Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) provides long lasting efficacy in the control of rheumatoid arthritis. Among factors associated with RTX failure are the occurrence of anti-drug antibodies (ADAb) and incomplete tissular B-cell depletion occurring in 30% of patients and associated with lower response (Bitoun et al JAMA network open 2023). However, the underling immunological mechanisms are poorly understood. Since tissular depletion is mainly performed thru antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by macrophages phagocytosis, we focused on CD47 a molecule expressed on all B-cells that provides a don’t eat me signal to macrophages. We hypothesized that CD47 signaling (don’t eat me signal) from B-cells to macrophages could diminish RTX efficacy by decreasing B-cell depletion in RA patients.
Methods: RA patients treated with rituximab from the prospective ABIRISK cohort that aimed to identify factors influencing anti-drug antibodies were included. Flow cytometry analysis was performed at baseline to monitor the levels of CD47 on B-cells. Response to RTX was defined by good or moderate EULAR response and delta DAS 28 at 6 months. ADAb were measured using a previously published Meso scale discovery-based assay developed for the ABIRISK study. Blood donors Monocyte derived macrophages (MDM) were obtained after culture with human serum. A phagocytosis assay between MDM and CFSE-stained B cells with RTX +/- anti-CD47 antibody was performed to investigate the impact of CD47 on RTX ability to induce ADCC.
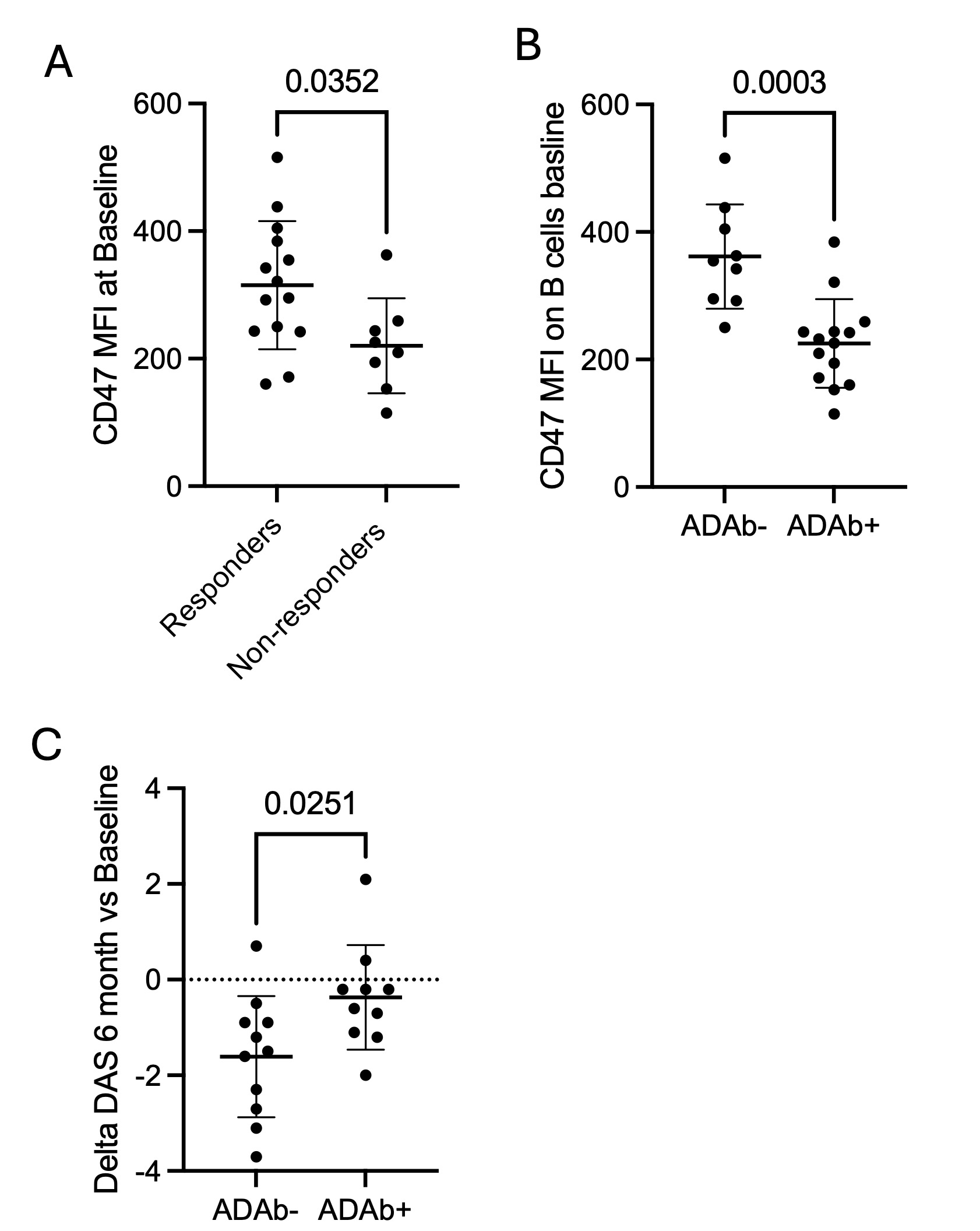
Results: CD47 expression on B cells was significantly lower in non-responders to rituximab contrarily to what was expected (figure 1A). Low CD47 on B cells was associated with presence of ADAb (Fig 1B) and we confirmed that ADAb were associated with lower clinical response to RTX at 6 months (Fig 1C).
Since ADAb are associated to low CD47, we hypothesized that ADAb could be favored by increased phagocytosis of B-cells/RTX complexes leading to presentation of RTX epitopes by macrophages to stimulate anti-RTX T cells and then anti-RTX B cells and plasma cells.
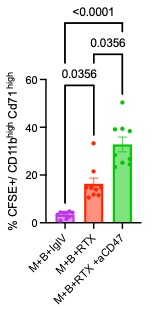
We confirmed this hypothesis since phagocytosis of B-cells/RTX complexes by monocytes-derived macrophages was increased in the presence of anti-CD47 and RTX compared to the RTX group alone and to a control IgG group (Figure 2). This underlined the harmful impact on response to RTX of low CD47 expression on B-cells.
Conclusion: RTX mediated phagocytosis of B-cells by macrophages is increased when CD47 expression is low on target B cells. But rather than leading to an increased response by increasing B-cell depletion, it is associated with higher levels of ADAb yielding lower response to RTX in RA patients.
(B) CD47 Mean fluorescence intensity on total B-cells at baseline is compared between anti-drug antibody negative and positive patients.
(C) Delta DAS 28 at six months is compared between anti-drug antibody negative and positive patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bitoun S, Ly B, Paoletti A, Menier C, Pallardy M, Maillere B, Mariette X. Low CD47 Expression on B Cells, Induces High B Cell Phagocytosis by Macrophages and Is a Predictive Biomarker of Anti-rituximab Antibodies and Lower Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-cd47-expression-on-b-cells-induces-high-b-cell-phagocytosis-by-macrophages-and-is-a-predictive-biomarker-of-anti-rituximab-antibodies-and-lower-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-cd47-expression-on-b-cells-induces-high-b-cell-phagocytosis-by-macrophages-and-is-a-predictive-biomarker-of-anti-rituximab-antibodies-and-lower-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/