Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a leading cause of mortality in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Although medications have improved their prognosis, optimal therapy remains undefined. The goal of this study was to compare time to clinical worsening (TTCW) and survival based on initial oral PAH therapy.
Methods: Using data from the PHAROS registry (a multicenter prospective observational study enrolling SSc patients with incident pulmonary hypertension), patients with group I PAH, 6 months of initial therapy with either an endothelin-receptor antagonist (ERA), phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5), or a combination of ERA/PDE5 were included. Patients treated initially with prostacyclins were excluded. The starting point for all analyses was the date of therapy initiation. Outcomes were survival and TTCW, defined as the first occurrence of death, PAH-related hospitalization, lung transplant, initiation of parenteral prostacyclin, or worsening symptoms.
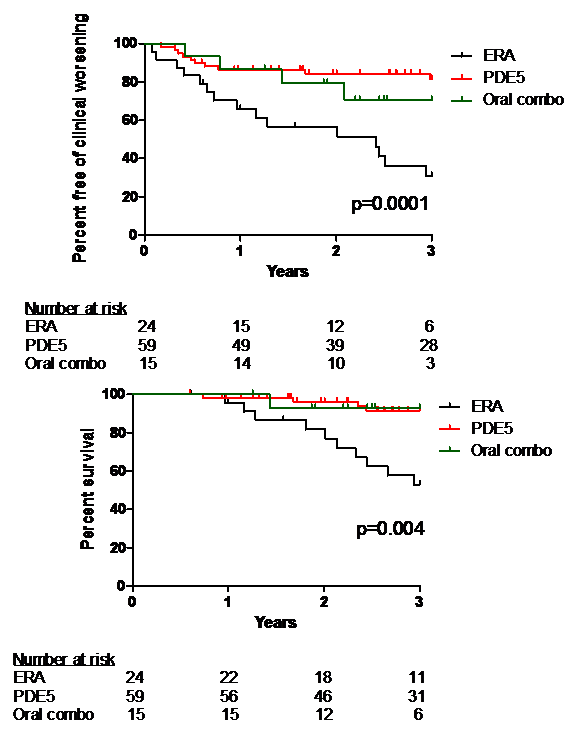
Results: Ninety-eight patients (initial ERA=24, initial PDE5=59, initial ERA/PDE5=15) were included; no significant differences in baseline variables existed. TTCW was significantly worse in patients initially started on ERA compared to PDE5 or ERA/PDE5 (p=0.0001, Fig 1). Baseline factors independently associated with shorter TTCW were initial ERA (HR 0.38, p=0.009), lower DLCO (HR 0.69 per 10% change, p=0.04), and higher PVR (HR 1.10 per Wood unit change, p=0.007). Three year survival was significantly worse in the initial ERA group (52.9%) compared to the PDE5 (91.5%) or ERA/PDE5 group (92.9%, p=0.004, Fig 2). The only baseline factor independently associated with risk for death in this cohort was initial ERA therapy (HR 0.22, p=0.004).
Conclusion: Compared to PDE5 or combination ERA/PDE5, initial therapy with an ERA in SSc-PAH patients was associated with a significantly worse TTCW and survival, even after adjustment for commonly accepted prognostic factors. Although these findings may be the result of unmeasured imbalances between groups, it is plausible that known ERA side effects such as fluid retention may have led to clinical worsening. Further study into the optimal initial oral therapy in patients with SSc-PAH is needed.
 |
Disclosure:
M. R. Lammi,
None;
L. A. Saketkoo,
None;
S. C. Mathai,
None;
R. T. Domsic,
None;
C. M. Bojanowski,
None;
V. D. Steen,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
8,
United Therapeutics,
5,
Gilead Science,
8,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
2,
CSL Berhing,
2,
Intermune,
2,
Bayer,
5;
D. E. Furst,
None;
P. Investigators,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/initial-therapy-with-an-endothelin-receptor-antagonist-is-associated-with-worse-outcomes-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-and-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-observations-from-the-pulmonary-hypert/
