Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: We aimed to identify biomarkers of disease activity in giant cell arteritis (GCA) patients treated with prednisone monotherapy and with prednisone in combination with tocilizumab (TCZ)
Methods: We mapped the serum proteome of GCA patients with active and inactive disease in an unbiased manner using high-throughput multiplexed mass spectrometry. Proteomic analyses were performed in 5 µl serum samples with 11-plexed tandem mass tag (TMT) technology using an Orbitrap Lumos mass spectrometer. A SEQUEST-based database search engine was employed for peptide identification. Quantification was based on TMT reporter ion intensities. All patients were sampled during their participation in the GiACTA trial,1 in which they received TCZ plus 26 weeks of prednisone (TCZ group) or placebo plus 26 or 52 weeks of prednisone (PRED group). Active disease was defined as the presence of cranial or PMR symptoms requiring treatment intensification regardless of ESR and CRP levels. Samples were selected if patients were in clear states of active or inactive disease at GiACTA systematic sample collection timepoints (baseline and weeks 4, 12, 24, 48). An exhaustive leave-2-out strategy was used to identify classification markers. Proteins with an absolute log2 fold concentration difference ≥0.5 between active and inactive samples and a P-value < 0.1 were retained and sorted based on the metric -log10(P-value)*absolute(log2 fold change). The accuracy of the top 10 biomarkers for classification of active versus inactive disease in each group was evaluated by determining areas under the curves (AUC) of receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves.
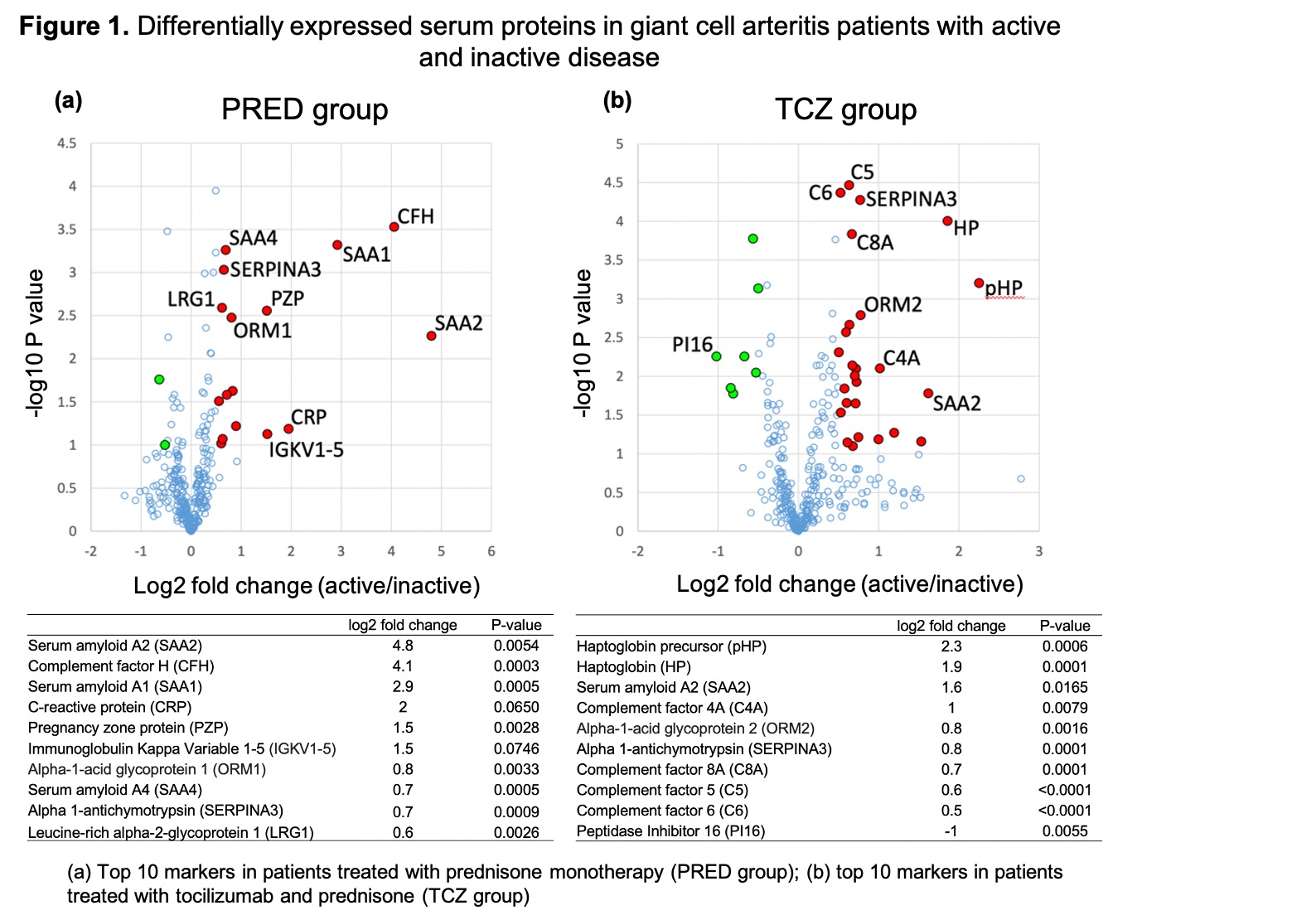
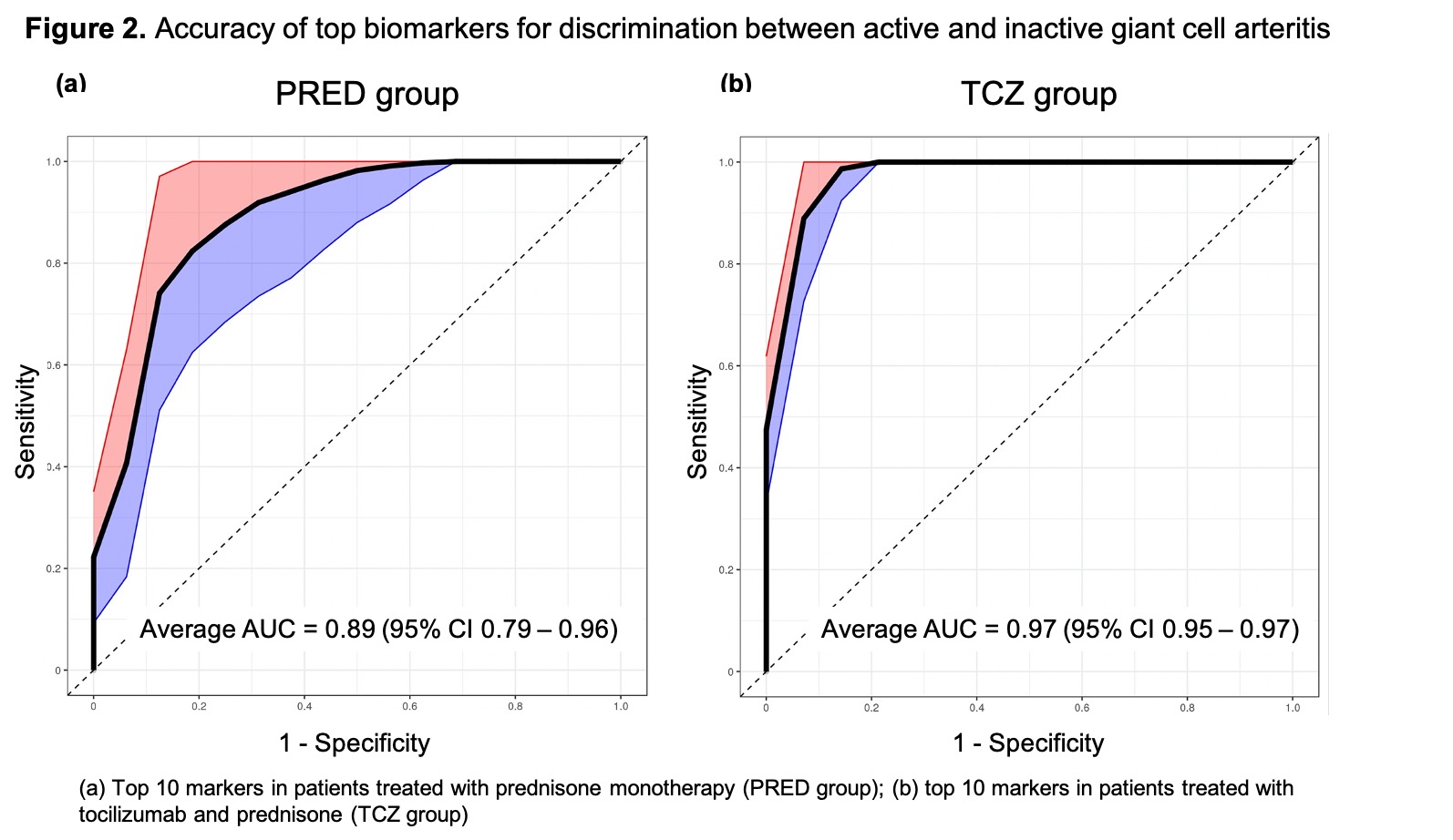
