Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Abatacept (ABA) is well tolerated and effective in patients with JIA.1 The Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group (PRCSG)/ Paediatric Rheumatology INternational Trials Organisation (PRINTO) registry monitors long-term safety and efficacy of ABA for JIA treatment.2 The objective of this analysis was to assess long-term (5-year) safety and efficacy of ABA in patients with JIA in a real-world setting using data from the PRCSG/PRINTO registry.
Methods: All patients with JIA receiving IV/SC ABA enrolled in the PRCSG/PRINTO registry with ≥ 5 years follow-up were included. Safety and efficacy were assessed at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 60 months. Safety was evaluated by recording serious adverse events (SAEs), events of special interest (ESI; incidence rate [IR]/100 patient-years (py) [95% CI]) and anti-ABA antibody levels. Efficacy outcomes: physician global assessment of disease activity, physician assessment of JIA severity, Juvenile Arthritis Multidimensional Assessment Report (JAMAR) functionality score, overall well-being score, number of active joints, joints with limited range of motion (LOM), clinical 10-joint Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score (cJADAS10), and JIA-ACR30, 50, 70, and 90. cJADAS10 used validated cut-offs for low disease activity (LDA), inactive disease (ID), and remission (ID for ≥ 6 months). As-observed analysis is presented.
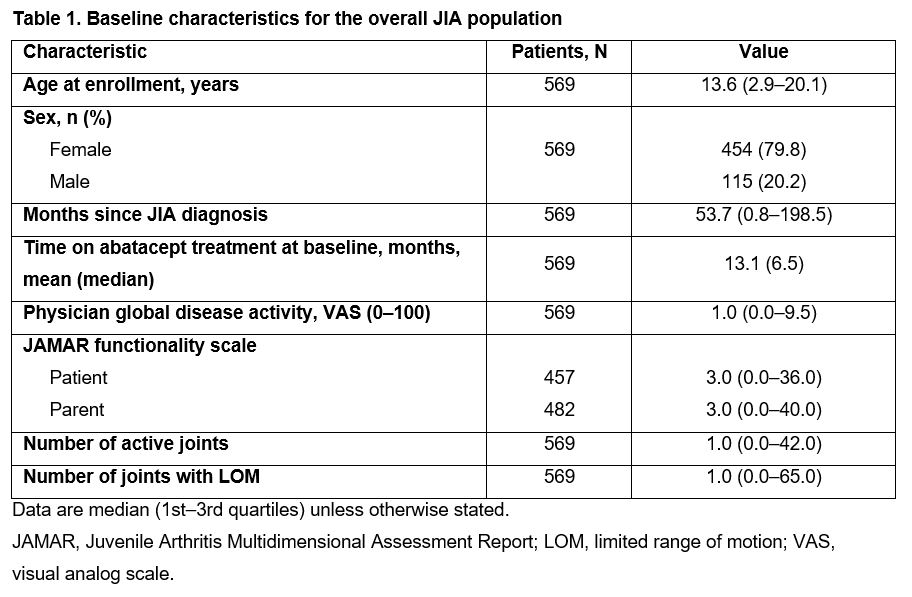
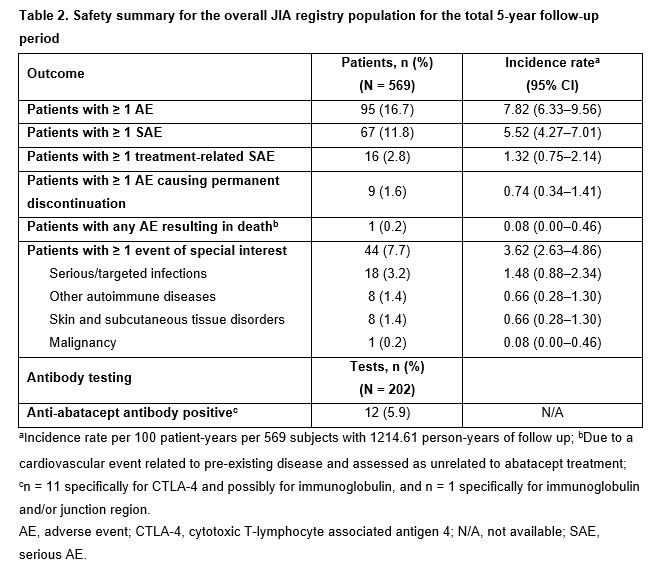
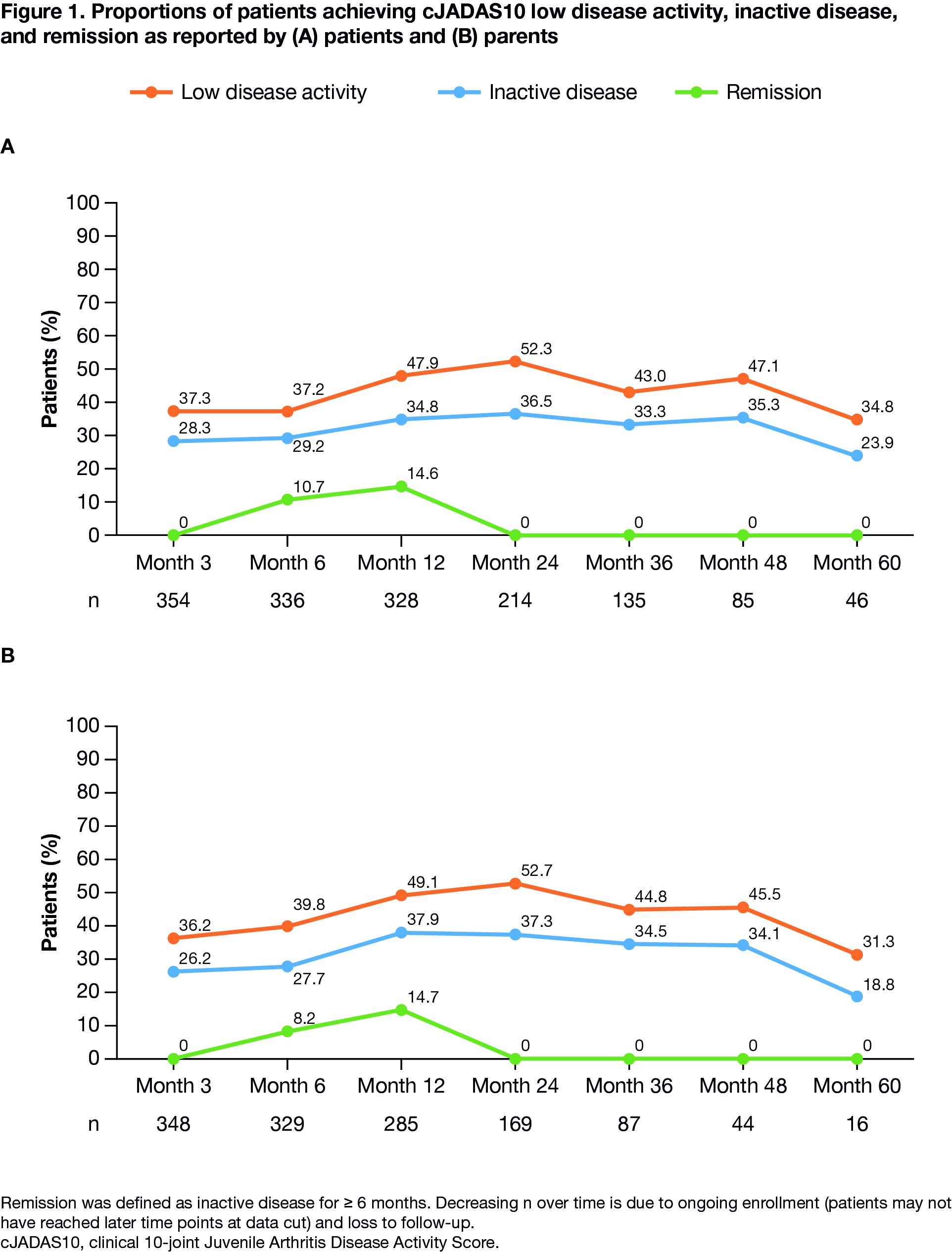
Results: Data for 569 patients (1214.61 py of follow-up) were available up to Mar 31, 2020. Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Over 60 months, IRs/100 py (95% CIs) of patients with ≥ 1 SAE, treatment-related SAE, or ESI were 5.5 (4.3–7.0), 1.3 (0.8–2.1), and 3.6 (2.6–4.9), respectively (Table 2). Overall, 5.9% (12/202) anti-ABA antibody tests were positive. From months 3–60, median physician global disease activity, number of active joints, and joints with LOM were unchanged. The proportion of patients with