Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Background: CD4 + T cells are important in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and therapies targeting the differentiation of osteoclasts are attracting attention. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMK4) is a molecule involved in T cell activation and osteoclast differentiation, but the role of CaMK4 in T cells and osteoclasts in RA remains unclear.
Objective: We investigated the role of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMK4) in the expression of joint injury in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Mice subjected to collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) were treated with KN-93, a CaMK4 inhibitor, and the clinical score was evaluated by micro-computed tomography (μ-CT) and histology. The effect of CaMK4 inhibition on inflammatory cytokines and humoral immune response was also examined. CAMK4 gene expression was measured in CD4+ T cells from healthy controls and patients with active RA. CD4+ cells were isolated from RA patients to determine the effect of KN-93 on T cell differentiation. We also isolated CD14+ cells from RA patients to investigate osteoclast differentiation.
Results: Treatment of CIA mice with KN-93 reduced significantly the arthritis clinical score and joint destruction as evaluated by μ-CT and histology. Further analysis revealed that CaMK4 inhibition in CIA mice suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, IL-17, G-CSF, and MCP-1. Expression of CAMK4 was significantly higher in CD4+ T cells from patients with RA compared with cells from healthy controls. CaMK4 inhibition mitigated IL-17 production by CD4+ cells from patients with RA. The number of in vitro differentiated osteoclasts from CD14+ cells from RA patients was significantly decreased in the presence of the CaMK4 inhibitor.
Conclusion: The present study provides evidence that CaMK4 inhibition ameliorates CIA by suppressing the production of Th17 cell-related cytokines. At the translational level, we demonstrate that CaMK4 is increased in CD4+ T cells from patients with active RA and that CaMK4 inhibition results in the decreased levels of osteoclast differentiation. Taken together, our findings indicate that CaMK4 inhibitors represent potential therapeutic agents in the treatment of patients with RA.
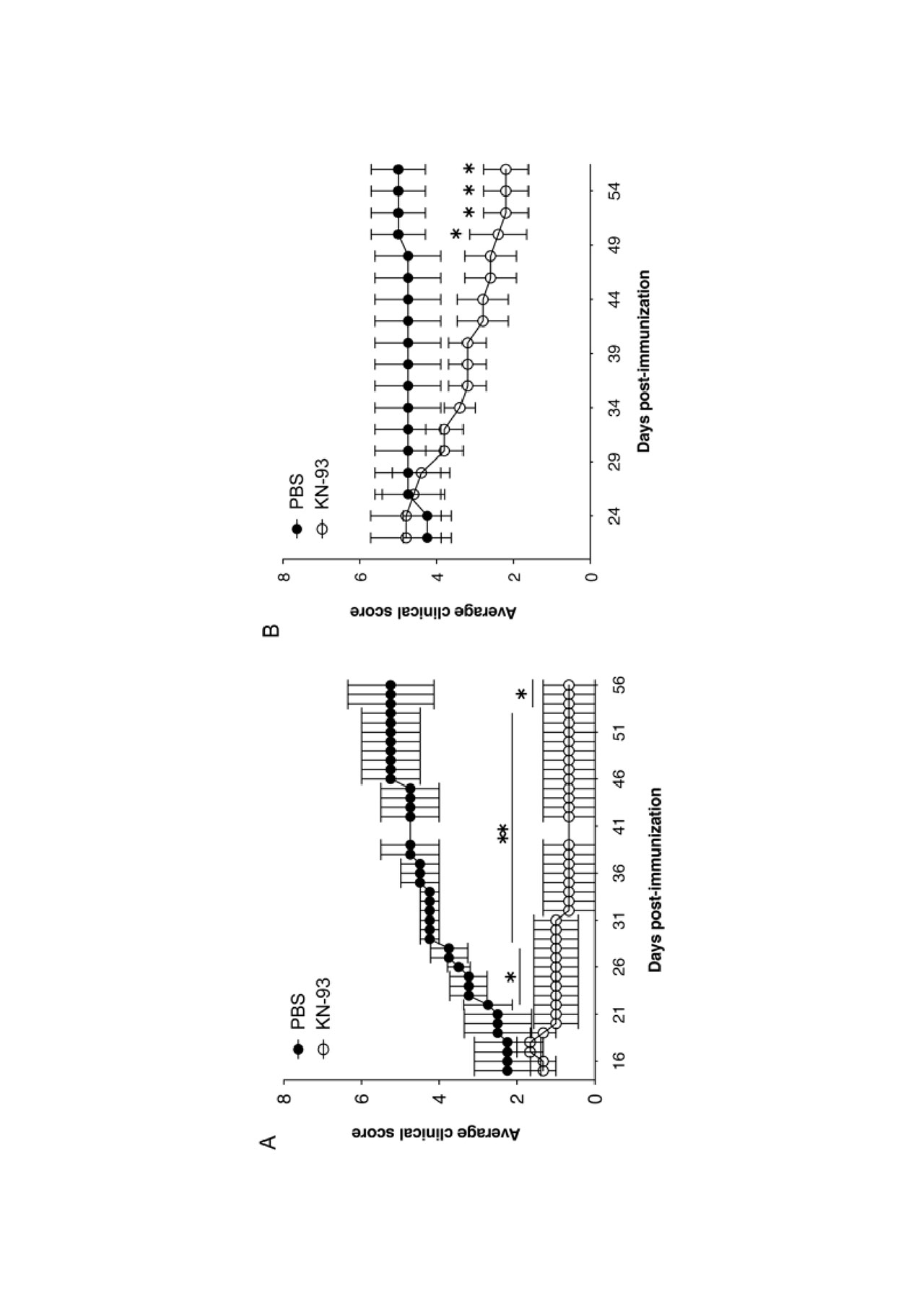
Mean clinical scores of CIA in mice treated with KN-93 or PBS prior to the onset of disease -n = 5 per group- -A- and after established disease -n = 5 per group- -B- *p < 0.05; mean ± SEM.
