Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1442–1487) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) may develop in up to 20% of patients with lupus nephritis (LN). The SLE disease activity generally declines after the development of ESRD and renal transplantation (RT). However, several studies reported SLE flares could occur after ESRD or RT. In this study, we performed a systematic literature review and meta-analysis to assess the frequency of SLE flares, in patients with ESRD or after RT.
Methods: We used PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library to search the literature from 1973 to 2023. PRISMA 2020 guidelines and checklist were used to conduct the meta-analysis. Studies investigating frequency of lupus flare in patients after renal replacement therapy (RRT) were included in the analysis. If the information was available, SLE flares were recorded separately for different RRT modalities such as hemodialysis (HD), peritoneal dialysis (PD), and RT. ACR 1997 revised classification criteria was utilized to ascertain SLE diagnosis. We excluded studies that did not mention lupus flares after the development of ESRD or RT. Two authors (O.N.P., A.D.) independently reviewed all articles and evaluated the data for consistency between the abstracts and tables to avoid bias. A forest plot was used to compare odds ratios (95% CI) of SLE flares after ESRD or RT. Study heterogeneity was assessed using I2. All analyses were performed using the R Statistical Software meta package (v4.2.1; R Core Team 2022).
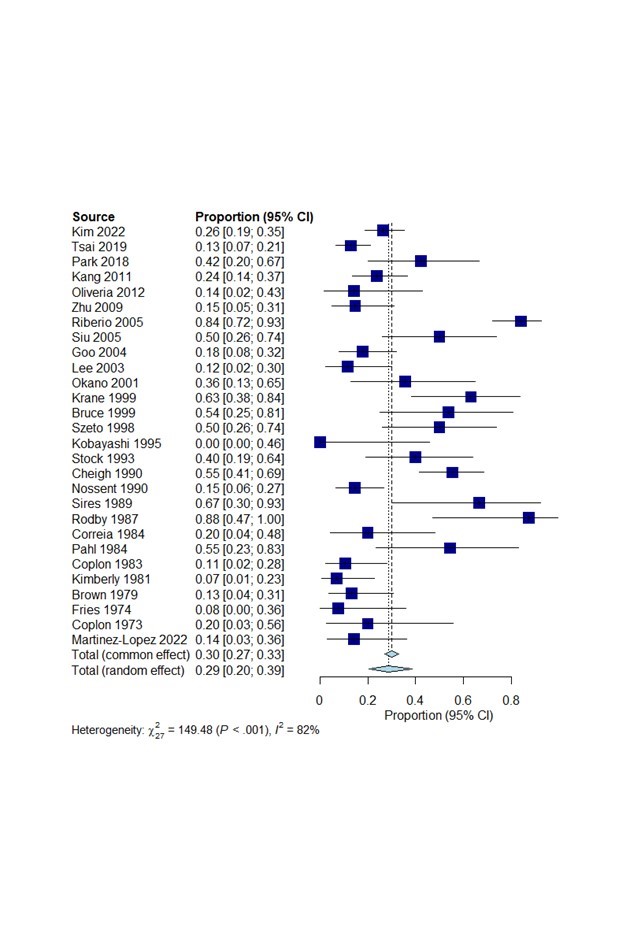
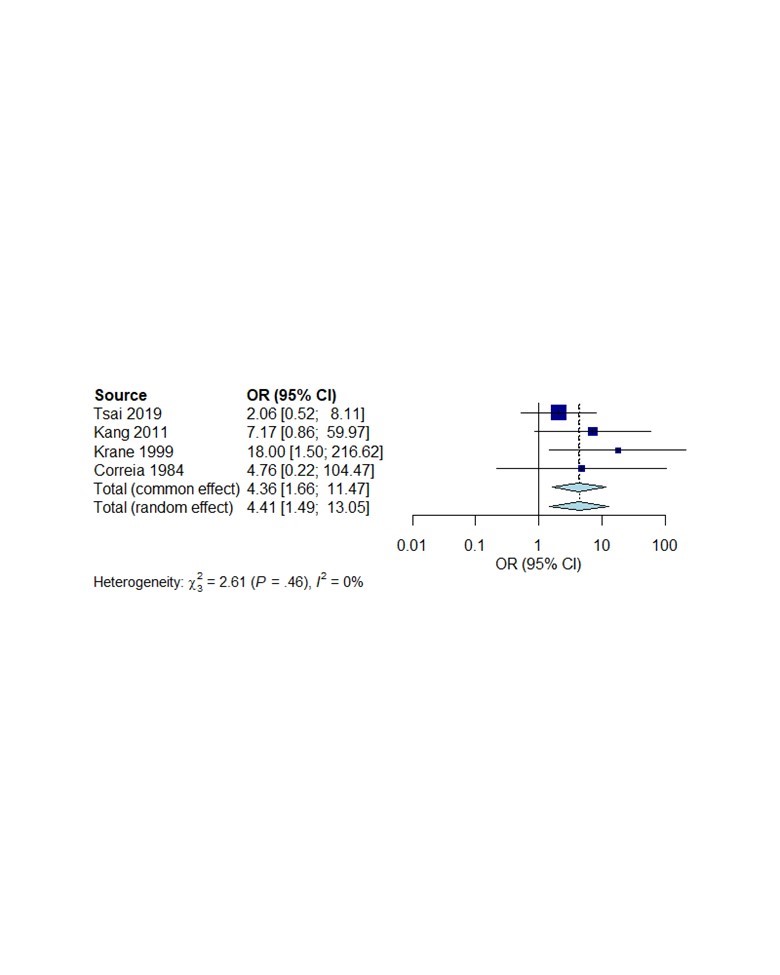
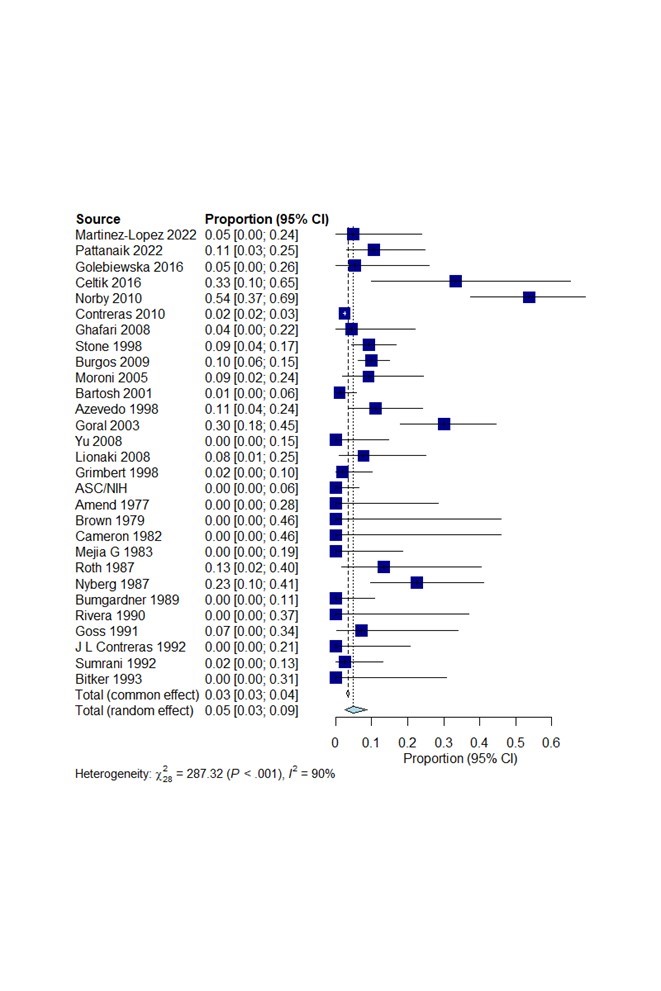
