Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science Poster (1468–1479)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: A suspension of empty large multilamellar vesicles (MLV) liposomes composed of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), is currently under clinical development for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA). In-vivo bio-distribution studies and ex-vivo wear tests have shown that following IA injection, the MLV liposomes are retained on the cartilage surface, providing lubrication, and leading to a reduction in wear of the cartilage. In a first-in-man study, a single injection of the MLV liposomes was demonstrated to lower pain in knee OA patients for up to 3 months.
Given the lubricating properties, cartilage wear reduction, and pain-lowering effect of the MLV liposomes, we hypothesized that their IA administration may also reduce OA progression.
The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the effects of three consecutive weekly IA injections of the MLV liposomes on cartilage degeneration in a rat surgical model of osteoarthritis.
Methods: Male Lewis rats underwent a unilateral medial meniscal tear (MMT) on study day 0. The rats (n=15 per group) were treated by the IA route on study days 7, 14, and 21 with the liposomes (50ml/knee), a vehicle control or left untreated. At day 28, joints were processed for histological analysis following staining with toluidine blue. Scoring for cartilage degeneration was based on chondrocyte death/loss, proteoglycan (PG) loss, and collagen loss or fibrillation and was measured by ocular micrometer. Substantial Cartilage Degeneration was identified by chondrocyte and proteoglycan loss extending through greater than 50% of the cartilage thickness. Gait analysis was performed at day 24 to confirm expected animal mobility post-surgery.
Results: Weekly IA treatment with the MLV liposomes (5.35 mg/knee) resulted in significant beneficial effects on cartilage damage and collagen degeneration in the rat meniscal-tear–induced model of OA as determined by evaluation of knee histopathology including significant reductions in substantial cartilage degeneration widths (38% reduction), summed cartilage degeneration scores (33%), total joint scores (25-26%), and combined severe to mild collagen degeneration widths (32%) as compared to the vehicle control. The treatment also resulted in significant reductions in subchondral bone sclerosis (16%) and osteophyte scores (16%) as compared to vehicle control rats. Rats treated with the liposomes had a statistically significant increase in synovial inflammation as compared to the vehicle control group with all animals showing minimal to mild synovitis. Animal body weight gain and mobility post-surgery in rats treated with the liposomes did not differ statistically from the vehicle control group.
Conclusion: Weekly IA treatment with the MLV liposomes resulted in significant reduction in cartilage damage and collagen degeneration in a rat model of OA as determined by evaluation of knee histopathology. The minimal to mild synovitis associated with the injected liposomes is expected from IA-injected particulate agents that lodge in the synovium. The above results indicate that treatment with large DPPC- and DMPC- based MLV liposomes has the potential to be a disease modifying OA therapy.
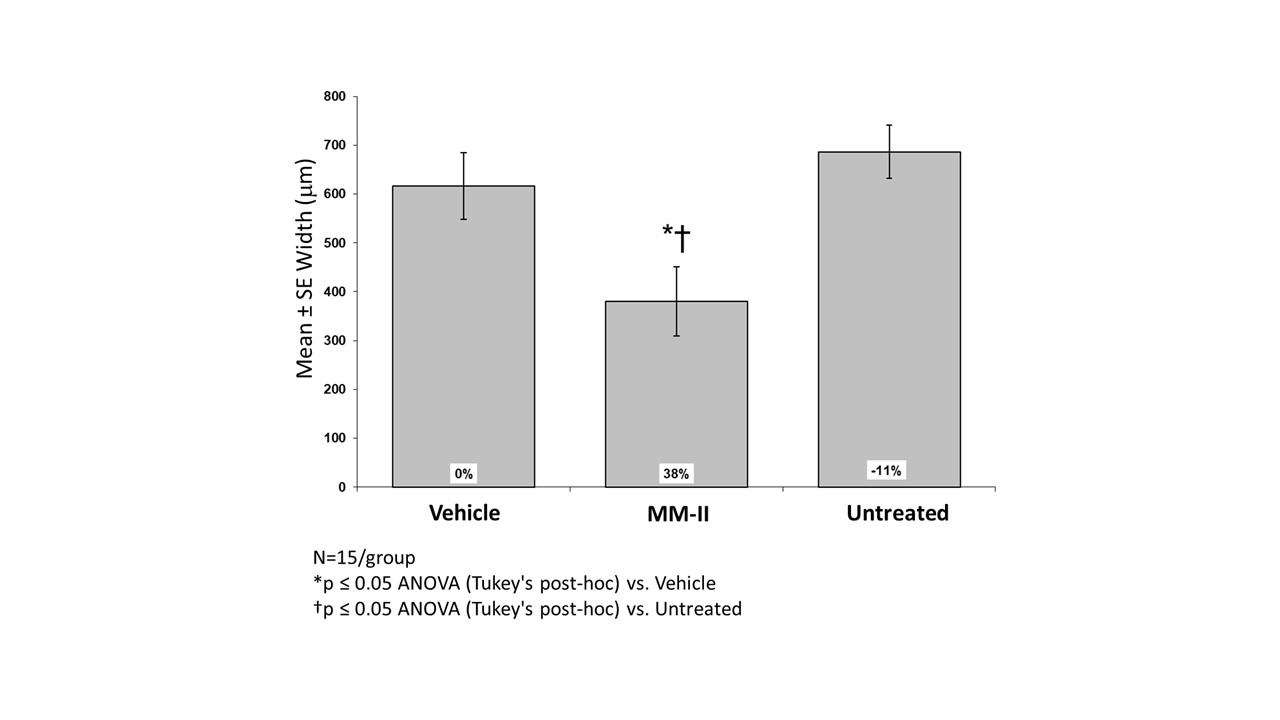 Figure 1. Substantial Tibial Cartilage Degeneration Width
Figure 1. Substantial Tibial Cartilage Degeneration Width
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bendele A, Favret J, Sarfati G, Pinkus R, Wechsler R. Intra-articular (IA) Injection of Empty Large Multilamellar Vesicles Liposomes Reduces Cartilage Degeneration in Rat Osteoarthritis Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intra-articular-ia-injection-of-empty-large-multilamellar-vesicles-liposomes-reduces-cartilage-degeneration-in-rat-osteoarthritis-model/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intra-articular-ia-injection-of-empty-large-multilamellar-vesicles-liposomes-reduces-cartilage-degeneration-in-rat-osteoarthritis-model/
