Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0357–0386) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The West Haven-Yale Multidimensional Pain Inventory (MPI) is a validated tool designed to assess the multidimensional aspects of chronic pain, including the 5 dimensions of pain: pain-related life interference, pain severity, affective distress, social support and life control. Originally developed in the US, the MPI has been successfully adapted and validated in German-speaking populations [1]. Chronic pain in rheumatic diseases often involves nociplastic and central sensitization mechanisms components. Therefore, the MPI, with its biopsychosocial framework, offers an opportunity to explore dimensions of pain in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).Our aim was to assess the construct validity of the MPI by examining its correlations with patient-reported outcomes (PRO) in the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society-Outcomes Measures in Rheumatology (ASAS-OMERACT) core domain set for clinical trials in axSpA [2].
Methods: The five MPI dimensions were assessed in axSpA patients with a pain score ≥ 4 (NRS 0-10) and results were correlated with the ASAS-OMERACT core domain set, including disease activity (ASDAS, CRP, BASDAI, patient global assessment (PtGA) of disease activity, physical function (BASFI), health-related quality of life (ASAS Hi, of the SF36 MCS/PCS), total back pain, morning stiffness, and spinal mobility (BASMI) as well as demographic and clinical data using Pearson´s correlations. Correlations were classified as weak (r≥0.1), moderate (r≥0.3), and strong (r≥0.5).
Results: 136 patients with axSpA were included and the MPI was completed by 109 (80.2%) patients (table 1). Pain-related life interference showed significant strong correlations with ASDAS, BASDAI, BASFI, PCS, fatigue and total back pain while moderate correlations were found for PtGA of disease activity, MCS, morning stiffness, and BASMI. For pain severity, significant strong correlations were observed with ASDAS, BASDAI and total back pain. Moderate correlations were found with PtGA of disease activity, BASFI, PCS and fatigue, weak correlations were found with MCS, ASAS HI and morning stiffness. Affective distress showed strong correlations only with MCS and weak or moderate correlations with all other assessments, while social support only showed a weak correlation with the PCS and the BASMI. For life control, a strong positive correlation was only found with MCS whereas moderate negative correlations were found with PtGA of disease activity and total back pain and weak negative correlations with ASDAS, BASDAI, BASFI, ASAS HI and fatigue.
Conclusion: The MPI provides valuable insights into the multidimensional aspects of pain in axSpA. Pain-related life interference and severity demonstrated strong correlations, while affective distress and life control showed weak to moderate correlations with the ASAS core domain set and thereby demonstrating construct validity. Apart from a weak correlation of social support with the PCS, the domains of social support and life control are not yet fully captured in the axSpA core domain set or other commonly used PROs in axSpA trials.
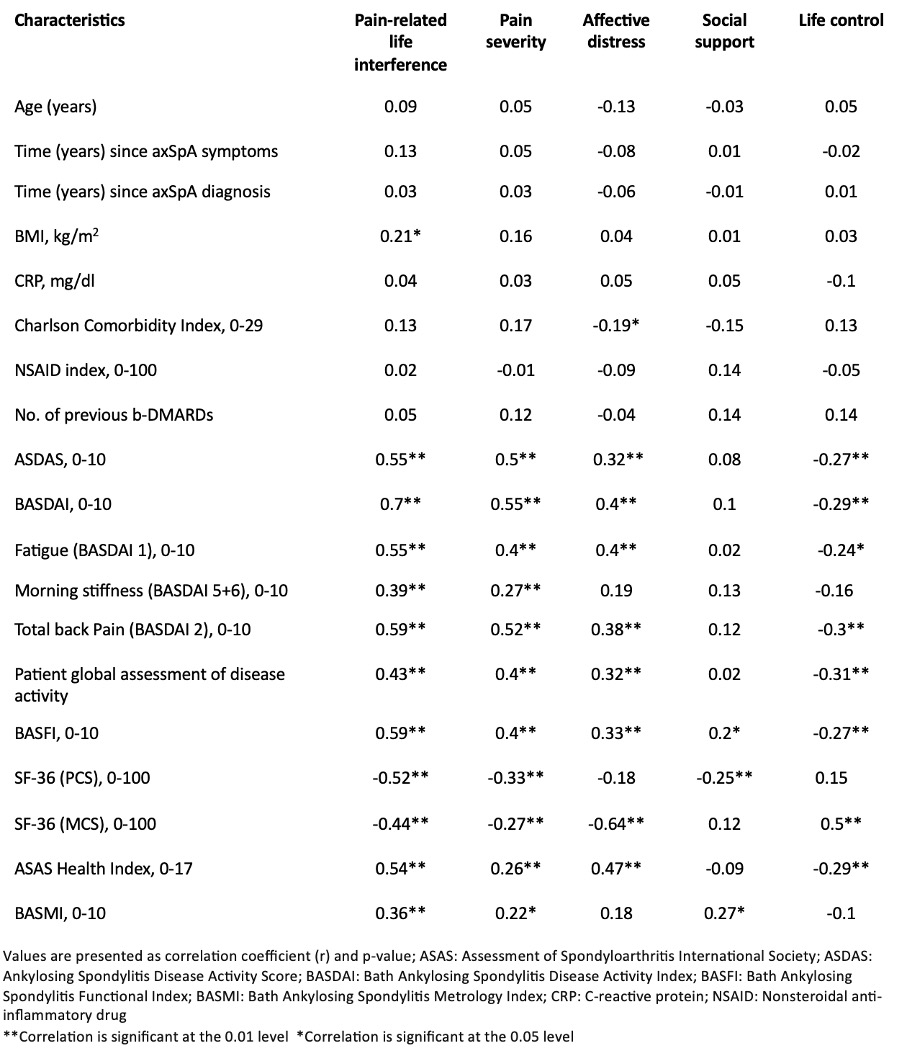 Table 1: Demographic and clinical data of baseline patients
Table 1: Demographic and clinical data of baseline patients
.jpg) Table 2: Correlations of MPI domains with axSpA assessments
Table 2: Correlations of MPI domains with axSpA assessments
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiefer D, Sonkaya Y, Krause D, Voglau M, Mintrop B, Redeker I, Baraliakos X, Kiltz U. Introducing the Multidimensional Pain Inventory as a Comprehensive Tool or Assessing Pain in Patients With Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/introducing-the-multidimensional-pain-inventory-as-a-comprehensive-tool-or-assessing-pain-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/introducing-the-multidimensional-pain-inventory-as-a-comprehensive-tool-or-assessing-pain-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/
