Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Persistent proteinuria increases the risk of comorbidities in lupus nephritis, and rapid reductions in protein have shown to be predictive of improved long-term renal health. Patients with Class V lupus nephritis may take longer to respond to therapy, and treatments that efficiently reduce proteinuria in this population are needed. We report here on a post-hoc analysis of voclosporin in patients with Class V lupus nephritis using three years of pooled data from the Phase 3 AURORA 1 and AURORA 2 studies.
Methods: AURORA 1 enrolled patients with biopsy-proven active lupus nephritis, urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) ≥1.5 mg/mg (≥2.0 mg/mg for pure Class V), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) >45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients completing AURORA 1 were eligible to enter AURORA 2 on the same blinded therapy (voclosporin or placebo) in combination with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose steroids for up to 3 years of treatment. Hazard ratios (HR) for the time to UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg and mean eGFR levels were assessed in patients with pure and mixed Class V lupus nephritis.
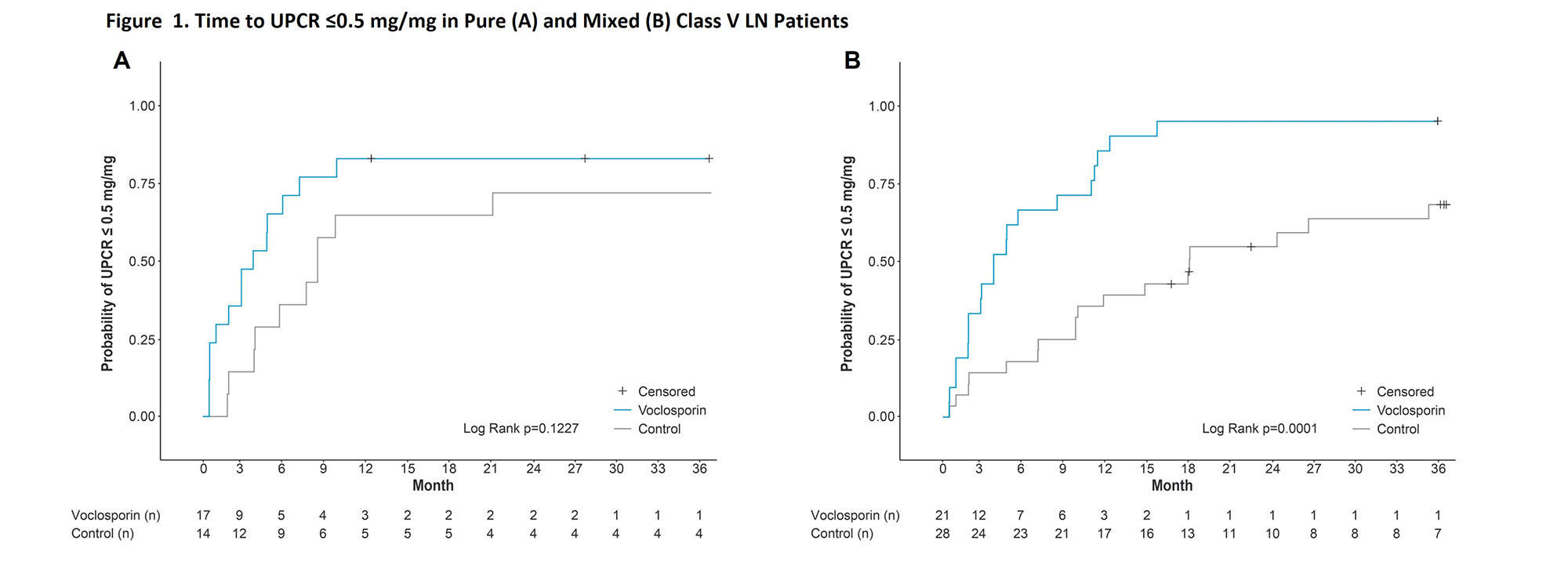
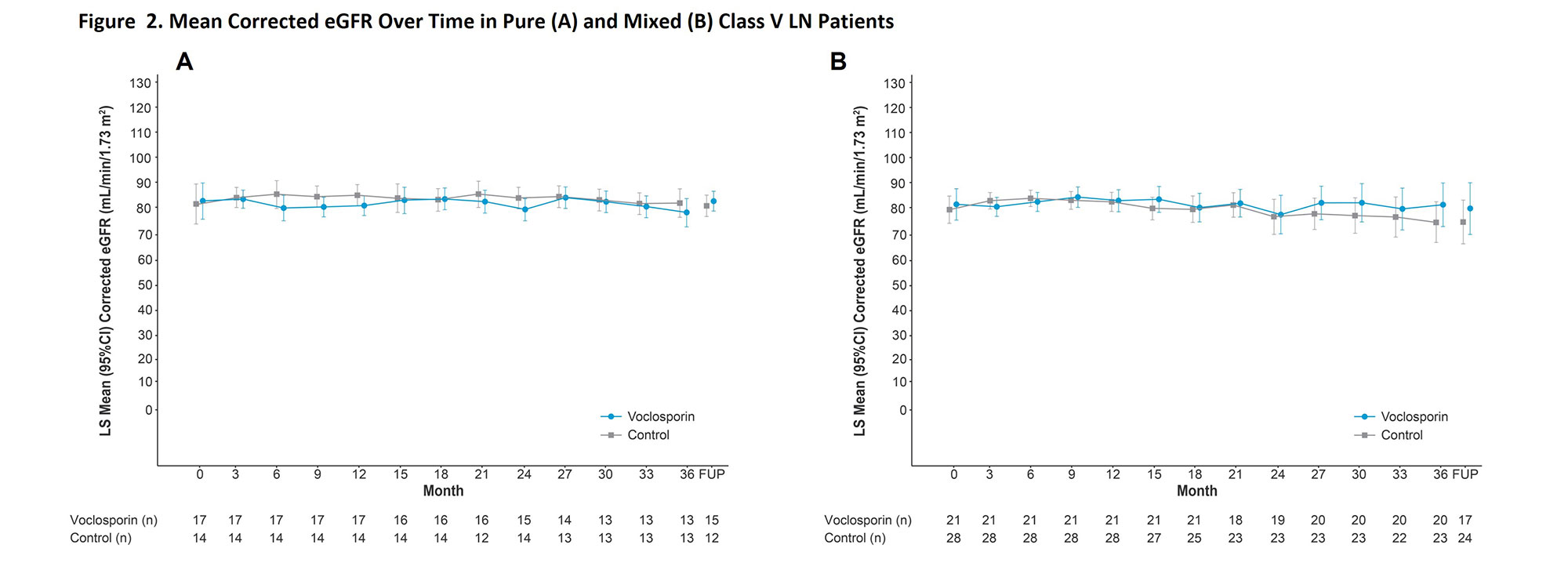
Results: A total of 80 patients with Class V lupus nephritis continued treatment in AURORA 2, 31 with pure Class V disease and 49 with mixed lesions. Mean baseline UPCR was 3.4 and 3.3 mg/mg in patients with pure Class V disease treated with