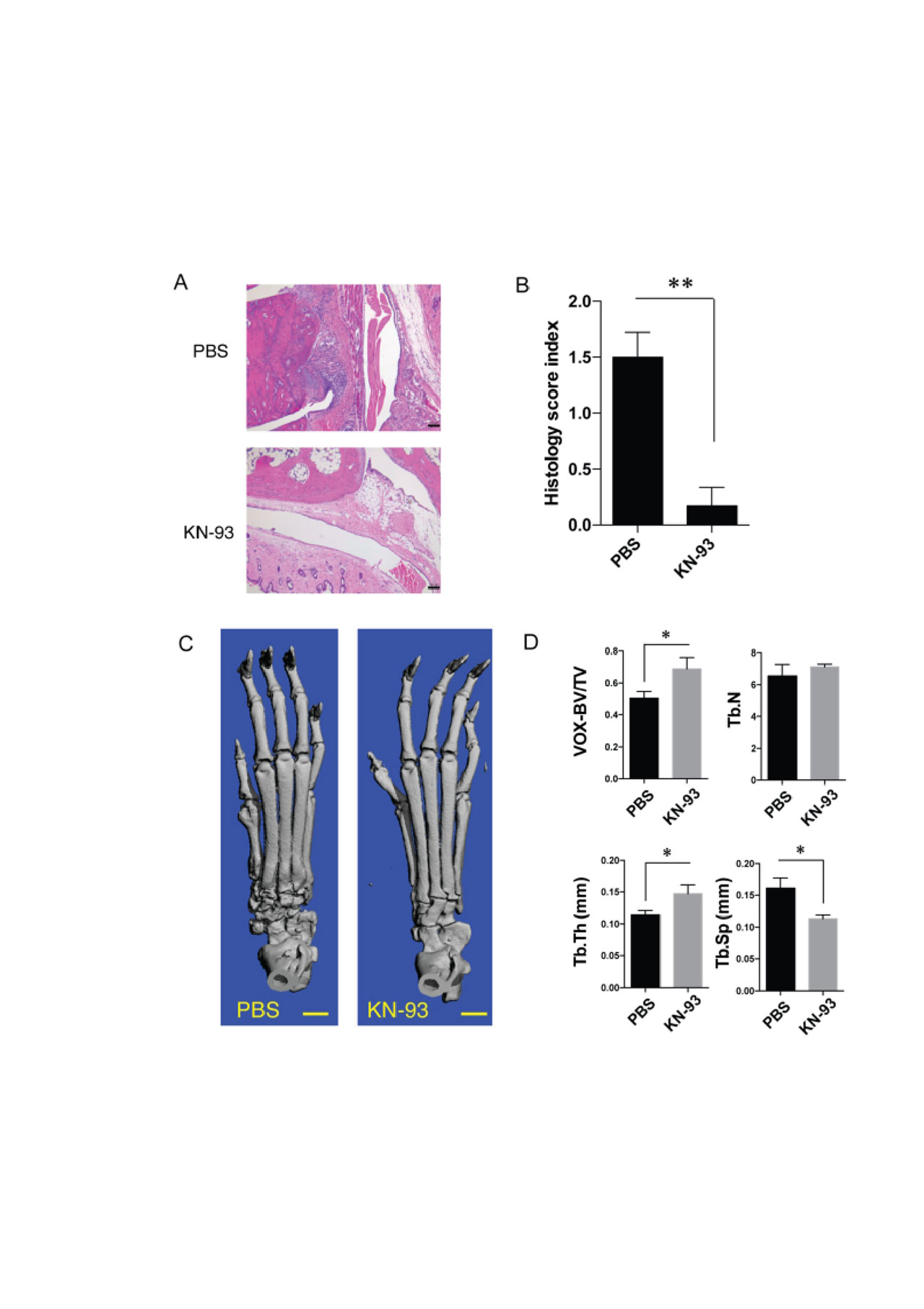
-A- Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of the ankle joints of KN-93 or PBS-treated mice with CIA. Scale bars represent 100 μm. -B- Pathology scores of each group were calculated and expressed as mean ± SEM -n=4-. * p< 0.05. -C- Microfocal computed tomographic images showing the dorsal surface reconstruction of the hind paws of PBS-treated -left- and KN-93 treated -right- mice. -D- Bone volume fraction -BV/TV-, trabecular number -Tb.N-, trabecular thickness -Tb.Th-, and trabecular spacing -Tb.Sp- in mice treated with PBS or KN-93. Data represent mean and SEM, *p < 0.05.
