Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Recent advances allow expanded identification of B cell subtypes of pathogenic potential in lupus. Of particular interest are IgD- CD27- double negative (DN2) B cells and activated naïve B cells (AN). These subsets are expanded in African American women with lupus and are progenitors of autoantibody producing cells. Less is known of these subsets in other ethnicities, their stability over time or their response to treatment. As part of the double-blind placebo controlled trial of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) for treatment of refractory lupus, we assessed B cell phenotypes at week 0, week 4, week 8 and week 24 in patients in the first cohort of participants. To prevent unblinding, we did not determine associations between B cell phenotypes and clinical response during this low dose cohort of the trial.
Methods: 41 lupus patients, primarily women (90%) and mixed ethnicities (49% Caucasian, 39% African American, 12% other) were enrolled. They were randomized to receive either 1×106 umbilical cord derived MSCs/kg or placebo at a 2/1 ratio. All patients met ACR criteria and had a SLEDAI >6 having failed immunosuppressive therapy. Patients with nephritis were included. Samples for B cell analysis were shipped to Emory for analysis via overnight delivery. Analyses were done by FLOW using 11 color flow. Comparative analyses were done with matched healthy controls and with previously analyzed samples in the Emory lupus cohort.
Results: As expected, there was significant heterogeneity of B cell phenotypes, as demonstrated in Figure 1, with 31.7% expressing a Naïve/Transitional phenotype and 26.9% having a DN2 extrafollicular phenotype. The B cell phenotype remained stable generally, but there were substantial shifts in some patients. Over 50% of lupus study patients had increased numbers of DN2 B cells compared to controls (Figure 2). There was a strong positive correlation between percent of DN2 B cells and AN B cells. Overtime, patients with a very high percentage of DN2 B cells retained this phenotype, where those with a moderate DN2 expansion at baseline, decreased significantly over time. Patients with low DN2 B cells at baseline retained this phenotype. Unswitched memory B cells were low and remained low compared to controls. There was considerable heterogeneity in switched memory B cells, but no population level differences from controls. Overall naïve B cells were similar between patients and controls, but some patients had very low levels of naïve cells.
Conclusion: These results indicate mixed ethnicity patients from 7 sites in the US, participating in the MSC trial, exhibited considerable B cell phenotypic heterogeneity, though the majority had a B cell Naïve/Transitional or DN2 extrafollicular phenotype. Longitudinal analysis reveals stability of B cell phenotype in many patients, while others have significant changes in B cell phenotype, predominantly due to decreased frequency of DN2 and AN B cells. Further characterization will determine clinical correlates between baseline B cell phenotype and lupus disease phenotype and differences in response to therapy based on initial B cell phenotypes.
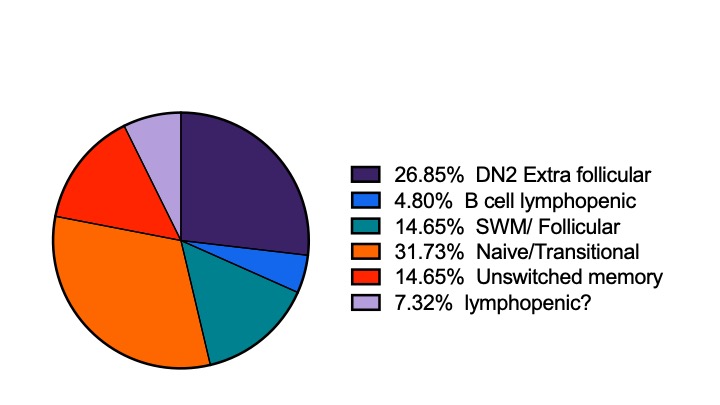 Slide1.jpeg”B cell phenotypes at baseline of the 41 patients enrolled into the MSCs in Lupus Erythematosus trial
Slide1.jpeg”B cell phenotypes at baseline of the 41 patients enrolled into the MSCs in Lupus Erythematosus trial
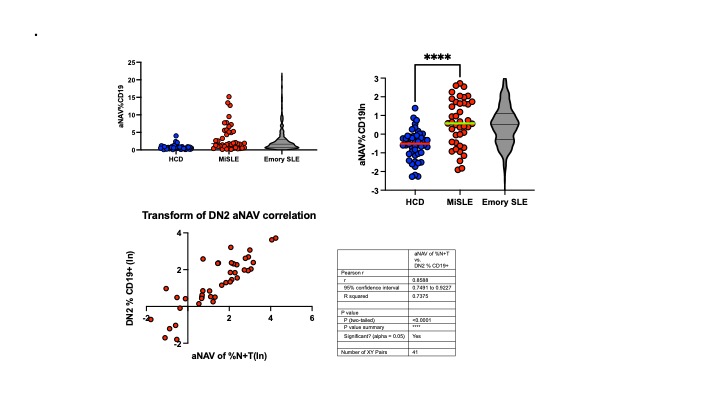 Slide2.jpeg”Activated naive B cells are expanded in patients with SLE. There is a strong correlation between percentage of activated naive and DN2 B cells in the patients in the trial.
Slide2.jpeg”Activated naive B cells are expanded in patients with SLE. There is a strong correlation between percentage of activated naive and DN2 B cells in the patients in the trial.
 Slide3.jpeg”Chronologic changes in DN2 B cells. Data presented is from patients whose baseline % of DN2 B cells was greater than 5%. As noted, patients with very high percentage of DN2 B cells tended to retain this phenotype while those with moderate increased percentage of DN2 B cells, the % DN2 cells trended down over the 24 weeks. Only 1/41 patients had an increased DN2 percentage during the trial period.
Slide3.jpeg”Chronologic changes in DN2 B cells. Data presented is from patients whose baseline % of DN2 B cells was greater than 5%. As noted, patients with very high percentage of DN2 B cells tended to retain this phenotype while those with moderate increased percentage of DN2 B cells, the % DN2 cells trended down over the 24 weeks. Only 1/41 patients had an increased DN2 percentage during the trial period.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kamen D, Lim S, Jenks S, Bugrovosky R, Hill A, Wei C, Drenkard C, Kalunian K, Shah U, Ishimori M, Ramsey-Goldman R, Sheikh S, Mahieu M, Wallace D, Goldmuntz E, Gilkeson G. Longitudinal Changes in B Cell Subsets in Patients in the Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Trial in Lupus: Analysis of the First Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-changes-in-b-cell-subsets-in-patients-in-the-mesenchymal-stromal-cell-trial-in-lupus-analysis-of-the-first-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-changes-in-b-cell-subsets-in-patients-in-the-mesenchymal-stromal-cell-trial-in-lupus-analysis-of-the-first-cohort/
