Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The REGENCY (NCT04221477) trial demonstrated superior efficacy of obinutuzumab and standard therapy (OBI+ST) over placebo and ST (PBO+ST) in patients (pts) with active lupus nephritis (LN). Although an acceptable safety profile was observed, insights related to IRRs and hematologic effects of OBI are needed to guide future management. In this study, we further characterize important non-infectious adverse events including the IRR profile of OBI and describe the occurrence of neutropenia in the REGENCY trial.
Methods: Incidence, severity and attribution of IRRs and hematologic abnormalities, including drug-related neutropenia, were determined in the REGENCY trial based on investigator and NCI CTCAE v5.0 adverse event grading. Descriptive analyses were performed comparing pts receiving OBI+ST vs PBO+ST. All pts met ACR SLE classification criteria and had biopsy-proven proliferative LN.
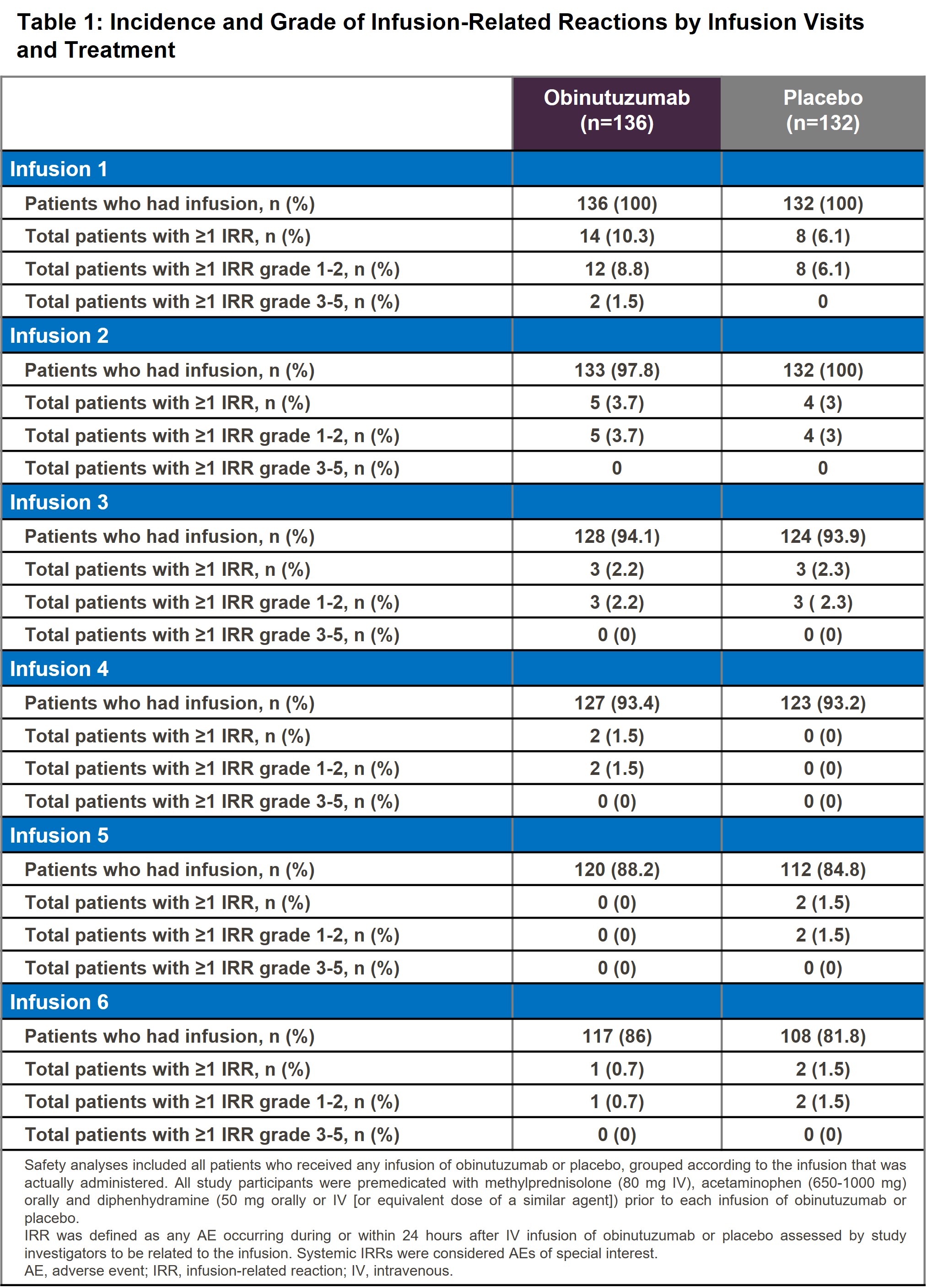
Results: The proportion of pts who experienced at least one IRR was higher in the OBI+ST arm vs the PBO+ST arm (21 [15.4%] vs 15 [11.4%], respectively) during the 76-week period. In the OBI+ST arm, the majority (19 [14.0%]) experienced IRRs of Grade (Gr) 1-2, which resolved following protocol guidance. Two pts (1.5%) experienced Gr 3-4 IRRs in the OBI+ST arm and both events resolved: one non-serious IRR of Gr 3 and one serious IRR of Gr 4, one leading to treatment discontinuation for this pt. No Gr 5 IRRs were observed. The most frequently reported signs and symptoms of IRRs in the OBI vs PBO arms respectively were nausea (4 [2.9%] vs 4 [3.0%]), headache (4 [2.9%] vs 3 [2.3%]) and vomiting (4 [2.9%] vs 2 [1.5%]). IRR incidence and severity was highest at first infusion, with Gr 3-4 observed only then, and decreased with additional infusions (Table 1).The frequencies of shifts observed from Gr 1-2 at baseline to Gr 3-4 post-baseline were notably different between the treatment arms only for neutrophils and lymphocytes. As