Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1517–1552) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
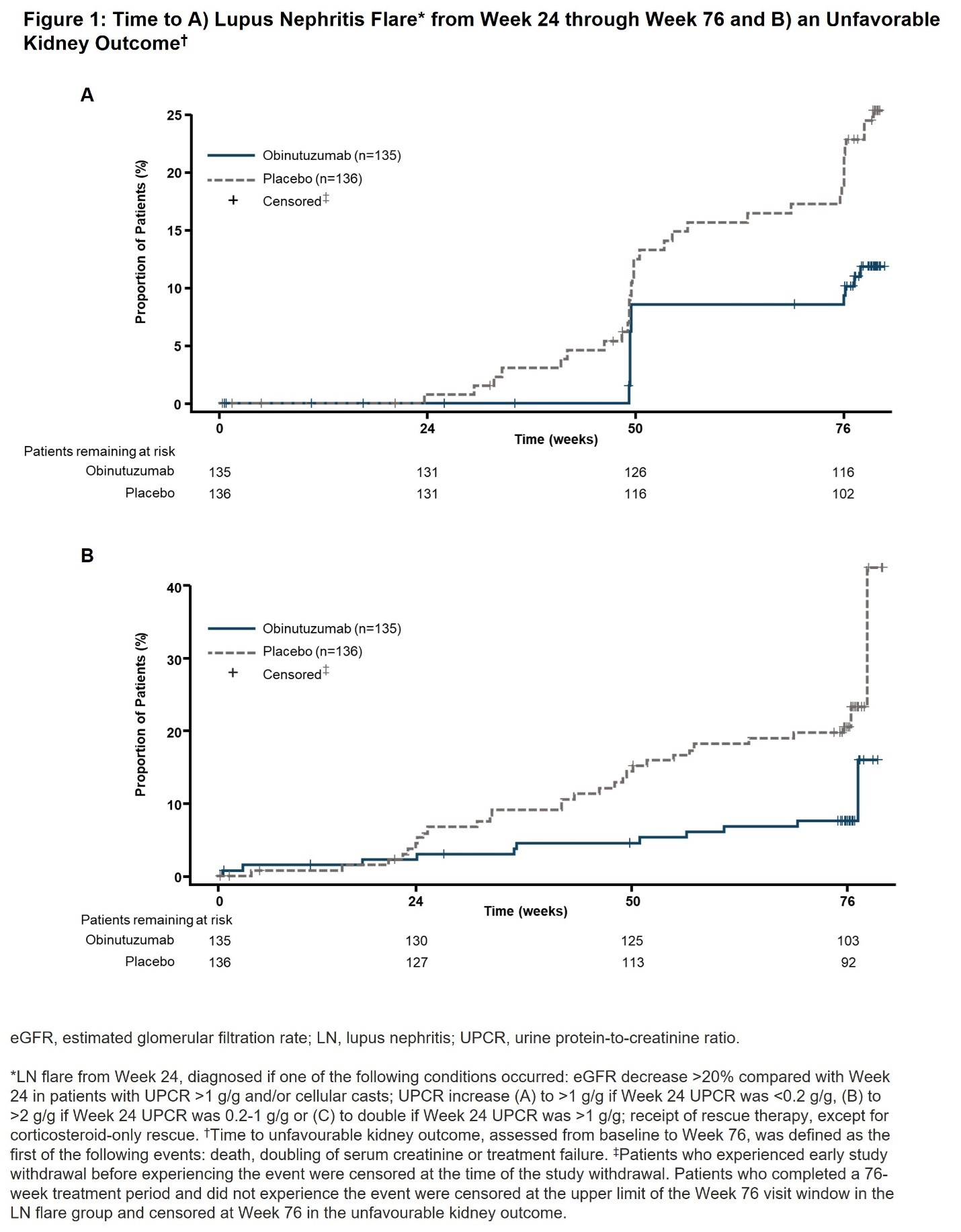
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is the most common, severe, organ-threatening manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase III REGENCY trial (NCT04221477) demonstrated superiority of obinutuzumab over placebo for achievement of complete renal response at Week 76 when added to standard therapy (mycophenolate mofetil plus glucocorticoids) in patients with active LN. This study assessed the effects of obinutuzumab on time to LN flare, time to an unfavorable kidney outcome and annualized estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) slope during the REGENCY trial.
Methods: In the REGENCY study, all patients met the ACR classification criteria for SLE and had biopsy-proven proliferative LN. In this pre-specified analysis of REGENCY, time to LN flare was assessed between Weeks 24 and 76 by Cox regression. The composite outcome of death, doubling of serum creatinine or treatment failure was defined as an unfavorable kidney outcome. Time to an unfavorable kidney outcome from baseline to Week 76 was also assessed by Cox regression after stratifying for race and region. Finally, linear mixed-effects modelling was used to assess eGFR slope between Weeks 12 and 76. These analyses were not controlled for type I error.
Results: Between Weeks 24 and 76, the proportion of patients with LN flare was lower in the obinutuzumab arm (11.1%) compared with the placebo arm (23.5%), with a hazard ratio of 0.44 (95% CI, 0.24 to 0.82; P=0.0074) (Figure 1A). The proportion of patients with unfavorable kidney outcomes in the obinutuzumab arm (8.10%) was also lower compared with the placebo arm (21.30%), with a hazard ratio of 0.37 (95% CI, 0.18 to 0.75; P=0.0039) (Figure 1B). Numerical attenuation of eGFR decline from Week 12 to Week 76 was observed in the obinutuzumab arm with the annualized eGFR slope calculated as −0.71 (SE=1.454) compared with −4.39 (SE=1.454) in the placebo arm, with a difference in eGFR slope of 3.68 (SE=2.055; P=0.0732), favoring patients treated with obinutuzumab (Table 1).
Conclusion: This pre-specified exploratory analysis of the REGENCY trial demonstrated that obinutuzumab significantly reduced the occurrence of LN flares and unfavorable kidney outcomes and attenuated the annualized decline in kidney function compared with placebo-treated patients. Together with the significantly higher proportion of patients achieving a complete renal response in the obinutuzumab arm, these findings suggest that obinutuzumab affords long-term kidney survival benefits compared with standard therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rovin B, Pendergraft W, Lightstone L, Daugas E, Furie R, Omachi T, Hassan I, Martins E, Schindler T, Garg J, Quintana L, Leszczyński P, Malvar A. Kidney-Related Outcomes With Obinutuzumab in Patients With Active Lupus Nephritis: A Pre-Specified Exploratory Analysis of the Clinical Trial Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kidney-related-outcomes-with-obinutuzumab-in-patients-with-active-lupus-nephritis-a-pre-specified-exploratory-analysis-of-the-clinical-trial-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/kidney-related-outcomes-with-obinutuzumab-in-patients-with-active-lupus-nephritis-a-pre-specified-exploratory-analysis-of-the-clinical-trial-data/

.jpg)