Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is the gold-standard DMARD in rheumatoid arthritis, however, it is unclear how exactly it works. Its effects on neutrophils may involve reduction in ROS production and neutrophil activation markers like CD177, CD11b and CD64.
Methods: This was a single-center cross-sectional study, which recruited patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and healthy controls. RA patients included naïve (could be on low dose steroids) and MTX treated patients (at least 15 mg/week for 6 months), labeled as naïve-RA and MTX-RA groups. Neutrophils were separated from blood using Hetasep and Ficoll density-gradient centrifugation. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) by dihydrorhodamine (DHR) was detected using flow cytometry after PMA stimulation (1.62 ug/ml) as Median Fluorescent Intensity (MFI). ROS by Luminol was detected after adding PMA (0.4 ug/ml) and Luminol (50 uM) and using a luminescence detector (area under curve over 30 mins). Activation markers CD177, CD11b and CD64 were detected by surface staining of neutrophils using FACS.
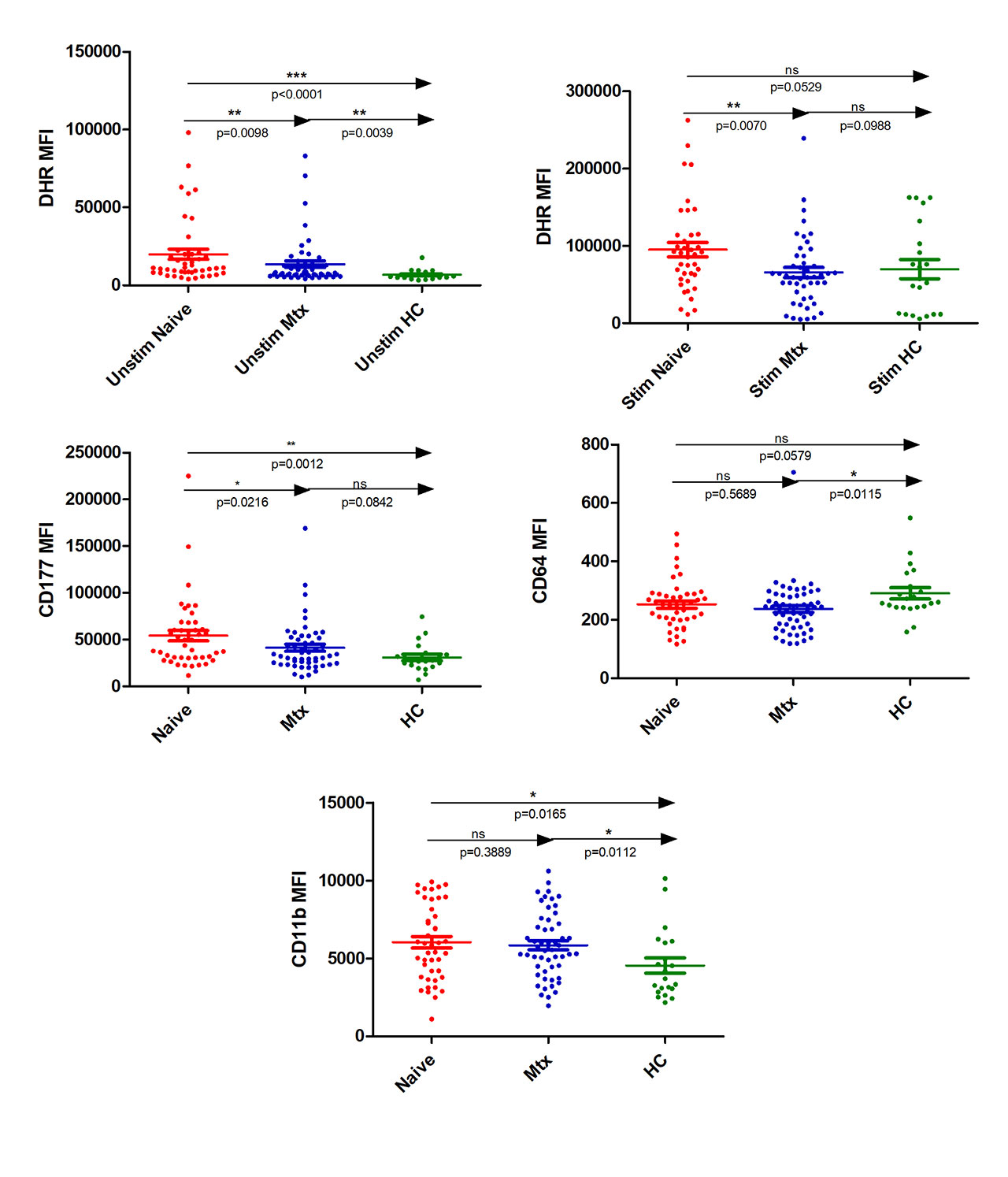
Results: This study included 53 (F:M= 43:10) patients of rheumatoid arthritis on methotrexate (MTX-RA), 47 (F:M=39:8) naïve (naïve-RA) and 21 healthy controls. There was no significant difference in the mean age (44.5, 47.6 years, p=0.17) between RA groups. There was a significant difference in the DAS28-3 between the naïve-RA and MTX-RA group (6.2, 4.9., p< 0.001). At baseline, there was higher level of ROS by DHR (MFI) in neutrophils of naive-RA compard to MTX-RA (11049, 7301, p=0.009). ROS levels by DHR (MFI) remained higher in naive-RA than MTX-RA (88805, 59637, p=0.0070) even after PMA stimulation. However there was no significant between MTX-RA and healthy controls after PMA stimulation. No significant difference was found in ROS by luminol between Naive-RA and MTX-RA patients. CD177 was found higher expressed (MFI) in naïve-RA compared to MTX-RA patients (46620, 34475, p=0.0216) and healthy controls (46620, 26855, p= 0.0012). No significant change for CD11b and CD64 levels was observed between naive and MTX treated patients. However, in comparison to healthy controls, MTX-RA patients had lower levels of CD64 (260, 241, p= 0.0115) while both MTX-RA and naïve-RA patients had higher levels of CD11b (3708, 5560, p= 0.0112 and 3708, 5978, p=0.0165).
Conclusion: MTX treatment in RA patients was associated with reduction (reaching healthy control levels) of ROS production in neutrophils. In addition, CD177 expression was also significantly reduced (reaching healthy controls) in MTX- treated patients. One of the ways MTX acts in RA may be through reducing neutrophil activation and ROS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kaundal U, Dhir V, Saikia B, Khullar A. Methotrexate Treatment Is Associated with Reduction of Neutrophil Reactive Oxygen Species and CD177 in RA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/methotrexate-treatment-is-associated-with-reduction-of-neutrophil-reactive-oxygen-species-and-cd177-in-ra-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/methotrexate-treatment-is-associated-with-reduction-of-neutrophil-reactive-oxygen-species-and-cd177-in-ra-patients/