Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: A disintegrin and metalloprotease 17 (ADAM17) controls ecto-domain shedding of TNFα and epithelial-growth factor ligands (EGFR) such as heparin-binding EGF (HB-EGF). TNFa and HB-EGF have both been implicated in kidney injury of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), yet targeting ADAM17 is limited by its essential role in protecting the skin and intestinal barrier. In contrast, mice lacking the inactive Rhomboid 2 (iRhom2), a key regulator of ADAM17 in myeloid cells, have normal development but are protected from TNFa-dependent septic shock and Rheumatoid Arthritis. iRhom2-deficient mice appear normal because the related iRhom1 supports ADAM17-dependent skin and intestinal barrier protection. Here, we sought to determine whether iRhom2/ADAM17 pathway contributes to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis (LN).
Methods: iRhom2 (gene name Rhbdf2) deficient mice were crossed with Fcgr2b-/- lupus-prone mice. Development of anti-dsDNA Abs and kidney injury was monitored by assessing proteinuria, BUN, kidney inflammatory cell infiltration, renal deposition of immune complexes and complement and histology. Molecular mechanism of renal damage was studied using RNA-sequencing analysis. Activation of iRhom2, ADAM17 and EGFR signaling was determined by qPCR and western-blot. To corroborate the contribution of both TNFa and EGFR signaling to renal injury, we treated Fcgr2b-/- mice with murine p75TNFRII-Fc or an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
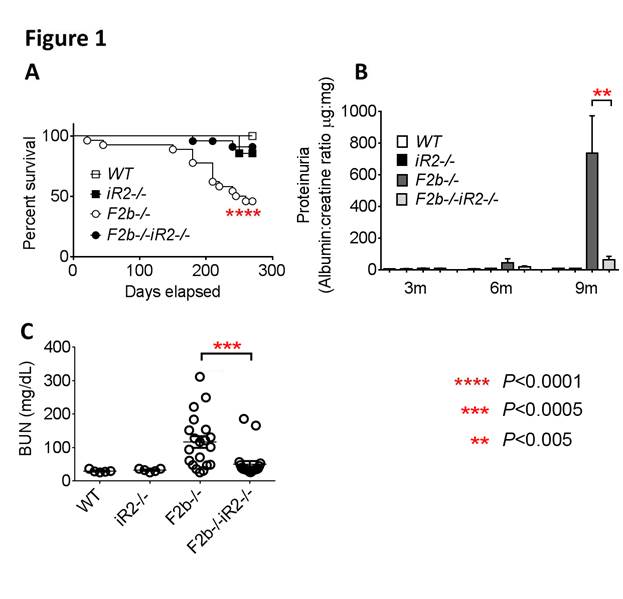
Results: Deficiency of iRhom2 almost completely protected Fcgr2b-/- mice from mortality (Fig. 1A). Development of severe proteinuria and elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in aged Fcgr2b-/- (F2b-/-) mice were ameliorated by iRhom2 deficiency (iR2-/-) (Fig. 1B, C). Glomerular and tubulo-interstitial damage and inflammatory cell infiltrates (neutrophils, monocytes and T cells) in Fcgr2b-/-kidneys were markedly and significantly reduced in the absence of iRhom2, while anti-dsDNA Ab production and renal deposition of IgG and C3 were minimally affected. These data suggest that iRhom2 targets the effector arm in SLE, rather than preventing development of autoimmunity. Strikingly, transcriptome profiling of mouse kidneys identified epithelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT) and TNF signaling as top pathways activated in Fcgr2b-/- kidneys, along with marked upregulation of Tnf and Hbegf transcripts in these kidneys. This is confirmed by findings that kidney damage in Fcgr2b-/- mice was associated with increased renal expression of phospho-EGFR and phospho-ERK1/2, which was significantly diminished in the absence of iRhom2. Finally, blockade of TNF-α or EGFR in protected Fcgr2b-/- mice from kidney injury.
Conclusion: Our findings provide the first evidence that iRhom2, a major regulator of ADAM17, plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of LN, most likely by processing TNFα and EGFR ligands in the diseased kidneys.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Qing X, Chinenov Y, Redecha PM, Madaio M, Issuree P, McIlwain D, Mak T, Blobel C, Salmon JE. iRhom2 Deficiency Protects Fcgr2b-/- Lupus-Prone Mice from Kidney Damage By Modulating ADAM17-Dependent Shedding of TNF-α and EGFR Ligand [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/irhom2-deficiency-protects-fcgr2b-lupus-prone-mice-from-kidney-damage-by-modulating-adam17-dependent-shedding-of-tnf-%ce%b1-and-egfr-ligand/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/irhom2-deficiency-protects-fcgr2b-lupus-prone-mice-from-kidney-damage-by-modulating-adam17-dependent-shedding-of-tnf-%ce%b1-and-egfr-ligand/