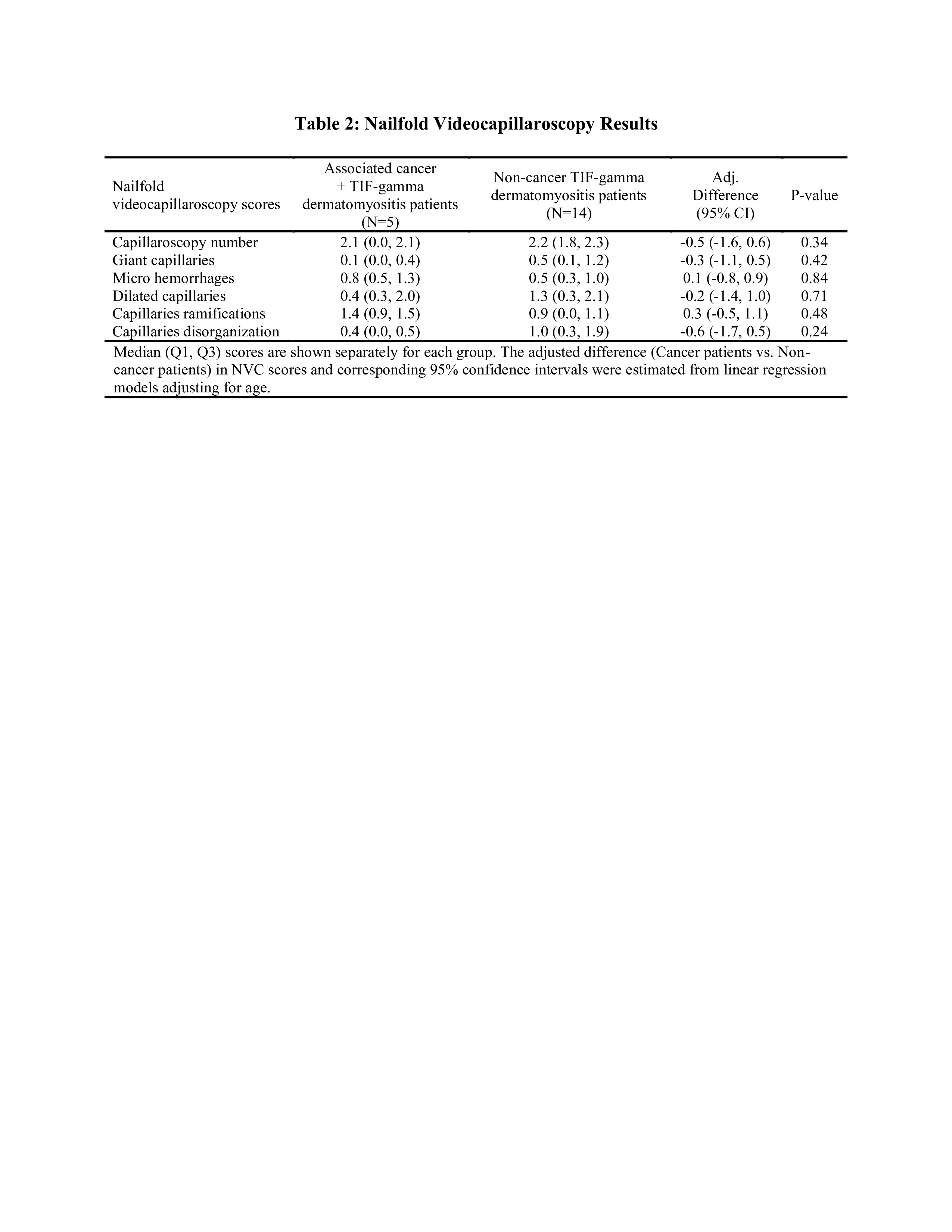
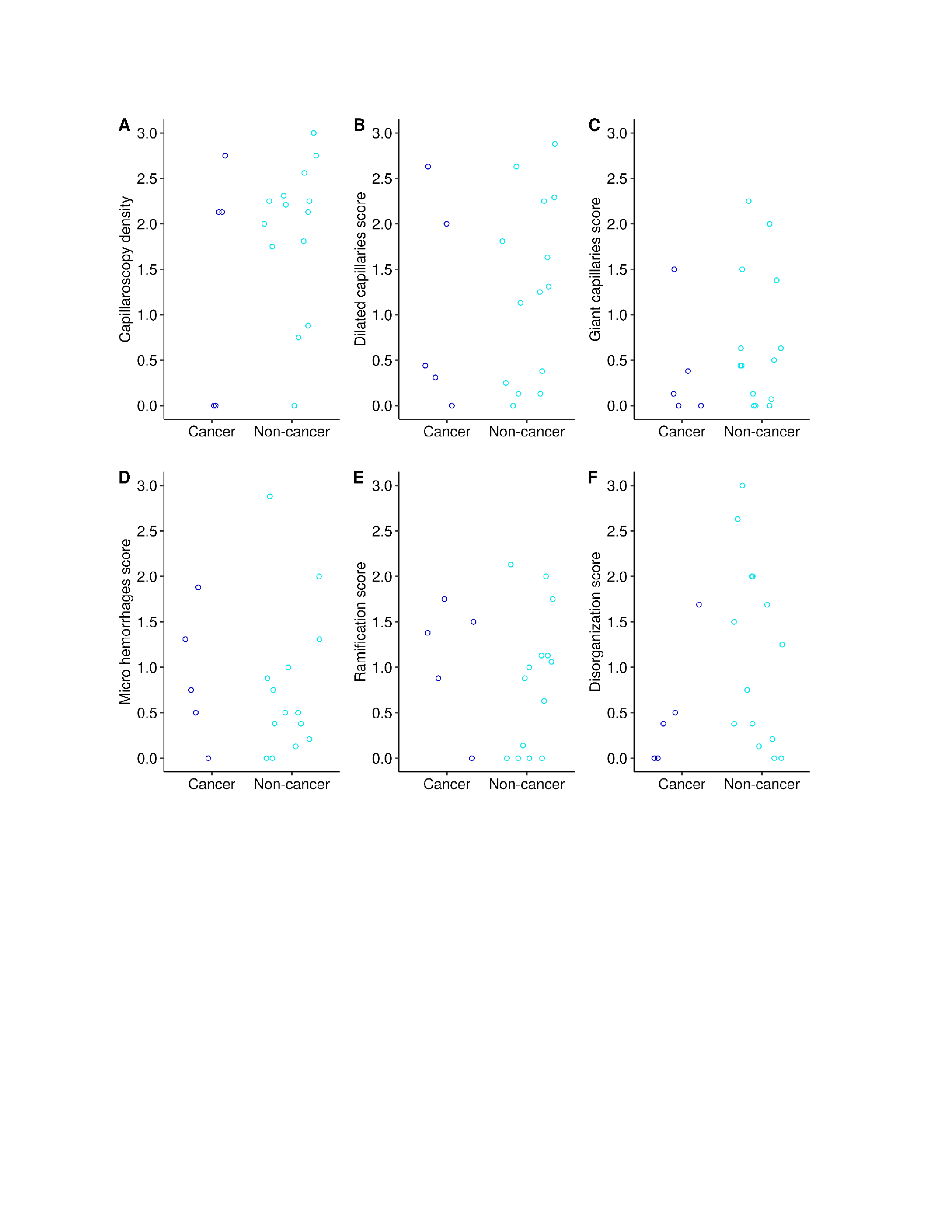
Results: 21 patients with TIF dermatomyositis were identified and NVC was performed on a total of 19 patients. 5 (26.3%) patients had cancer, 94.7% were female and there were no significant differences in race with 100% Caucasian patients (Table 1). Mean age was 56 years in the cancer subset and 58 years in the non-cancer group. TIF dermatomyositis patients with cancer were more likely to have inflammatory arthritis (80% vs 14%), muscle weakness (80% vs 64%) and neurological involvement while non-cancer subset had more skin involvement (93% vs 40%, Table 1). TIF dermatomyositis subset with cancer had higher NVC scores of capillary microhemorrhages and ramifications compared to patients without cancer (Table 2). Non-cancer TIF dermatomyositis patients had more enlarged ( >20 but < 50 microns) and giant ( >50 microns) capillaries with higher disorganization (Table 2).
Conclusion: TIF dermatomyositis patients with cancer were more likely to present with inflammatory arthritis, muscle weakness and neurological symptoms while patients without cancer had more frequent skin involvement. NVC differences between cancer and non-cancer TIF dermatomyositis were observed indicating microvascular differences with a potential for predicting cancer development and need to be further investigated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mumtaz S, Sullivan M, Diaz Menindez M, Craver E, Berianu F. Microvascular Differences Between Cancer and Non-cancer Anti-transcriptional Intermediary Factor 1 Gamma Antibody (anti-TIF1-γ) Associated Dermatomyositis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microvascular-differences-between-cancer-and-non-cancer-anti-transcriptional-intermediary-factor-1-gamma-antibody-anti-tif1-%ce%b3-associated-dermatomyositis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microvascular-differences-between-cancer-and-non-cancer-anti-transcriptional-intermediary-factor-1-gamma-antibody-anti-tif1-%ce%b3-associated-dermatomyositis-patients/