Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic and progressive disease characterized by high rates of early joint erosions, which have been associated with impaired quality of life and increased mortality rates1,2. However, the relationship between the number of erosions at baseline (BL) and response to biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) therapy has not been thoroughly investigated. In this post-hoc analysis, we assessed the efficacy of placebo (PBO), ixekizumab (IXE) or adalimumab (ADA) on patients (pts) with erosions visible on hand radiographs at BL.
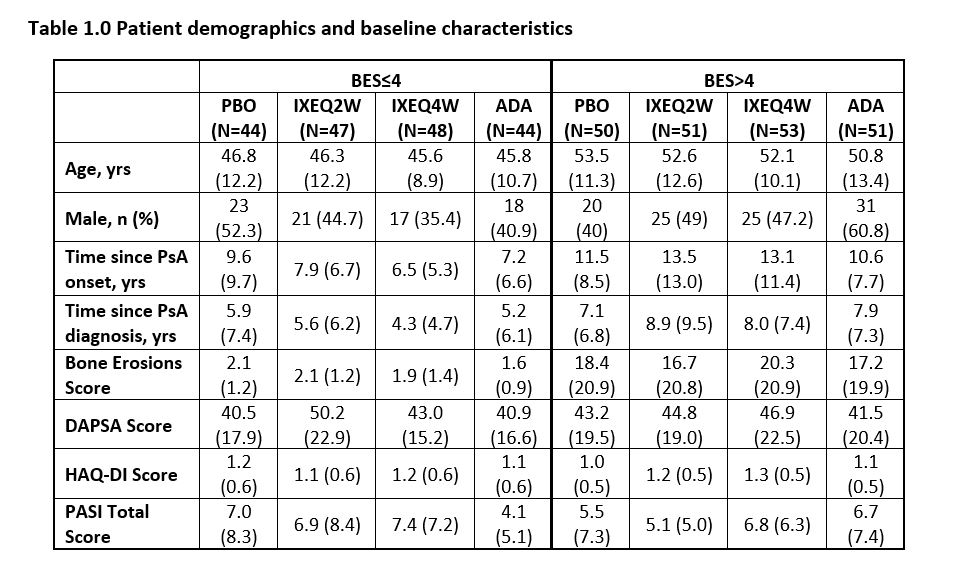
Methods: Biologic-naïve pts with PsA (SPIRIT-P1, NCT01695239) were randomly assigned to PBO, IXE 80-mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) or 4 weeks (Q4W) after a 160-mg starting dose, or ADA 40-mg Q2W. Pts were stratified into two groups based on the number of BL erosions (erosion component of the modified total sharp scores ≤4 and >4). At week 24, outcomes analyzed for different baseline erosion score (BES) groups included American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 20%, 50%, 70%, Disease Activity index for PSoriatic Arthritis-Low Disease Activity (DAPSA-LDA), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and Minimal Disease Activity-Psoriasis Area Severity Index (MDA-PASI). Missing data were imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI) for categorical, and modified baseline observation carried forward (mBOCF) for continuous outcome variables. Comparisons between PBO and treatment within each BES group used logistic models for categorical, and ANCOVA for continuous outcome variables, adjusting for BL values, disease duration, geographic region, and prior conventional DMARD (cDMARD) experience.