lymphopenia is an expected pharmacologic effect of anti-CD20 therapies, this analysis focused on drug-related neutropenia. The proportion of pts who experienced at least one drug-related neutropenia was higher in the OBI+ST arm vs the PBO+ST arm (17 [12.5%] vs 5 [3.8%], respectively). Most cases of neutropenia were incidentally detected during routine hematology labs at scheduled study visits. Median time for resolution was 16 days (d) (min-max: 4-378 d) and 50.5 d (min-max: 21-371 d) in the OBI+ST and PBO+ST arm, respectively. Seven pts (4.1%) had Gr 3-4 drug-related neutropenia (including 1 febrile neutropenia) in the OBI+ST arm, whereas none in the PBO+ST arm had Gr 3-4 neutropenia. All drug-related neutropenia resolved with treatment by protocol guidance except for one PBO pt whose neutropenia was recovering/resolving at the clinical cutoff. No Gr 5 neutropenia was observed. Five patients received G-CSF treatment for drug-related neutropenia (4 in the OBI+ST arm vs 1 in the PBO+ST arm).
Conclusion: Although the incidence of IRRs and drug-related neutropenia was higher in pts receiving OBI+ST compared with PBO+ST, these risks remained low overall; many were Gr 1-2, self-limited, easily manageable and without consequence for most pts. These data provide insights into adverse events related to OBI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Baczkowska T, Saxena A, Hassan I, Yoo B, Lanza B, Sehgal H, Boissard F, Garg J, Schindler T, Martins E, Pendergraft W, Rovin B. Infusion-Related Reactions (IRRs) and Hematologic Events Associated With Obinutuzumab in Lupus Nephritis: A Secondary Analysis of a Phase III Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infusion-related-reactions-irrs-and-hematologic-events-associated-with-obinutuzumab-in-lupus-nephritis-a-secondary-analysis-of-a-phase-iii-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infusion-related-reactions-irrs-and-hematologic-events-associated-with-obinutuzumab-in-lupus-nephritis-a-secondary-analysis-of-a-phase-iii-trial/

.jpg)