Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Sarcoidosis is a multisystem granulomatous disease which can affect the GI system in about 5-10% of cases, out of which 11-80% can have hepatic sarcoidosis (HS). Clinical presentation of HS varies from asymptomatic liver enzymes elevation to jaundice, pruritus, or abdominal pain. Elevated ALP is the most reliable indicator for liver involvement. Definitive diagnosis is based on liver biopsy. The goal of the treatment is to prevent the development of portal hypertension and cirrhosis. Evidence based guidelines for the treatment of HS are lacking but most studies support the use of steroids, urodeoxycholic acid (UDC), MTX, azathioprine, MMF, or infliximab . This study explores the efficacy of these medications in treatment of HS
Methods: We searched for the patients using the ICD codes for both sarcoidosis (ICD-10: D86) and granulomatous hepatitis (ICD-10: K75.3) at OLSU Health Shreveport. 150 unique medical record numbers were generated. We retrospectively reviewed notes, labs, liver biopsies, imaging, and medications in EMR. We used descriptive statistics to calculate the percentages using open source software
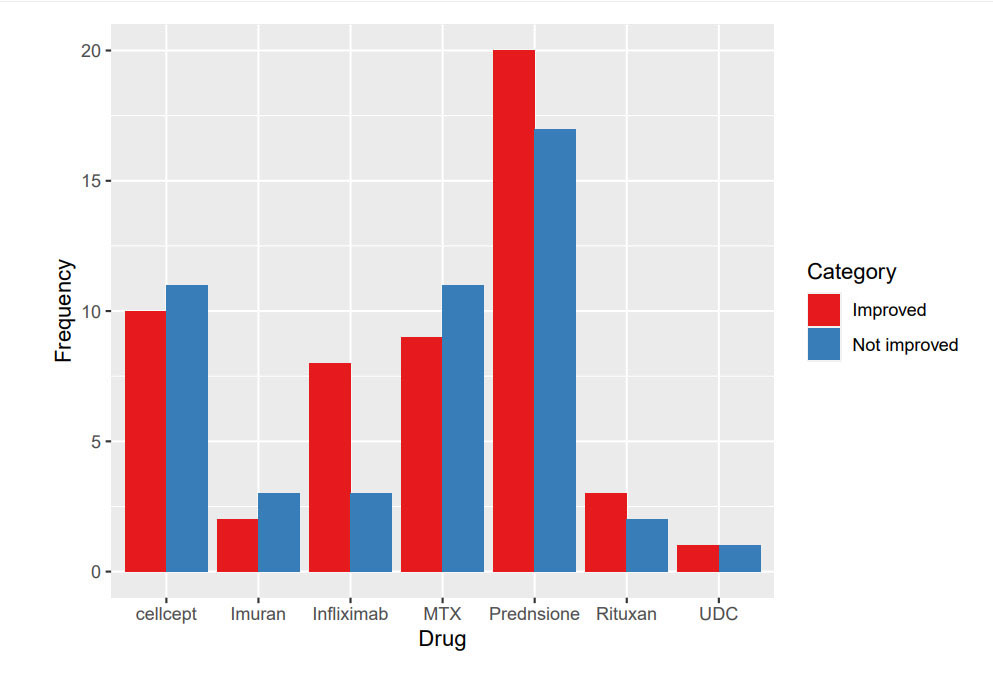
Results: 47 patients had a diagnosis of HS. 78% were females in the age range of 20-40 years and 93% were African Americans. 25% of patients had sole liver involvement and 75% had multiorgan involvement. 72% of patients had ALP elevation of >200. 48% of patients had liver USG and 27% had liver biopsies. 36(76%) patients received steroids, 20 (42%) had MTX, 5 (10%) had azathioprine, 5 (10%) had Rituximab, 12 (25%) had infliximab, 3 (6%) had UDC, 21 (44%) had MMF. 12 patients received combination of prednisone with either MTX, azathioprine, MMF, infliximab or Rituximab. Treatment response was measured based on the ALP improvement. 55% of patients responded to prednisone, 45% to MTX, 40% to azathioprine, 60% to Rituximab, 66% to infliximab, 47% to MMF and 30% to UDC
Conclusion: Majority of the patients presented with ALP elevation of >200. Liver biopsy was performed in only 27% of the patients, further emphasizing the need to rule out the other causes of ALP elevation and granulomatous liver changes. Liver involvement was seen most commonly in patients with multisystem sarcoidosis. UDC, despite being one of the recommended initial therapies for HS, was used in only 3% of patients. Steroids were most commonly used. Among all the steroid sparing agents, infliximab had shown the best efficacy. Infliximab infusion given every 4-6 weeks in refractory cases had resulted in disease remission. Similarly, methotrexate showed improvement but it was generally avoided due to the risk of hepatotoxicity. Azathioprine, MMF and rituximab were used either in combination or as sole therapies and have shown improvement in ALP. Given the development of serious complications like cirrhosis and portal hypertension, it is crucial to recognize the liver involvement early in the disease course using the appropriate diagnostic approach. Further studies are required to determine the efficacy of steroid-sparing medications in the protection against progressive liver disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Muzaffar K, Hasan S, umer S, Bhuiyan M, Vadlamudi K, Sondhi M, Ali A, Muutu T, Hayat S. Management of Hepatic Sarcoidosis, a Retrospective Analysis of Patients at a University Hospital [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/management-of-hepatic-sarcoidosis-a-retrospective-analysis-of-patients-at-a-university-hospital/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/management-of-hepatic-sarcoidosis-a-retrospective-analysis-of-patients-at-a-university-hospital/