Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) have become the primary treatment option for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from 2010 in Taiwan. Tocilizumab is an interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor (IL-6Ri) and Tofacitinib is Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi), in treating RA patients. They have much similar mechanism and efficacy. To address this concern, we conducted a comparison of the safety outcomes of Tocilizumab and Tofacitinib in RA patients in real-world clinical settings.
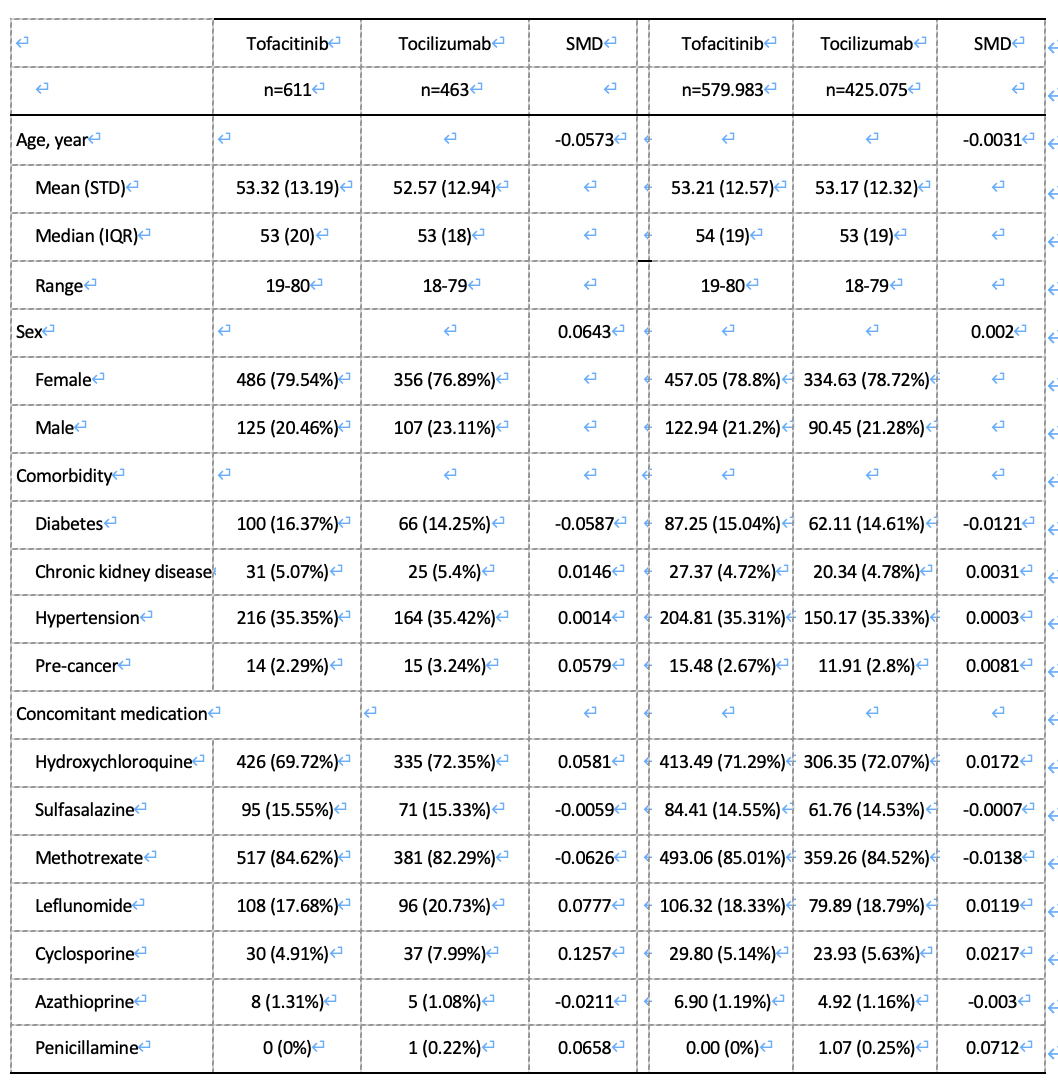
