Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The benefit of RTX has been suggested for interstitial lung disease (ILD) associated with connective tissue disorders (CTD). Preliminary data have suggested that B cell depletion measured 2 weeks after the first RTX infusion was predictive of short-term treatment response at 6 months in systemic sclerosis (SSc)-ILD. Our aim was to determine whether the quality of B cell depletion was associated with therapeutic response to RTX in CTD-ILD.
Methods: Retrospective monocentric study including all patients treated at least 1 year with RTX for SSc- or MCTD-ILD. The observation period was defined by to the time from the first to the last RTX infusion. ILD was identified based on high-resolution CT. The results of forced vital capacity (FVC) and carbon monoxide diffusion capacity (DLCO) were collected at the time of the first RTX infusion, at month 12 and at the time of the last RTX infusion. B cell immunophenotyping was performed the day of each RTX infusion (Aquios, Beckman Coulter). B cell depletion was defined by CD19 < 18/mL. The primary outcome was the absolute change from baseline of FVC (L) at 12 months and at the last RTX infusion according to B cell depletion within the observation period. Secondary outcomes were the course of DLCO at the same time points according to B cell depletion and the analysis of the % of good RTX responders at 12 months and at the last RTX infusion, defined by at least 5% improvement in %FVC compared to baseline.
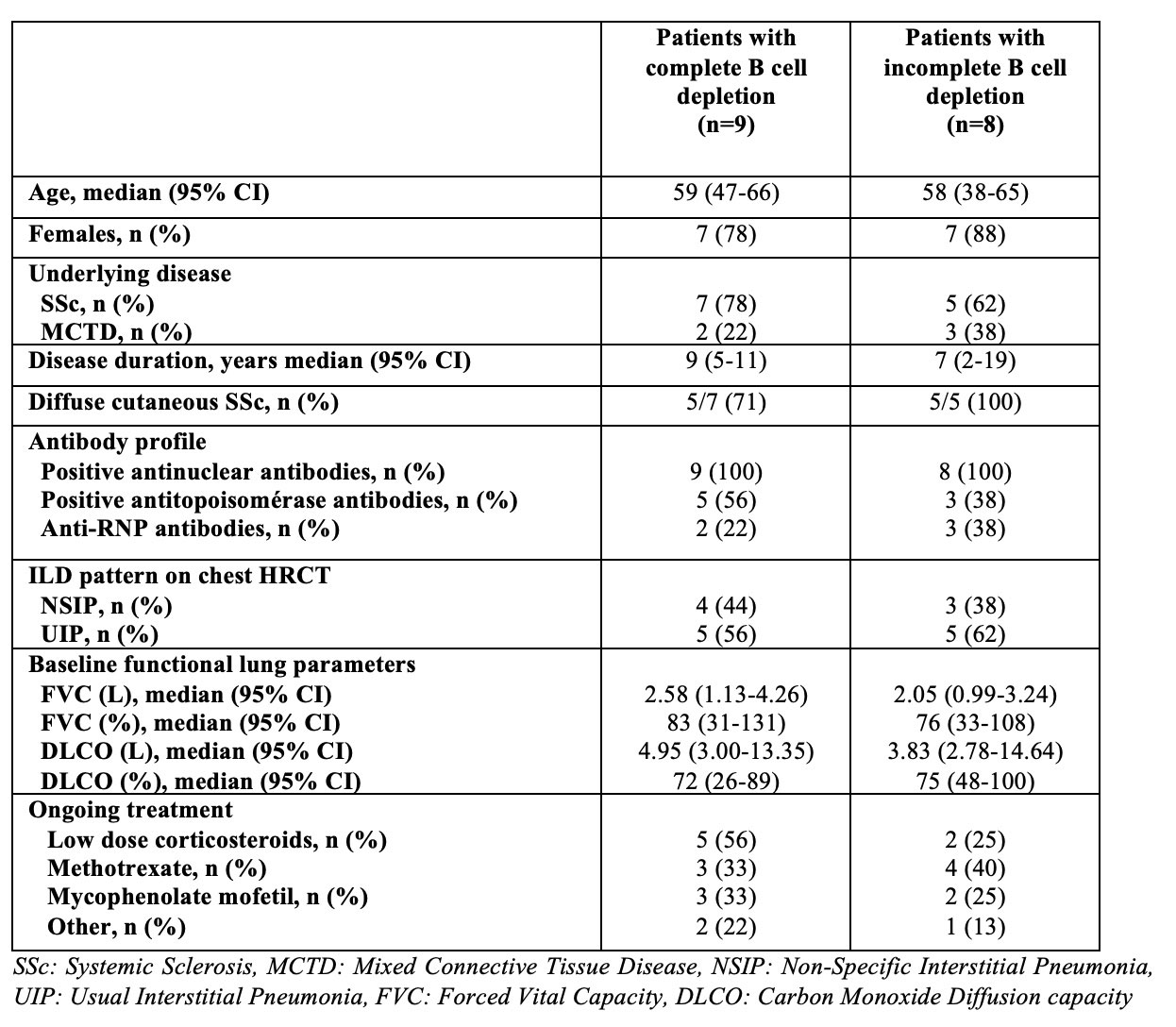
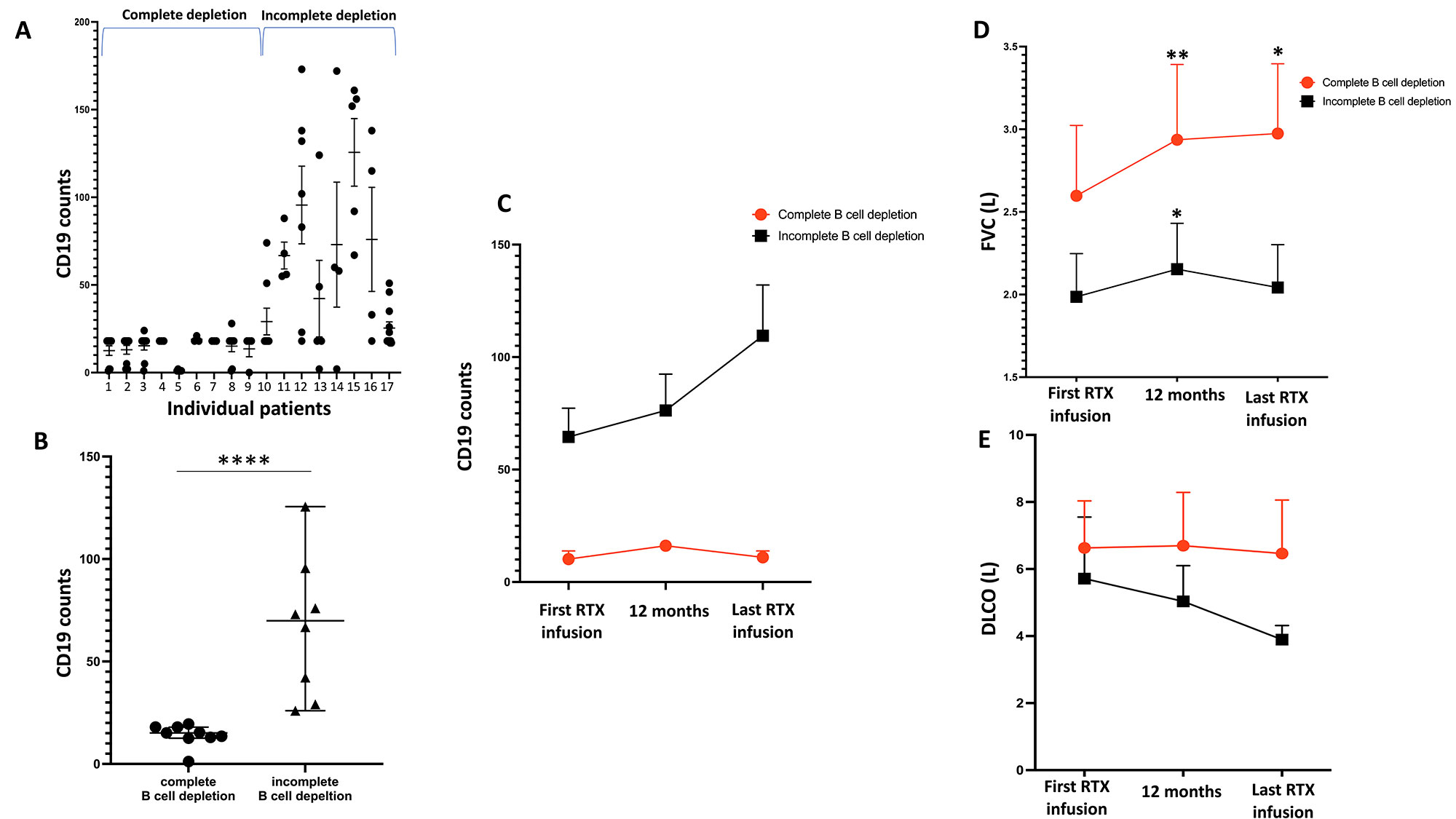
Results: 17 patients (12 SSc and 5 MCTD) were included, with a median age of 59 years and a median disease duration of 8 years (Table 1). The duration of RTX exposition was 45 months (95% CI 19-90 months), the median number of infusions was 8/patient (95% CI 5-14) and the cumulative RTX dose was 7g (95% CI 5-14g). These parameters were similar in the 9 patients with complete B cell depletion (CD19: 15/μL, 95% CI 13-18 /μL, Figure 1A-B) and the 8 patients with incomplete B cell depletion (CD19: 50/μL, 95% CI 26-126 /μL, Figure 1A-B). The absolute change from baseline of the FVC was different according to B cell depletion during the observation period. In the subset of patients who maintained complete B cell depletion (Figure 1C), median FVC increased from 2.58 L (95% CI 1.13-4.08 L) to 3.08 L (95% CI 1.34-4.64 L) at month 12 (p=0.004) and 3.22 L (95% CI 1.57-4.19 L) at the last RTX infusion (p=0.019) (Figure 1D). Conversely, in the subset of patients with constant incomplete B cell depletion (Figure 1C), FVC initially increased from 2.04 L (95% CI 0.99-3.24 L) to 2.23 L (95% CI 0.83-3.35 L) at month 12 (p=0.039) before decreasing to 1.89 L (95% CI 1.00-3.24 L) (p=0.37) (Figure 1D). The absolute change from baseline of DLCO did not significantly differ according to B cell depletion, but a trend was observed for a more pronounced decrease of this parameter in patients with constant incomplete depletion. In addition, The % of RTX responders was higher in the subset of patients who maintained complete B cell depletion at 1 year (8/9, 89% vs. 5/8, 63%) and at the last RTX infusion (7/9, 78% vs. 4/8, 50%).
Conclusion: These results highlight the importance of obtaining and maintaining B cell depletion to gain clinically relevant efficacy of RTX in CTD-ILD. CD19 measurement at each infusion is a relevant tool to monitor RTX efficacy in daily practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Avouac J, Ghossan R, Al Tabaa O, Combier A, Steelandt A, Thomas M, Allanore Y. Maintained Complete B Cell Depletion Is Associated with Rituximab Efficacy in Connective Tissue Disorder Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maintained-complete-b-cell-depletion-is-associated-with-rituximab-efficacy-in-connective-tissue-disorder-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maintained-complete-b-cell-depletion-is-associated-with-rituximab-efficacy-in-connective-tissue-disorder-interstitial-lung-disease/