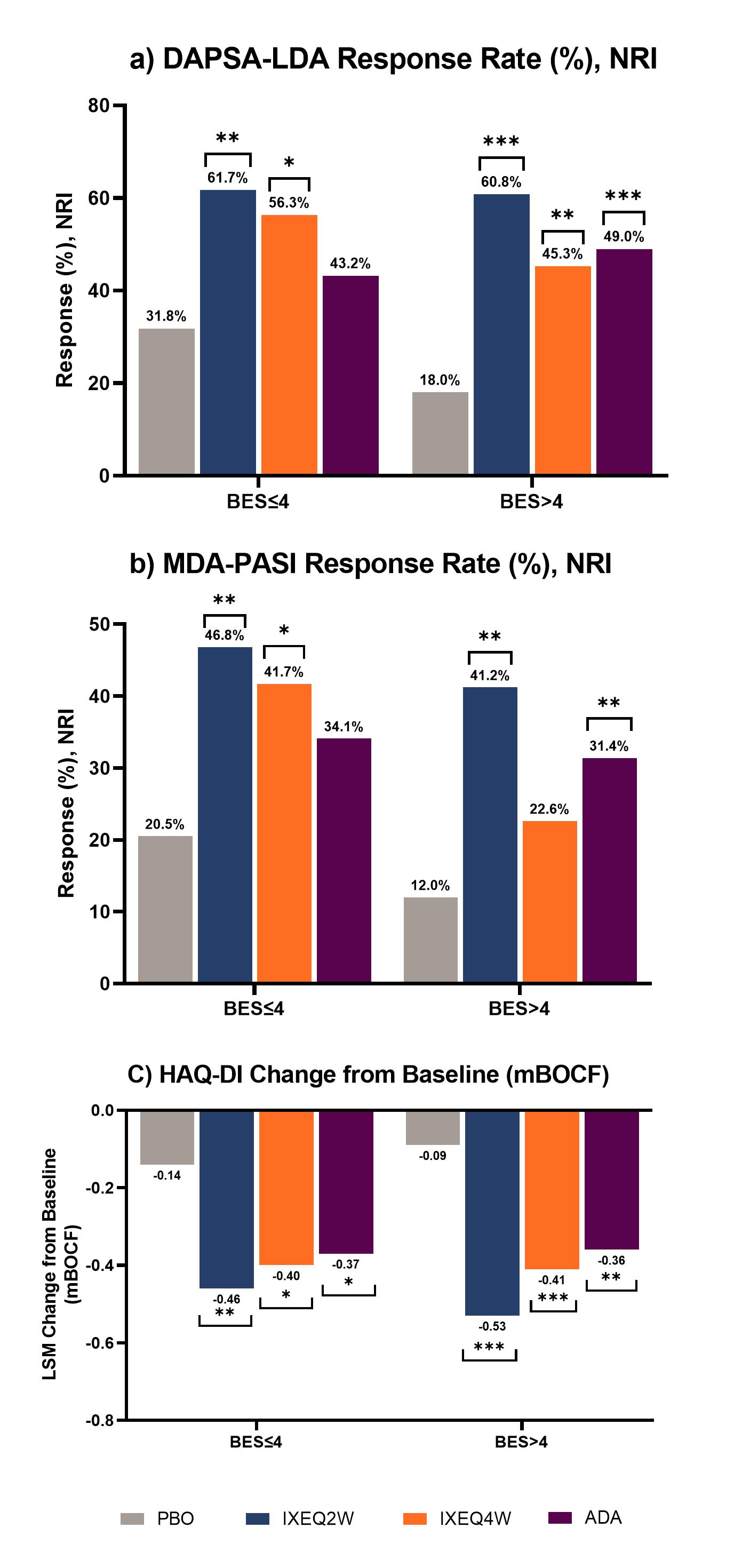
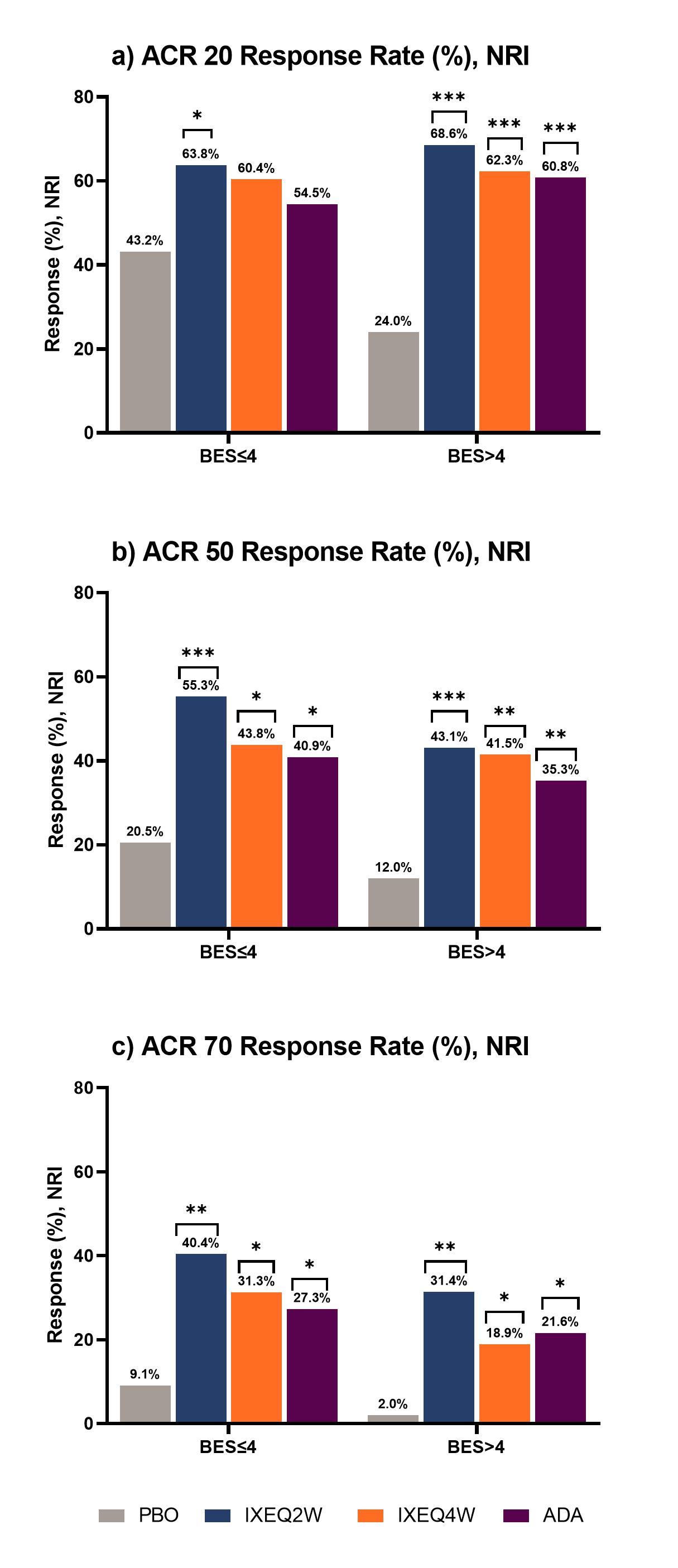
Results: 183 pts with BES≤4 and 205 pts with BES >4 at BL were included. At week 24, pts with BES >4 on PBO had worse outcomes across all parameters compared to those with BES≤4. There was significant improvement in DAPSA-LDA response rates in pts treated with IXE regardless of BES, whereas significant response rates were seen in ADA treated pts with BES >4 (Figure 1a). MDA-PASI response rates were significant in patients treated with IXEQ2W and IXEQ4W who had BES≤4, whereas pts with BES >4 demonstrated a significant response rate with IXEQ2W and ADA (Figure 1b). Change from baseline in HAQ-DI was significant for all pts treated with bDMARDS, regardless of BES (Figure 1c). Similarly, regardless of BES, significant differences in ACR50 and ACR70 response rates versus PBO were seen for pts treated with bMDARDS (Figure 2b and 2c).
Conclusion: Pts with higher BES in the PBO group experienced worse outcomes. Higher response rates (e.g., ACR50/70) were also harder to achieve in pts with higher BES. Irrespective of BES, IXE treated pts showed greater improvement compared to PBO in the achievement of LDA and functional outcomes.
References:
Touma, Z., et al. J. of Rheumatology. 2016; 43(6)
Gladman, D. D. et al. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 1998; 41(6)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Husni M, Chandran V, Lisse J, Bolce R, Diaz C, Zhu B, Lui E, Coates L. Irrespective of the Number of Erosions at Baseline, Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Ixekizumab Show Improved Clinical Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/irrespective-of-the-number-of-erosions-at-baseline-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ixekizumab-show-improved-clinical-outcomes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/irrespective-of-the-number-of-erosions-at-baseline-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-ixekizumab-show-improved-clinical-outcomes/