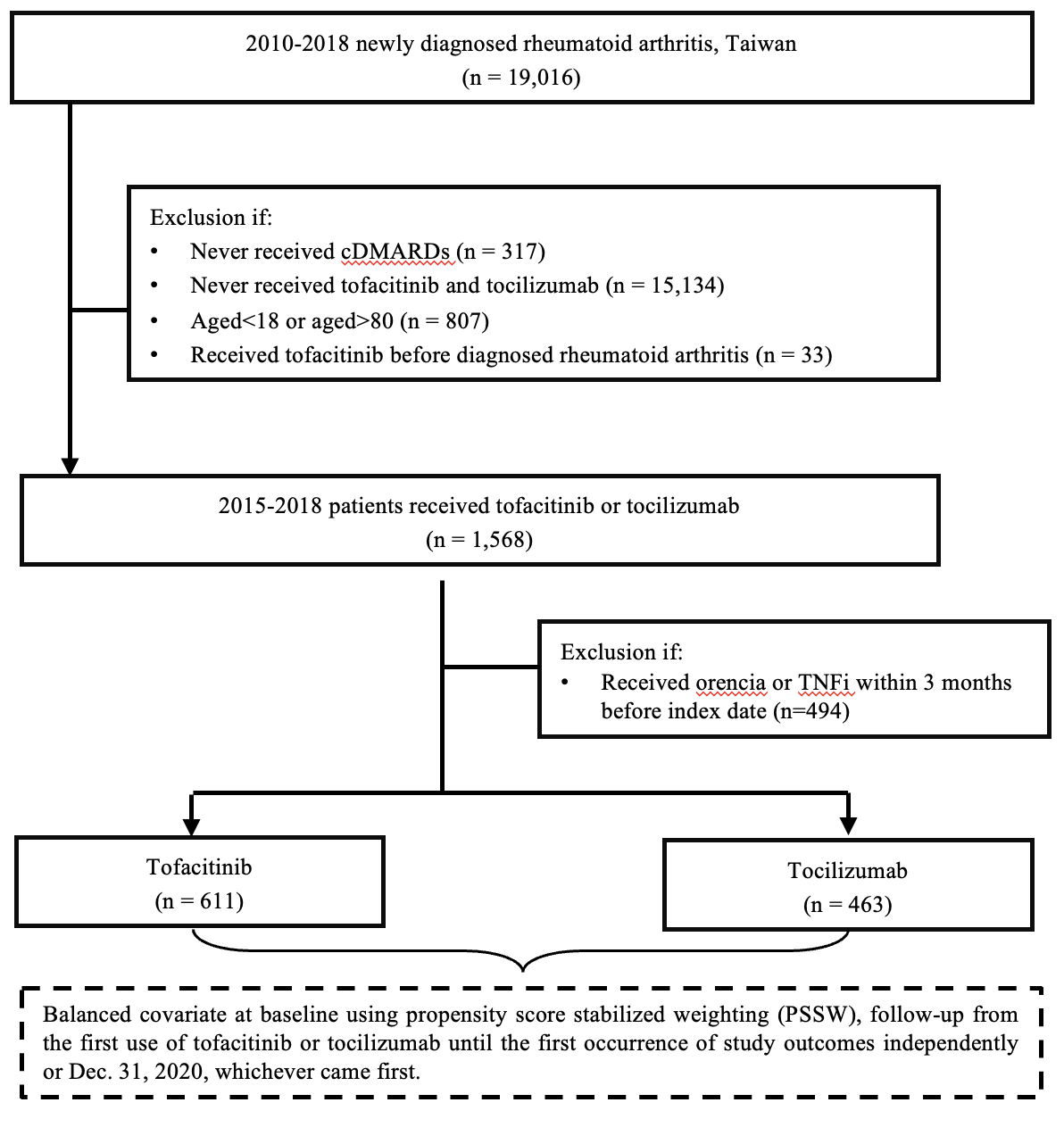
Methods: Patients diagnosed with RA between 2010 and 2018 were identified from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database and followed till 2020. Propensity score stabilized weighting (PSSW) was used to balance the baseline characteristics of the Tocilizumab and Tofacitinib groups. The incidences of safety outcomes, namely cardiovascular (CV) events, total hip replacement (THR), total knee replacement (TKR), tuberculosis (TB), herpes zoster infection, cancer and all-cause mortality, were compared between the study groups.
