Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: RA – Treatments I: Novel RA Treatments & Mechanisms of Action
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: The lymphatic system serves as a conduit for transporting immune cells and inflammatory molecules present in arthritic joints to lymph nodes (LN), playing a critical role in the pathology of RA1, yet all bDMARDs are dosed systemically potentially limiting the delivery to the target site of action. Therefore, targeting bDMARDs, like etanercept, to joint draining lymphatics could increase neutralization of inflammatory molecules and reduce unwanted immune cell activation that propagates the inflammatory cascade in RA. Nanotopography-microneedles (NTM) have previously been shown to increase the infusion of etanercept into the peripheral lymphatics and draining LNs in collagen-induced arthritic rats2. Here we report results from a 10-patient Phase 1b clinical trial in RA patients with an inadequate response to 50 mg etanercept SC injections who were switched to 25 mg peripheral lymphatic infusions of etanercept via the NTM device. All patients had been on SC injections of etanercept for more than 3 months prior to the study.
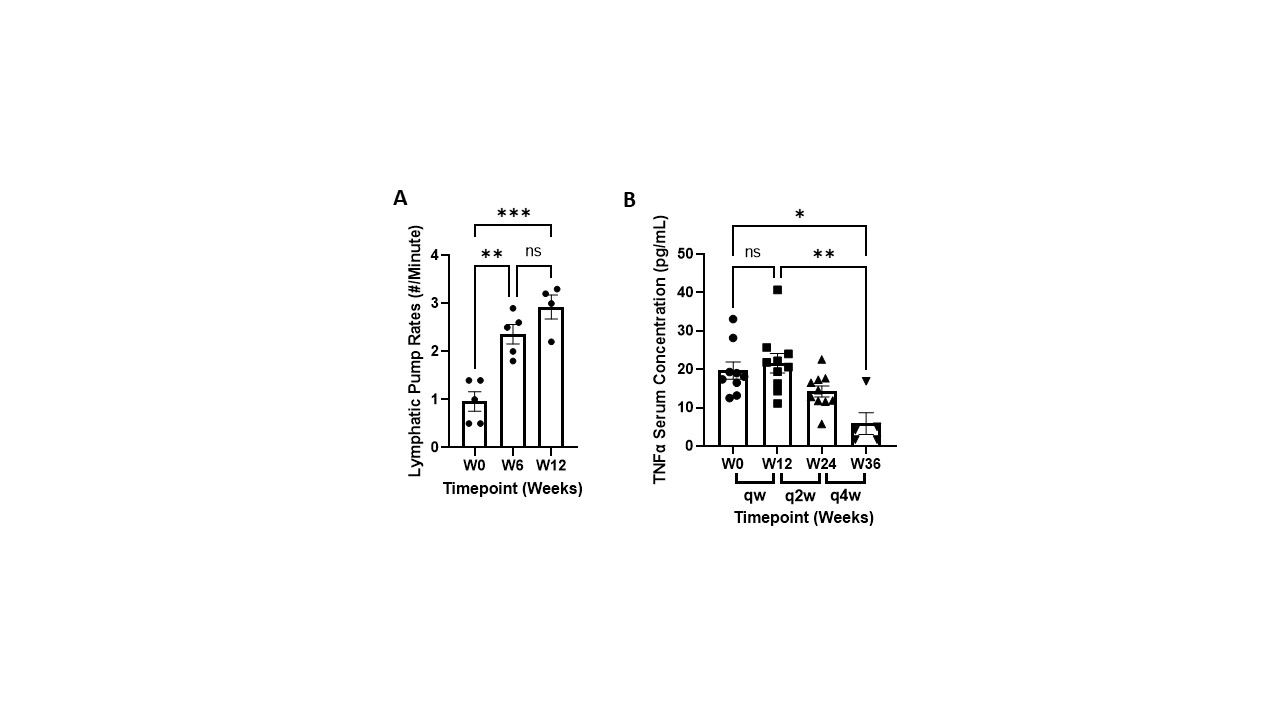
Methods: The NTM device was applied to the dorsal forearm and 25 mg of etanercept was infused for 1.25 hours. Once weekly dosing was performed for the first 12 weeks, followed by biweekly and monthly dosing to explore reduced dose frequency in responding patients for a total of 36 weeks. The device was alternated between the left and right dorsal forearm every other dose. Lymphatic imaging was conducted using Near-Infrared Fluorescence with indocyanine green dye2to measure lymphatic pump rates before and after etanercept lymphatic infusions.