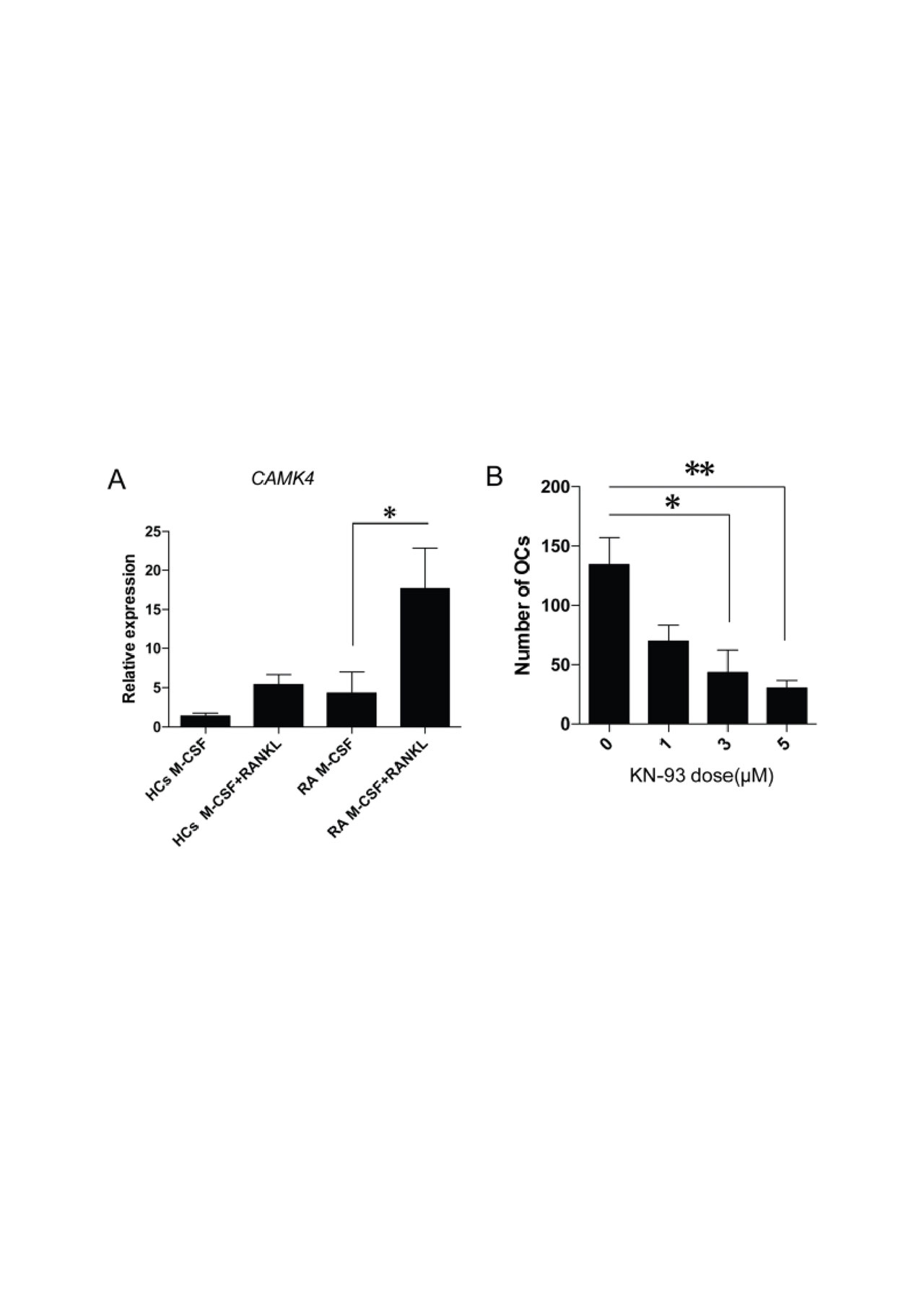
-A- CAMK4 mRNA expression in CD14+ monocytes from patients with RA or HCs determined by qPCR. -* p< 0.05; median with interquartile range-. -B- Active RA patients had significantly lower numbers of osteoclasts in the presence of KN-93 -* p< 0.05, ** p < 0.01; mean ± SD; n = 4-. -C-
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koga T, Sato T, Endo Y, Tsuji S, Takatani A, Shimizu T, Sumiyoshi R, Igawa T, Kawashiri S, Iwamoto N, Ichinose K, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Yoshida N, Umeda M, Tsokos G, Kawakami A. Inhibition of Calcium/calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase IV in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Dual Effect on Th17 Cell Activation and Osteoclastogenesis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inhibition-of-calcium-calmodulin-dependent-protein-kinase-iv-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-dual-effect-on-th17-cell-activation-and-osteoclastogenesis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inhibition-of-calcium-calmodulin-dependent-protein-kinase-iv-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-dual-effect-on-th17-cell-activation-and-osteoclastogenesis/