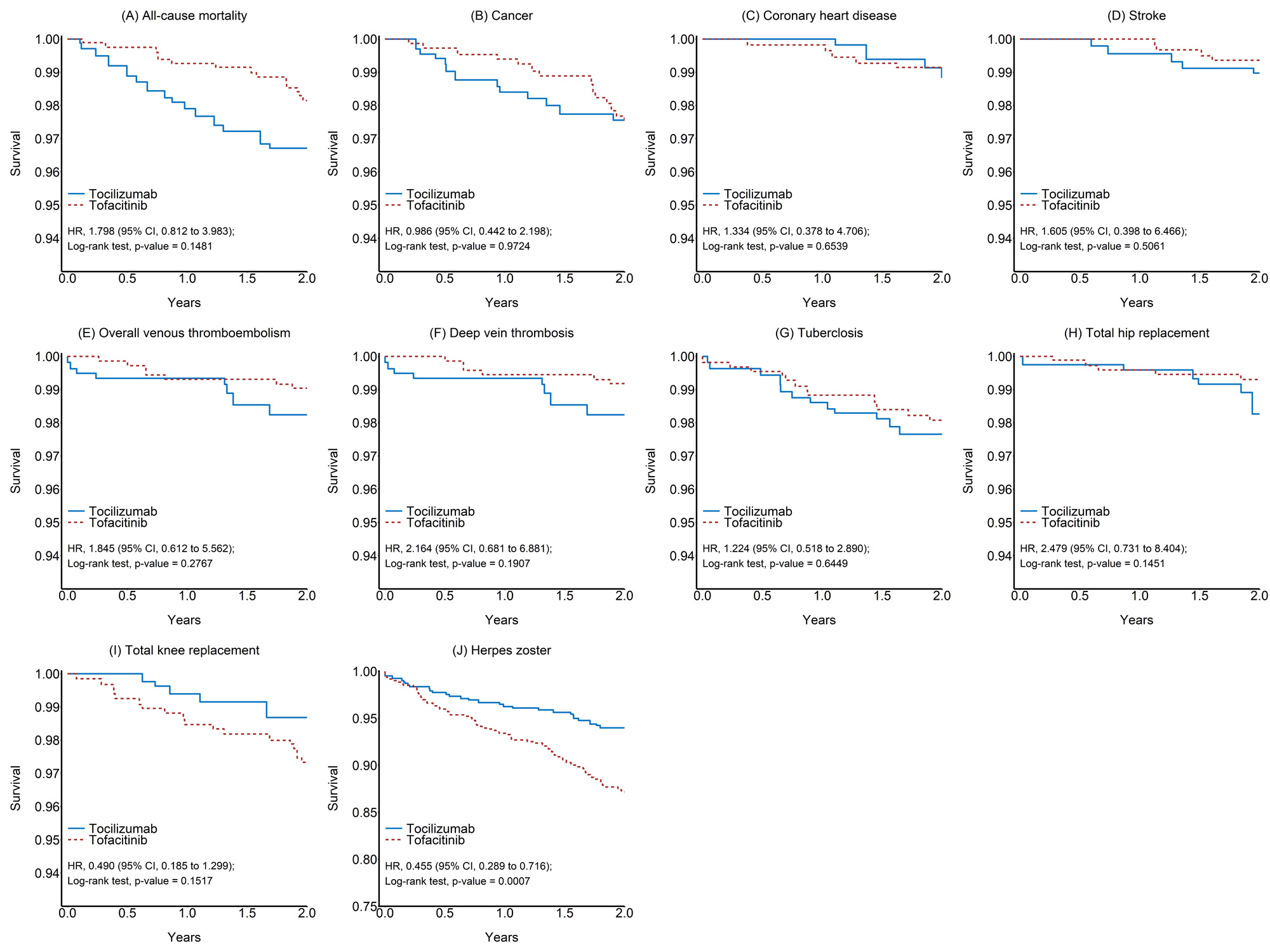
Results: A total of 1,074 patients with RA who were administered Tocilizumab (n = 463) and Tofacitinib (n = 611) were included in this study. The mean follow-up duration was 1.96 years in Tocilizumab group and 1.98 in the Tofacitinib group. A lower incidence rate of herpes zoster infection was observed in the Tocilizumab group than in the tofacitinib group. All-cause mortality, CV events, THR and TB infection had higher incidence rate but all without statistical significance.
Conclusion: Although, the mechanism of Tocilizumab and Tofacitinib are much similar. Lower herpes zoster incident rate was observed in Tocilizumab group compared with Tofacitinib. Other safety issues and mortality rates revealed comparable incidences in both groups with RA patients treated in real-world settings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fang Y, See L, Chang S. Lower Herpes Zoster Rate of Tocilizumab and Tofacitinib in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lower-herpes-zoster-rate-of-tocilizumab-and-tofacitinib-in-patients-undergoing-treatment-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lower-herpes-zoster-rate-of-tocilizumab-and-tofacitinib-in-patients-undergoing-treatment-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/