Results: The PRED group included 21 patients (active, n = 16; inactive, n = 5) and the TCZ group included 21 patients (active, n = 14; inactive, n = 7). Compared to inactive PRED-treated patients, active PRED-treated patients showed significant overexpression of several acute phase reactants including serum amyloid A1 and 2 (SAA1, SAA2) and complement factor H (CFH) (Fig. 1a). The magnitude of concentration change and the level of statistical significance observed for SSA1, SSA2 and CFH in PRED-treated patients were higher than those of CRP (Fig. 1a). Compared to inactive TCZ-treated patients, active TCZ-treated patients demonstrated significant overexpression of multiple biomarkers including haptoglobin, haptoglobin precursor, SSA2 and complement factor 4A, and underexpression of peptidase inhibitor 16 (Fig. 1b), a protein involved in vascular and regulatory T cell biology. Sets of 10 biomarkers resulted in a classification of active versus inactive disease with ROC AUCs of 0.89 (95% CI 0.79-0.96) in the PRED group (Fig. 2a) and 0.97 (95% CI 0.95-0.97) in the TCZ group (Fig. 2b).
Conclusion: We identified several differentially expressed serum proteins in GCA patients with active and inactive disease receiving prednisone monotherapy or TCZ-based treatment regimens. In both treatment groups, a signature of biomarkers classified disease activity status with high accuracy. Haptoglobin, a readily available laboratory test, may be useful in monitoring disease activity in GCA patients receiving IL-6 blockade therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Unizony S, Morris R, Kreuzer J, Haas W, Stone J. Mass Spectrometry Identifies Novel Biomarkers in Giant Cell Arteritis, Useful in Patients on Interleukin-6 Receptor Blockade [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mass-spectrometry-identifies-novel-biomarkers-in-giant-cell-arteritis-useful-in-patients-on-interleukin-6-receptor-blockade/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mass-spectrometry-identifies-novel-biomarkers-in-giant-cell-arteritis-useful-in-patients-on-interleukin-6-receptor-blockade/