Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Aberrant regulation of the Wnt pathway is a key element in the pathogenesis of Ankylosing spondylitis (AS). We previously found that miR-29a was significantly upregulated in AS patients.
Methods: We enrolled 45 AS patients and 48 healthy controls. ESR, CRP and HLA-B27 were performed. BASDAI, BASFI, ASDAS and mSASSS were calculated. The levels of miR-29a and mRNA of DKK-1, GSK-3¦Â, ¦Â-catenin, ALP and OC from PBMCs were determined by real-time qPCR. Corresponding protein levels were measured by ELISA. Independent t-test was used to test for the differences between two groups. Correlation analysis was conducted using Spearman¡¯s correlation test. P <0.05 was considered statistically significant. The target prediction of miR-29a was performed. The luciferase activity levels were measured using Promega dual-luciferase reporter assay system. The miR-29a mimic or inhibitor or NC was co-transfected with constructed wt or mut-3¡¯UTR luciferase reporter into HEK293T cells. The miR-29a mimics (50 nmol/L) or inhibitor or NC was co-transfected to hFOB1.19 and MC3T3-E1 cells. The mRNA and protein level of DKK-1, GSK-3¦Â, ¦Â-catenin, OC, ALP, collegen X, Wnt-3a and Runx2 was detected at 48 and 72 hours.
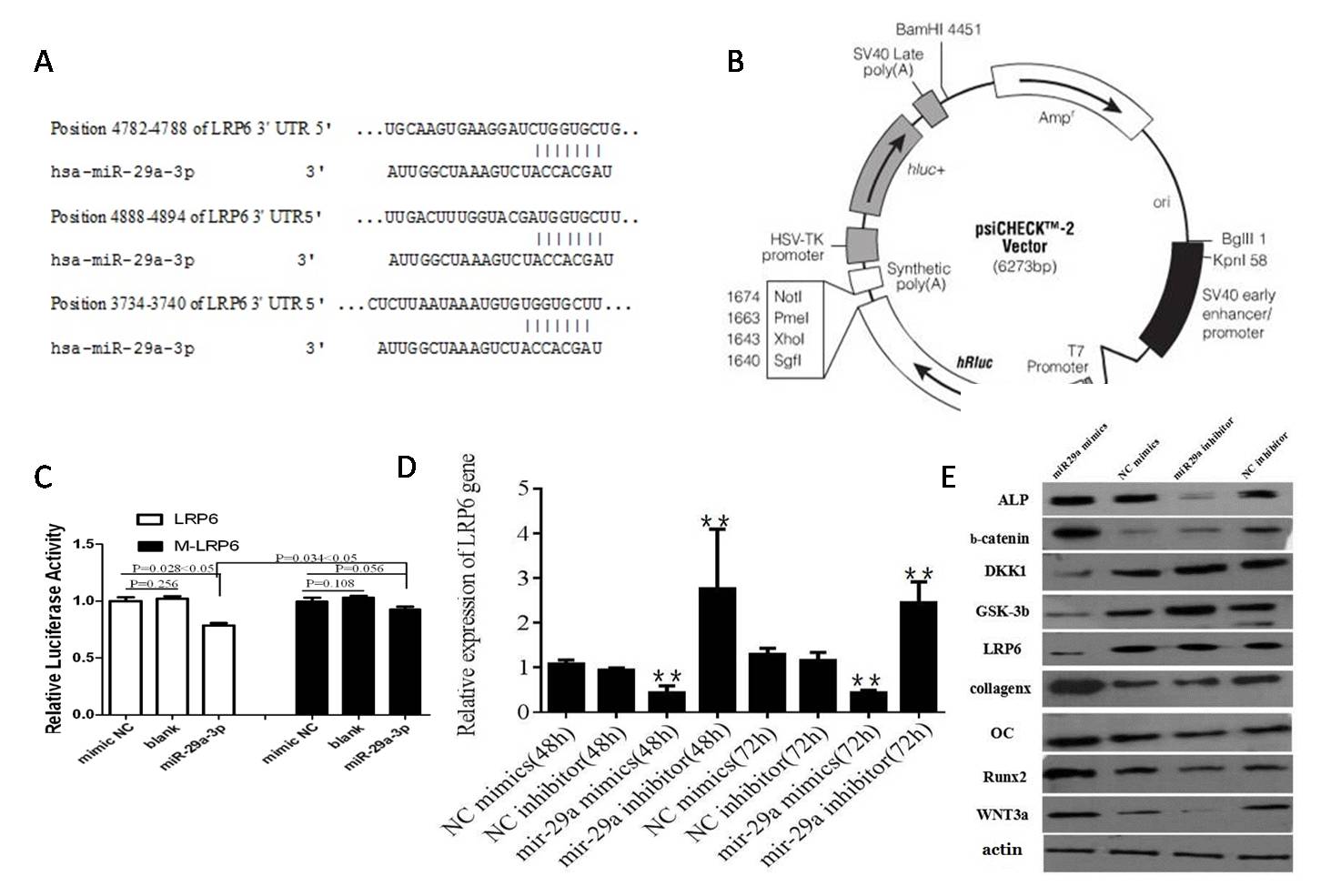
Results: The levels of DKK-1 was significantly higher in AS patients than that in healthy controls, with no correlation with any clinical parameter. No significant difference was observed for other markers.The levels of miR-29a, Dickkopf (DKK)-1, ¦Â-catenin and Runx2 mRNA were significantly higher in AS patients than those in controls (p<0.05). In contrast, the levels of Gsk-3¦ÂmRNA was significantly lower in AS patients than that in healthy controls (p<0.05). Gsk-3¦ÂmRNA was positively correlated with¦Â-catenin mRNA expression (p<0.05) and no other correlation was observed between any other markers (p>0.05). Only DKK-1 mRNA expression was negatively correlated with disease course (p<0.05) and no other correlation was observed between markers and clinical measurements (p>0.05). The luciferase reporter analysis showed that LRP6 was a target of miR-29a. miR29a suppressed LRP6, GSK-3¦Â, DKK-1 expression and facilitated ¦Â-catenin, Wnt-3a, Runx2, OC, ALP, collegen X expression. (Figure 1)
Conclusion: Alteration of bone turnover markers in canonical Wnt pathway was observed in AS which partially explain the complicated mechanism of bone formation. Bioinformatics and ex vivo studies proved that LRP6 is a target gene of miR-29a in AS.
Figure legend: A. The has-miR-29a-3p conserved putative sites of LRP6 3¡¯UTR predicted by TargetScan and miRDB. B. XhoI and Not¢ñ restriction sites of PsicheckTM-2 Vector dual-luciferase miRNA target vector. C. Luciferase reporter result of miR29a mimics or inhibitor transfection to wildtype and mutated LRP6. D. LRP6 was negatively regulated by miR29a at mRNA level by qPCR. E.Wnt signaling markers expression after microRNA transfection by Western blot.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang J, Yin Z, Fu Z, Ye Z, Zhang L. Microrna-29a Activation of Canonical Wnt Signaling By Targeting LRP6 in Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microrna-29a-activation-of-canonical-wnt-signaling-by-targeting-lrp6-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microrna-29a-activation-of-canonical-wnt-signaling-by-targeting-lrp6-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/