Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Allopurinol, effectively regulates and controls serum uric acid levels but may cause allopurinol-induced life-threating severe cutaneous adverse reaction (SCAR). Previous studies reported that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) rs3117583 and rs9263726, as well as HLA-B*5801, were genetic markers for allopurinol-induced SCAR. This study aims to investigate the allele frequency of rs3117583 and rs9263726 in patients with hyperuricemia and/or gout, and the possible effect on predicting allopurinol-induced SCAR.
Methods: We enrolled 100 patients with hyperuricemia and/or gout, diagnosed by clinicians at our University in Southern China. Genomic DNA was extracted and the alleles were tested by liquid chip using a Luminex 200 analyzer. Allele frequencies and allele carrying rates were calculated. We investigated the relationship between rs3117583, rs9263726 and HLA-B*5801. We used Plink software to explore the linkage disequilibrium analysis of rs3117583 and rs9263726.
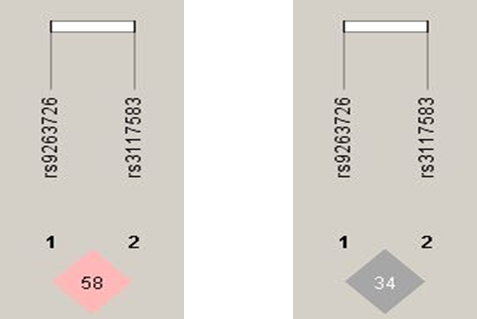
Results: Observed genotype frequencies for rs3117583 (AG&GG) were 22%, while the risk allele G frequency was 11.5%. Similarly, rs9263726(AA&AG) exhibited the same genotype frequencies as rs3117583, and the risk allele frequency was 11.5%. HLA-B*5801 was observed in 19% of patients. Patients who carried the HLA-B*5801 allele, tended to carry the risk allele of rs3117583(G), with an odds ratio (OR) of 25.55 (95%CI:7.28-89.64, p<0.01), and rs9263726, with an OR of 468.00 (95%CI:45.97-4764.48). Rs3117583 showed a weak linkage disequilibrium with rs9263726 (D¡¯=0.58, r2=0.34).
Conclusion: The technology of liquid chip can allow rapid and reliable detection of HLA-B*5801 and SNPs to identify individuals at risk of allopurinol-induced SCAR. Our study suggests that, since there is no strong linkage disequilibrium between rs31173583 and rs9263726, prospective screening combining these two SNPs and HLA-B*5801 genotyping can improve the predictive value of prescreening for allopurinol-induced SCARs in Southern Chinese patients.
Table 1 genotype of rs3117583, rs9263726 and HLA-B*5801 in patients with hyperuricemia and/or gout
|
|
Rs3117583 |
|
Rs9263726 |
||||
|
|
AA |
AG |
GG |
|
GG |
AG |
AA |
|
HLA-B*5801 (+) |
5 |
13 |
1 |
|
0 |
18 |
1 |
|
HLA-B*5801(-) |
73 |
8 |
0 |
|
78 |
3 |
0 |
|
Total |
78 |
21 |
1 |
|
78 |
21 |
1 |
Figre1
The linkage disequilibrium analysis between rs3117583(A>G) and rs9263726(G>A). A: parameter D¡¯ of linkage disequilibrium analysis; B: parameter r2 of linkage disequilibrium analysis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li X, Wei Q, Schlesinger N, Gu J. Investigation on Allele Frequency of Rs3117583 and Rs9263726 in Patients with Hyperuricemia or Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/investigation-on-allele-frequency-of-rs3117583-and-rs9263726-in-patients-with-hyperuricemia-or-gout/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/investigation-on-allele-frequency-of-rs3117583-and-rs9263726-in-patients-with-hyperuricemia-or-gout/