Results: Our literature review revealed 583 relevant articles, 487 were deemed unsuitable by title or abstract. We reviewed the full text of remaining 96 articles and 69 fulfilled study entry criteria. Twenty-eight studies (862 SLE patients) evaluated clinical SLE disease flares after RRT (HD and PD). Overall 30% of patients with ESRD had at least one flare after RRT (Figure 1). Seven studies (307 SLE patients) compared SLE disease flares after PD or HD initiation. The frequency of SLE flares was similar in both PD (25.6%) and HD (25.3%) (OR: 1.05, 95% CI: 0.57-1.94, p=0.88). Clinical SLE disease flares were evaluated in 5 studies after RT (91 patients). 14.3% of patients had at least one clinical SLE flare (95%CI: 8.5-23.1%). Four studies (204 SLE patients) compared lupus flares in SLE patients with PD/HD or RT. Flare risk was significantly higher in PD/HD group when compared to RT (OR: 4.36, 95%CI: 1.66-11.47, p=0.0028) (Figure 2). Twenty-nine studies (7890 SLE patients with RT) analyzed the recurrence of the LN after RT. LN had been diagnosed in 3.4% of patients (95%CI: 3-3.8%) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis showed lupus flares can still occur in up to 30%of patients with ESRD on RRT. The risk of flare is increased in patients on dialysis as compared to after RT. The flare risk is similar in patients on either HD or PD. A small percentage of SLE patients get recurrence of LN even after transplant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pamuk O, Daoud A, Dweik L, Desai N, Hasni s. Lupus Flares More Common in Patients on Dialysis Compared to After Renal Transplant: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-flares-more-common-in-patients-on-dialysis-compared-to-after-renal-transplant-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lupus-flares-more-common-in-patients-on-dialysis-compared-to-after-renal-transplant-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/