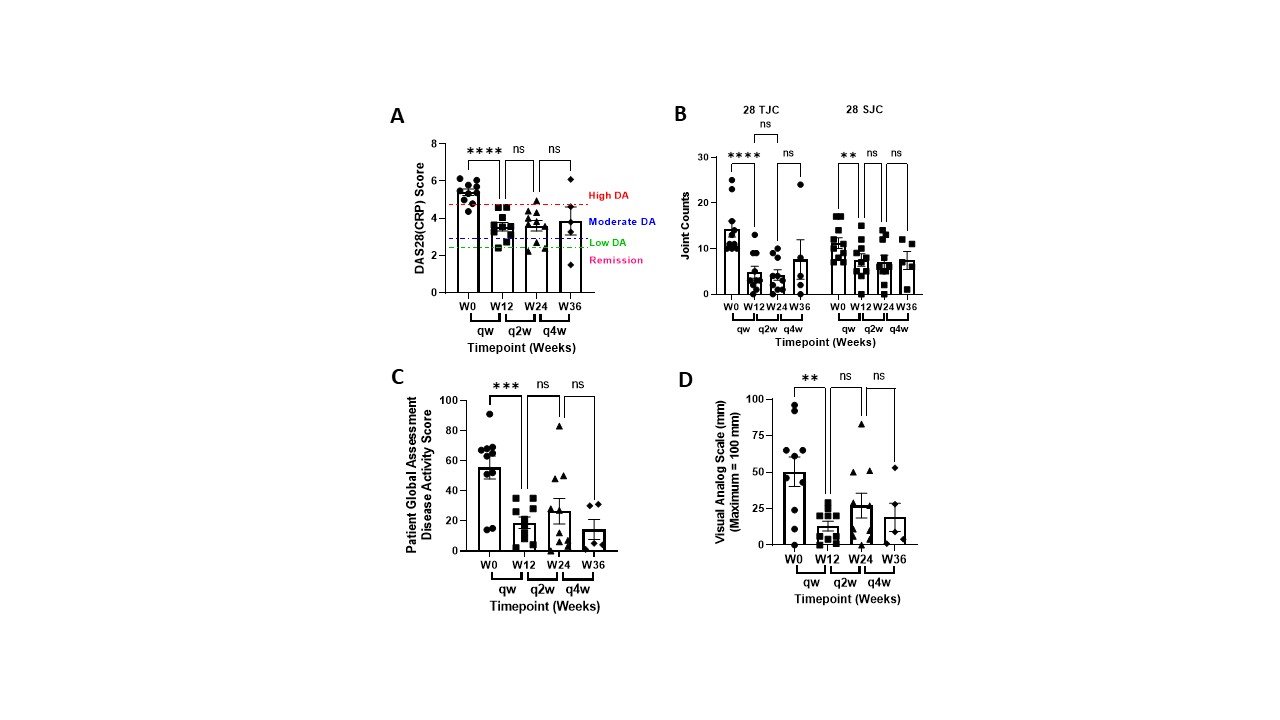
Results: Switching patients from weekly 50 mg SC injections to 25 mg NTM infusions significantly reduced global disease activity without drug delivery-related immune responses. DAS28(CRP) scores were reduced from 5.40 ± 0.16 to 3.55 ± 0.21 and Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity and Pain decreased by 66% and 77%, respectively, in the first 12 weeks and remained stable as dosing frequency was reduced to biweekly and monthly dosing (Figure 1). SJC and TJC were concomitantly decreased and remained stable (Figure 1). Lymphatic pumping rates increased from 1.0 ± 0.2 to 2.9 ± 0.3 pumps/minute after 12 weeks and TNFα levels initially increased and were significantly reduced by week 36 (Figure 2). No SAEs were reported, and primary AEs consisted of mild erythema at the NTM infusion site.
Conclusion: The NTM device effectively infused etanercept into the peripheral lymphatics that drain to the LN. The NTM device was well accepted by all patients with an application pain rating of 3.8 ± 3.6 mm on a 100 mm VAS scale. DAS28(CRP) scores, 28TJC and 28SJC, and Global Disease Activity and Pain were improved in all patients infused with the NTM device at half the SC injection dose administered weekly, biweekly, and monthly. These results suggest that administering TNFα inhibitors to arthritic joint draining LN may reduce dose frequency and improve both TNFα neutralization and impaired lymphatic function, and reduce unwanted immune cell activation that contributes to the inflammatory cascade in RA.
1.Yousef, M et al.: J Pharm Pharm Sci 2021; 24: 533-47
2. Aldrich, MB et al.: Arth Res Ther 2017; 19:1–13
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ross R, Strand V, Querubin R, Goldman J, Leff R, Melson A, Roerig P, Smith A. Infusion of Etanercept into the Peripheral Lymphatics Significantly Reduces Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Inadequate Response to Subcutaneous Injections [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infusion-of-etanercept-into-the-peripheral-lymphatics-significantly-reduces-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-inadequate-response-to-subcutaneous-injections/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infusion-of-etanercept-into-the-peripheral-lymphatics-significantly-reduces-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-inadequate-response-to-subcutaneous-injections/