Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Inflammatory arthritis (IA) treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs lead to secondary osteoarthritis (OA) due to inflammation, aging, and other factors. Inflammatory arthritis can start in middle-aged adults with OA. Discrimination between these two conditions can pose a significant challenge, especially when there are no makers for inflammatory arthritis.
The aim is to clarify the importance of IL6 concentration in synovial fluid for treatment purposes.
Methods: Sixty-nine patients with symptomatic swelling of the joints were undergone aspiration of synovial fluid. All patients received intraarticular steroid injections for therapeutic purposes. Then decision about treatment was depended on the IL6 concentration level in synovial fluid. IL6 concentration was determined by immunochemical luminescence method. Patients with low IL6 concentration continued therapy as OA or secondary OA patients with physiotherapy, without DMARD escalation, but high IL6 concentration DMARD treatment was prescribed or adjusted.
Primary diagnosis was made based on classification criteria for certain diseases (RA, PsA, AS, OA), and the conclusion was based on clinical presentation, current lab results, and IL6 level in synovial fluid.
Results: Primarily 51 patients were classified as having IA (AS-1; RA-1; Undifferentiated IA-2; JIA-2; ReA-32; PsA-7; RA-6). 18 patients were classified as having OA. After IL6 analysis 36 patients were re-classified as having IA (Undifferentiated IA-1; JIA-1; ReA-24; PsA-4; RA-6) and 33 patients were re-classified as having OA. Out of these 33 OA patients, 20 patients were previously classified as having IA and 5 patients of the 36 IA patient’s group were previously classified as having OA. (Table 1). In 33 OA patients, the median IL6 concentration was 100 pg/ml (IQR 41.0 to 204.0). In 36 IA patients, the median was 2430.5 pg/ml (IQR 1277.0 to 5552.0). The Mann-Whitney U test showed a statistically significant difference (p< 0.001) between these two groups. (Figure 1). In the 20 patients, primarily diagnosed as IA and then classified as OA, the median IL6 concentration was 75.1 pg/ml (IQR 38.9 to 169.5). In the five patients, primarily diagnosed as OA and then classified as IA, the median IL6 concentration was 1800 pg/ml (IQR 1394.0 to 7738.0). In this group three patient were without any serological and genetic markers for inflammatory arthritis such as RF, anti-CCP, HLA-B27.
Conclusion: IL6 concentration in synovial fluid is different between IA and OA and may be helpful as an additional factor in the decision-making process.
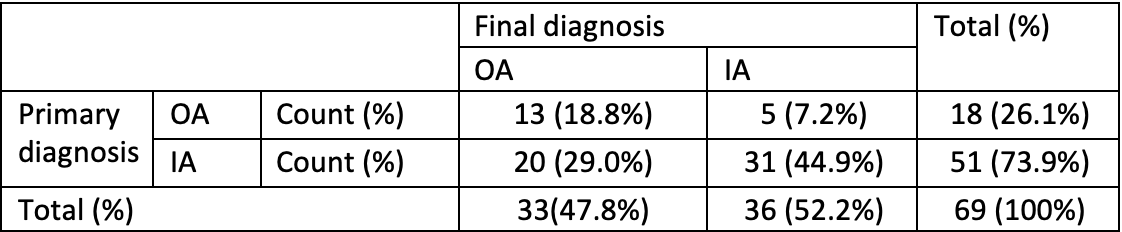 Table1.jpeg”Table 1 Primary diagnosis and final diagnosis crosstabulation
Table1.jpeg”Table 1 Primary diagnosis and final diagnosis crosstabulation
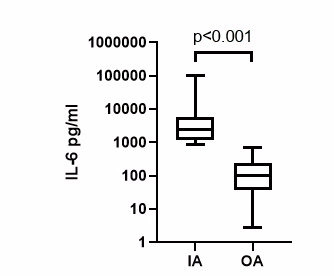 Screenshot 2021-05_31 at 12.55.06.jpeg”Figure 1 IL-6 concentration comparison in OA and IA patient groups
Screenshot 2021-05_31 at 12.55.06.jpeg”Figure 1 IL-6 concentration comparison in OA and IA patient groups
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Veckalns I, Mihailova A. Interleukin 6 Concentration in Synovial Fluid and Its Clinical Significance [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-6-concentration-in-synovial-fluid-and-its-clinical-significance/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-6-concentration-in-synovial-fluid-and-its-clinical-significance/