physician-assessed mild JIA increased from 86% to 96%; corresponding proportions of patients with moderate or severe JIA decreased from 11% to 4% and from 3% to 0%, respectively. Median JAMAR functional scores were 2.0 (patient) and 3.0 (parent) at month 3, and 1.0 each at month 60; a similar pattern was observed for overall well-being scores. Median cJADAS10 scores were 4.0 (patient) and 4.5 (parent) at baseline, and 4.3 (patient) and 3.3 (parent) at month 60. As early as month 3, cJADAS10 LDA and ID were achieved by 37% and 28% of patients, respectively, and sustained over time (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Overall, in patients with JIA, abatacept was well tolerated with no new safety signals. Treatment with abatacept resulted in well-controlled disease activity, with approximately 30% of patients achieving cJADAS10 ID by month 3, which was sustained over 2 years. For the majority of patients, initial improvement on abatacept occurred prior to registry enrollment; therefore the ability to maintain response with ongoing treatment is reflected. These real-world data support the safety and efficacy profile of abatacept as seen in clinical trials.
References:
1. Lovell DJ, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67:2759–2770.
2. Lovell DJ, et al. ACR 2020. Abstract 0714.
Medical writing: Rachel Rankin, PhD (Caudex), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brunner H, Lovell D, Henrickson M, Carrassco R, Minden K, Grebenkina L, Nocton J, Louw I, Wagner-Weiner L, Vega Cornejo G, Kamphuis S, Chasnyk V, Walters H, Appenzeller S, Anton J, Dominique A, Wong R, Dong L, Kou T, Martini A, Ruperto N. Long-term Safety and Effectiveness of Abatacept Treatment in Patients with JIA: 5-year Results from the PRCSG/PRINTO JIA Real-World Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-safety-and-effectiveness-of-abatacept-treatment-in-patients-with-jia-5-year-results-from-the-prcsg-printo-jia-real-world-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-safety-and-effectiveness-of-abatacept-treatment-in-patients-with-jia-5-year-results-from-the-prcsg-printo-jia-real-world-registry/