voclosporin and control, respectively, and 3.4 and 3.9 mg/mg in voclosporin- and control-treated patients with mixed lesions. The differences between treatment arms in UPCR reductions were apparent within the first month and sustained at three years in both pure and mixed disease. For patients with pure Class V disease, the median times to UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg were 3.6 and 8.3 months in the voclosporin and control arms, respectively (HR 1.93; p=0.167, Figure 1). For patients with mixed lesions, the median times to this outcome were 3.7 and 18.0 months, respectively (HR 5.07; p< 0.0001). Mean corrected eGFR levels were similar in all treatment arms and stable throughout the study (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Voclosporin-treated patients with pure and mixed Class V lupus nephritis saw substantial reductions in UPCR that occurred faster than in those treated with MMF and low-dose steroids alone. Voclosporin may be beneficial in limiting the negative long-term impact of proteinuria in this population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saxena A, Caster D, Almaani S, Rosales A, Leher H. Long-term Use of Voclosporin in Patients with Class V Lupus Nephritis: Results from the AURORA 2 Continuation Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-use-of-voclosporin-in-patients-with-class-v-lupus-nephritis-results-from-the-aurora-2-continuation-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-use-of-voclosporin-in-patients-with-class-v-lupus-nephritis-results-from-the-aurora-2-continuation-study/