Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes I: Assessment Tools
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) symptoms often require patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) to monitor disease progression. The CLE quality of life (CLEQoL) instrument was devised as a disease-specific PROM. However, its 37-item length can be time-consuming. Creating a brief version could reduce respondent burden and increase clinical utility. Thus, we sought to develop a brief version of the CLEQoL, while maintaining clinical relevance and psychometric properties including internal consistency, structural and convergent validity.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study analyzed data from CLE patients recruited in outpatient dermatology clinics at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center and Parkland Health from June 2016 to November 2022. Patients completed the CLEQoL, Short-Form-36 (SF-36), and a visual analogue scale (VAS). Item reduction was conducted by evaluating each item’s response distribution and local dependency with other items. Internal consistency of the reduced scale was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha. Structural validity was examined via exploratory factor analysis with principal component analysis and varimax rotation. Convergent validity was determined via Spearman correlations between CLEQoL, SF-36, VAS, and Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity (CLASI) scores. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 29.0 and significance was set at p< 0.05.
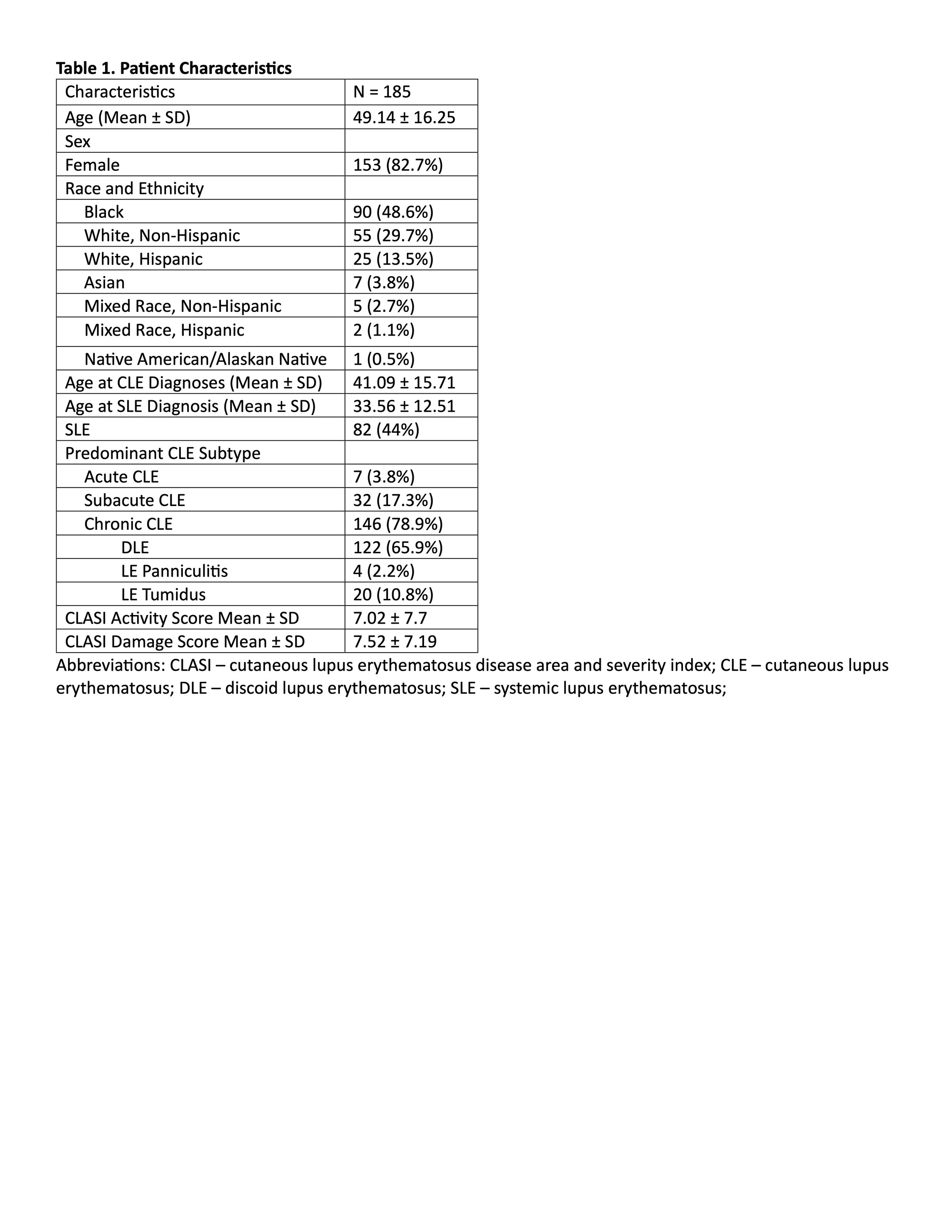
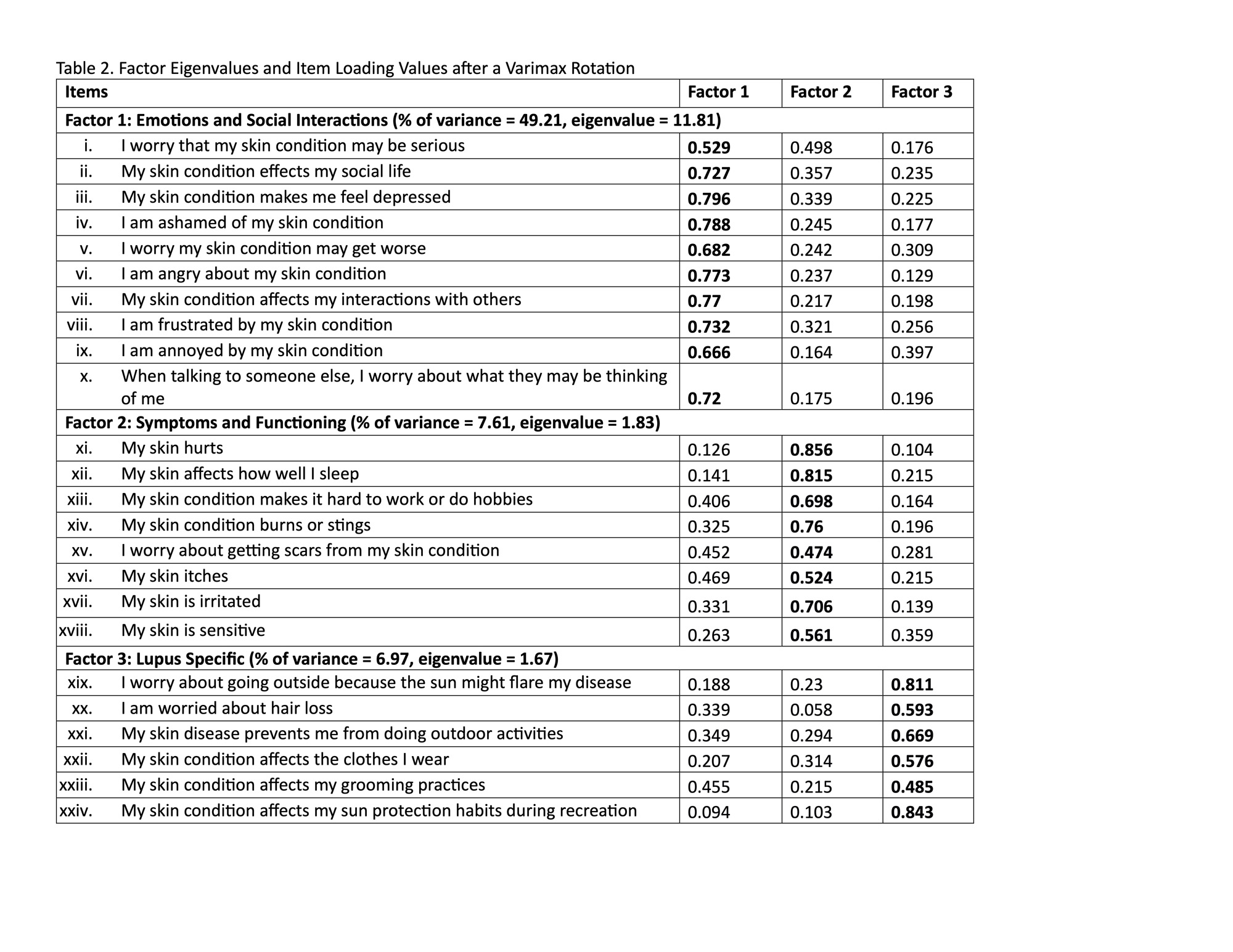
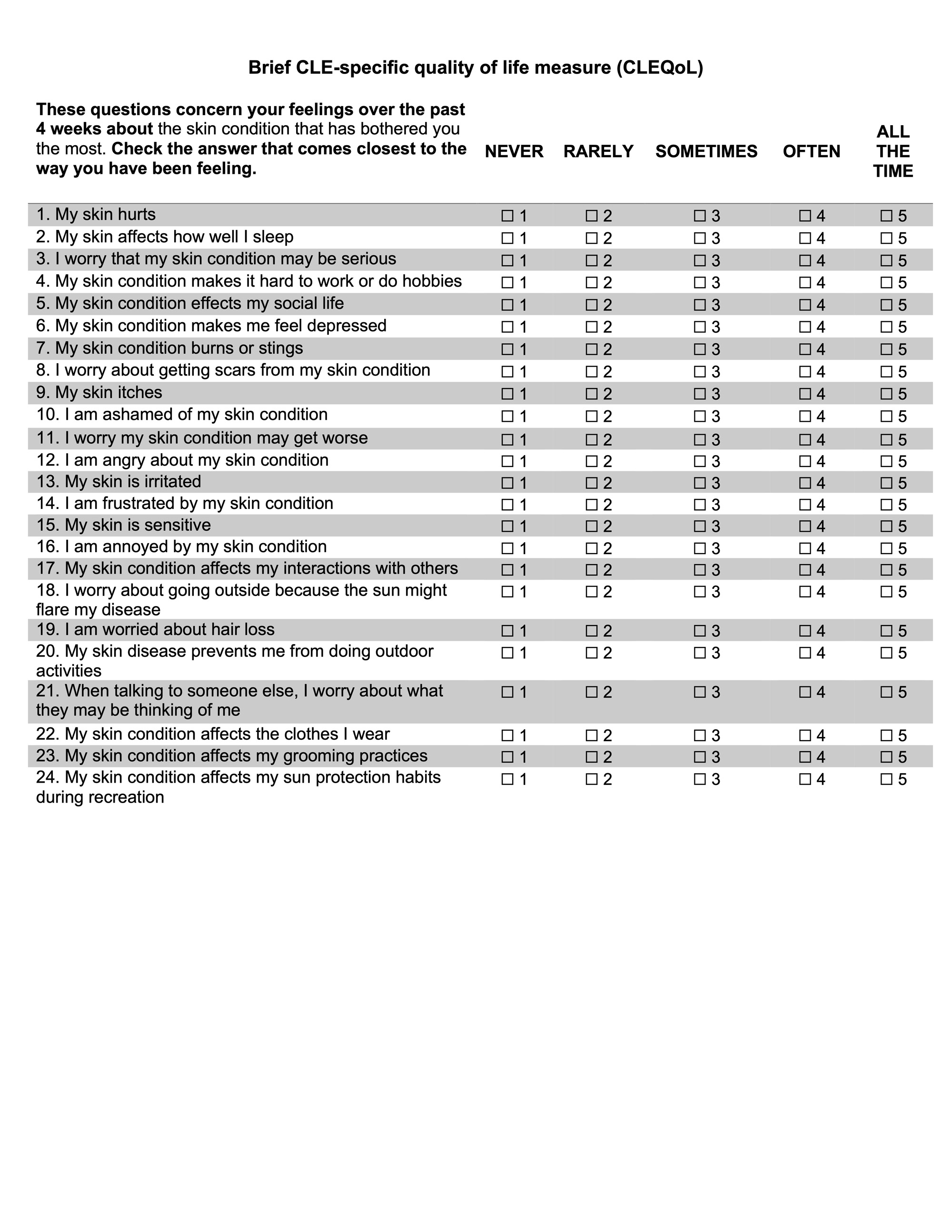
Results: 185 patients completed the CLEQoL (Table 1). Thirteen items were removed, resulting in a 24-item scale (Figure 1). Internal consistency was satisfactory (Cronbach’s alpha: 0.842-0.939). Exploratory factor analysis identified three domains (each with and eigenvalue greater than 1): “Emotions and Social Interactions,” “Symptoms and Functioning,” and “Lupus Specific Questions”– each factor had an eigenvalue greater than 1 and contributed more than 5% unique variability (Table 2). The brief CLEQoL demonstrated convergent validity with relevant domains of the SF-36 (r range: -0.243 to -0.172) and VAS (0.348 – 0.671). However, it did not demonstrate convergent validity with CLASI activity or damage scores. The limited convergent validity between the scale and CLASI scores may be attributed to the small range of observed CLASI activity scores (median 5, IQR 1.25-10).
Conclusion: The brief 24-item CLEQoL was found to be a valid and reliable PROM for assessing CLE patients’ quality of life, and establishing its psychometric properties is crucial for its use in outpatient clinics and clinical trials. The nonconvergence between the brief CLEQoL and CLASI can be attributed to their measurement of different constructs. The brief CLEQoL captures subjective patient experiences such as social functioning, and emotional well-being. In contrast, the CLASI relies on clinical observations to assess disease severity. Integrating information from both measures allows for a more comprehensive and holistic assessment of the patient’s condition. Future plans involve prospectively administering the brief CLEQoL to a larger and more heterogeneous CLE patient cohort to further evaluate its psychometric properties.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Adams M, Hynan L, Ogunsanya M, Chong B. Item Reduction and Validation of the Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Quality of Life Questionnaire [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/item-reduction-and-validation-of-the-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-quality-of-life-questionnaire/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/item-reduction-and-validation-of-the-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-quality-of-life-questionnaire/