Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Determining the pathologic functions of T cells that infiltrate target tissues remains a central challenge in autoimmune diseases. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the formation of T cell-B cell aggregates and differentiation of plasma cells within synovium suggest a pathologic role for synovial T cells with B cell-helper function. The prevailing view considers CD4+ T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, identified as PD-1+ CXCR5+, as the principal T cell population capable of promoting B cell differentiation. However, Tfh cell migration is largely restricted to secondary lymphoid organs. It is thus difficult to reconcile the lymphoid-homing migratory patterns of Tfh cells with the development of T cell-B cell aggregates in inflamed synovium.
Methods: We used mass cytometry and multidimensional flow cytometry to interrogate T cells that express markers of activation, including PD-1, MHC II, CD69, CD25, and CD38, in synovial tissue, synovial fluid, and blood from patients with seropositive RA and other inflammatory arthritides. Sorted PD-1hi T cells from blood and synovial samples were analyzed by RNAseq, RT-PCR, intracellular flow cytometry, and in vitro B cell helper assays. Synovial tissue was also evaluated by immunofluorescence microscopy.
Results: Mass cytometric analysis of seropositive RA synovial tissue cells revealed a strikingly expanded population of PD-1hi CXCR5– CD4+ T cells, which constituted ~25% of synovial CD4+ T cells and outnumbered Tfh cells by 8-fold. PD-1hi CXCR5– cells were similarly enriched in synovial fluid from patients with seropositive RA, but not seronegative inflammatory arthritides. PD-1hi CXCR5– cells, but not Tfh cells, were also expanded in the circulation of seropositive, but not seronegative, RA patients and decreased with DMARD therapy. Surprisingly, these cells were not exhausted, but instead highly expressed factors that enable B cell help, including IL-21, CXCL13, ICOS, SAP, and MAF. Like Tfh cells, PD-1hi CXCR5– cells from synovial tissue, synovial fluid, and blood induced plasma cell differentiation in vitro, which was blocked by neutralization of IL-21 or SLAMF5. However, RNAseq transcriptomics robustly separated circulating PD-1hi CXCR5– cells from Tfh cells. Compared to Tfh cells, PD-1hi CXCR5– cells expressed high levels of chemokine receptors that direct migration to inflamed sites, such as CCR2, CX3CR1, and CCR5, and a decreased Bcl6/Blimp1 ratio. Flow cytometry confirmed CCR2 expression on ~50% of synovial PD-1hi CXCR5– T cells. By microscopy, PD-1hi CXCR5– T cells were frequently found adjacent to B cells in RA synovium. 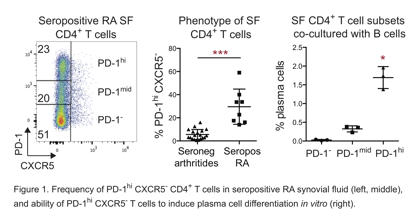
Conclusion: We suggest that PD-1hi CXCR5– T cells represent a T peripheral helper (Tph) cell population, analogous to T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, that supports B cell responses in non-lymphoid tissues. Given their marked expansion in seropositive RA, these cells may be important in driving pathologic B cell responses and autoantibody production.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rao D, Gurish M, Slowikowski K, Fonseka C, Marshall J, Liu Y, Donlin LT, Henderson L, Mizoguchi F, Teslovich N, Weinblatt M, Massarotti E, Coblyn J, Helfgott SM, Lee YC, Todd DJ, Bykerk VP, Goodman SM, Pernis AB, Ivashkiv L, Karlson EW, Nigrovic P, Filer A, Buckley C, Lederer J, Raychaudhuri S, Brenner M. Integrated High-Dimensional Analyses Reveal a Pathologically Expanded ‘Peripheral’ B Cell-Helper T Cell Population in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-high-dimensional-analyses-reveal-a-pathologically-expanded-peripheral-b-cell-helper-t-cell-population-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrated-high-dimensional-analyses-reveal-a-pathologically-expanded-peripheral-b-cell-helper-t-cell-population-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
