Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Research Methodology Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Abnormally applied forces across the knee during walking play a central role in knee osteoarthritis (OA) disease pathways. Biomechanical data collected continuously during gait analysis are often presented as summary measures (e.g., peak), which overlooks the full range of the data. The purpose of this study was: 1) to identify distinct biomechanical patterns among people with symptomatic knee OA utilizing the full spectrum and richness of gait data, and 2) to examine relationships between the modes of variation of vertical and anterior-posterior (AP) ground reaction force (GRF) curves and baseline sociodemographic and clinical features.
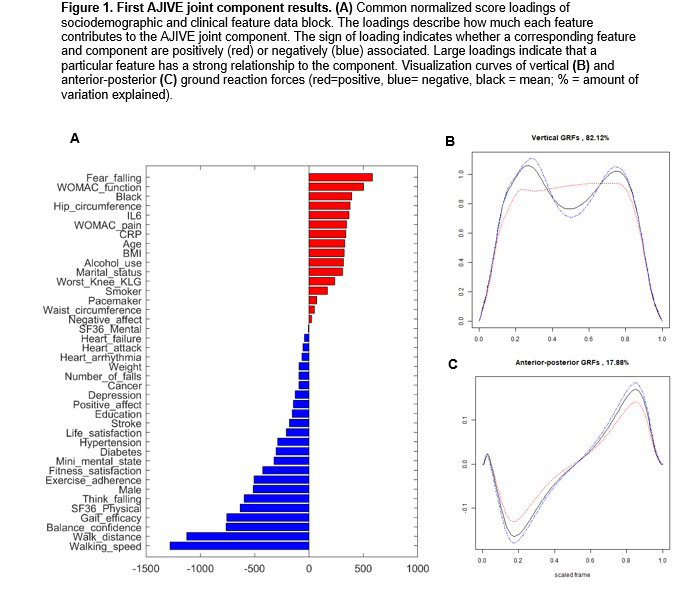
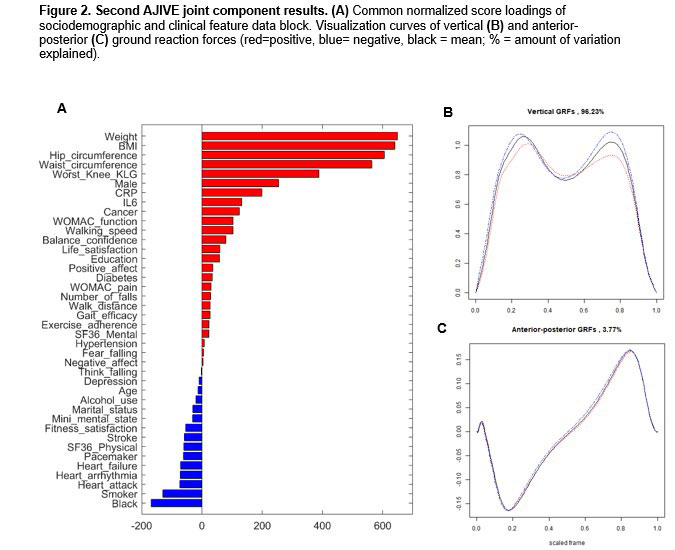
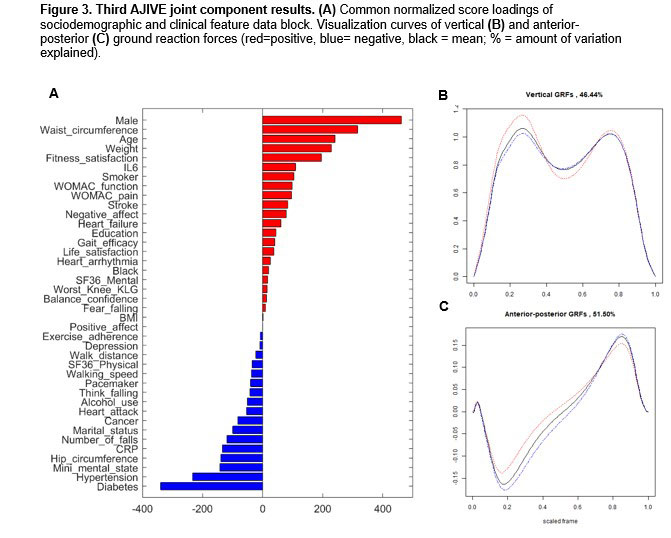
Methods: Data were from the Intensive Diet and Exercise for Arthritis (IDEA) study, a clinical trial of exercise and weight loss among 454 participants with symptomatic knee OA and a body mass index 27-37 kg/m2. Each participant walked over a force plate three times per lower limb (right/left) at their self-selected pace. For analyses, we removed vertical and AP GRF curves that lacked two distinct peaks. We used Angle-based Joint and Individual Variation Explained (AJIVE) to analyze the shared variation between the GRF modes of variation data block and the patient-level features data block, which included measures of sociodemographics, anthropometry, pain, physical function, gait, falls, self-efficacy, physical and mental health, knee OA, inflammatory biomarkers, and comorbid conditions. We visualized the common normalized score (CNS) loadings of the two data blocks using bar plots. We combined the corresponding principal component (PC) scores of each GRF amplitude and phase mode of variation into one data block. We produced two curves visualizing the negative and positive extremes (highest and lowest score for each PC) of all amplitude (curve height) and phase (curve timing) variations used in the GRF PC score data block for vertical and AP GRFs, using the CNS loadings as weights.
Results: The final analysis set included 2,394 curves from 431 participants. The first AJIVE joint component of the GRF PC score data block showed that a faster walking speed was associated with more force upward and downward for the vertical GRF and a faster backward (braking) and forward (propulsion) AP GRF (Figure 1, blue loadings and curves). For the second AJIVE joint component (Figure 2), reduced height of the first and second vertical GRF peaks occurred with a larger body size (weight, BMI, waist and hip circumference, red loadings and curves); no notable differences were observed for the AP GRFs. For the third AJIVE joint component (Figure 3), comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) were related to later occurrence of the first peak of vertical GRFs and greater magnitude of AP GRF peaks (blue loadings and curves).
Conclusion: These analyses confirm associations of greater peak vertical and AP GRFs with faster walking speed while also providing new insights into the alterations of GRFs with body size and comorbid conditions. Future analyses will determine how these GRF curve patterns change after the 18-month IDEA study interventions of exercise and weight loss, and how these changes relate to clinical outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Golightly Y, Xiang S, Borgert E, Arbeeva L, Loeser R, Messier S, Nelson A, Marron J. Influence of Sociodemographic and Clinical Features on Ground Reaction Force Variability Among Individuals with Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: A Novel Computational Approach [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-sociodemographic-and-clinical-features-on-ground-reaction-force-variability-among-individuals-with-symptomatic-knee-osteoarthritis-a-novel-computational-approach/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-sociodemographic-and-clinical-features-on-ground-reaction-force-variability-among-individuals-with-symptomatic-knee-osteoarthritis-a-novel-computational-approach/