Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Elevated rheumatoid factor (RF) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with higher disease activity. A significantly lower efficacy of TNF inhibitors (TNFi) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), Infliximab (IFX) and Adalimumab (ADL) as well as the fusion protein etanercept, in seropositive RA patients with high RF levels has been described1,2. Certolizumab pegol (CZP), a Fc-free pegylated mAb anti-TNF has shown comparable efficacy irrespective of baseline RF status 3. RF binds the Fc fragment of IgG1 which is the subtype used to engineer the majority of TNFi mAbs. Augmented clearance of mAbs in the presence of high titers of FR, due to the formation of large immune complexes, may likely explain reported negative impact of RF titers in mAbs efficacy. We aim to evaluate in clinical practice whether RF and ACPA levels in RA patients influence serum drug levels of 3 TNFi with differentiated molecular structures.
1 Bobbio-Pallavicini F. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66(3):302–7 2 Potter C. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68(1):69–74 3 Tanaka Y. APLAR 2020. Oral Communication
Methods: We evaluated retrospectively a cohort of consecutive RA patients treated with either IFX, ADL or CZP. Clinical, laboratory and demographic data were collected for all patients at baseline (T0) and after 6 months (T6) of treatment. RF and ACPA titers, serum drug levels were measured at T0 and T6 using nephelometry and ELISA respectively. Patients were stratified into quartiles based on baseline RF [seronegative ( < 20 UI/ml, low (20-57.0), medium (57.0-380), and high ( > 380)] and ACPA [negative ( < 25.0 IU/ml), low (25.0–167 IU/ml), medium (167–1582 IU/ml) and high ( >1582 IU/ml)]. Association between baseline RF and ACPA titers and drug levels were assessed using non-parametric test (Mann-Whitney).
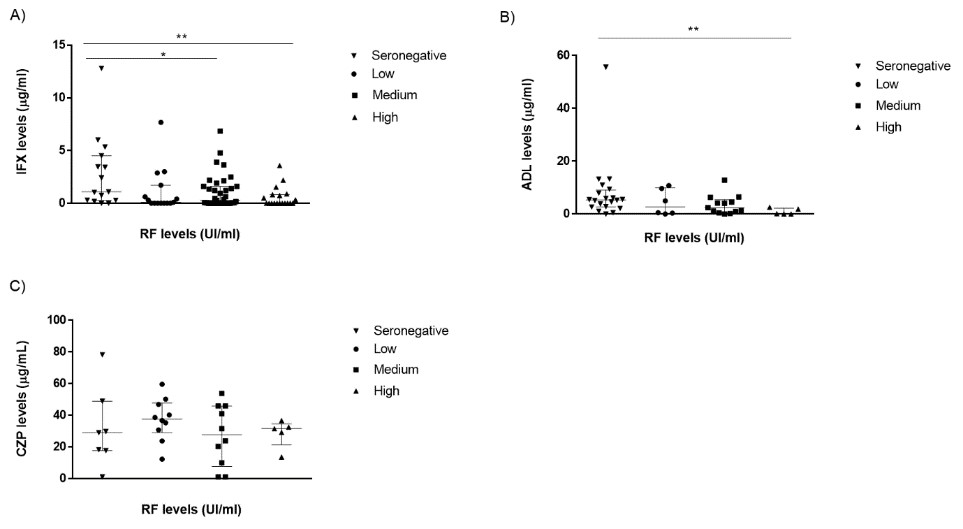
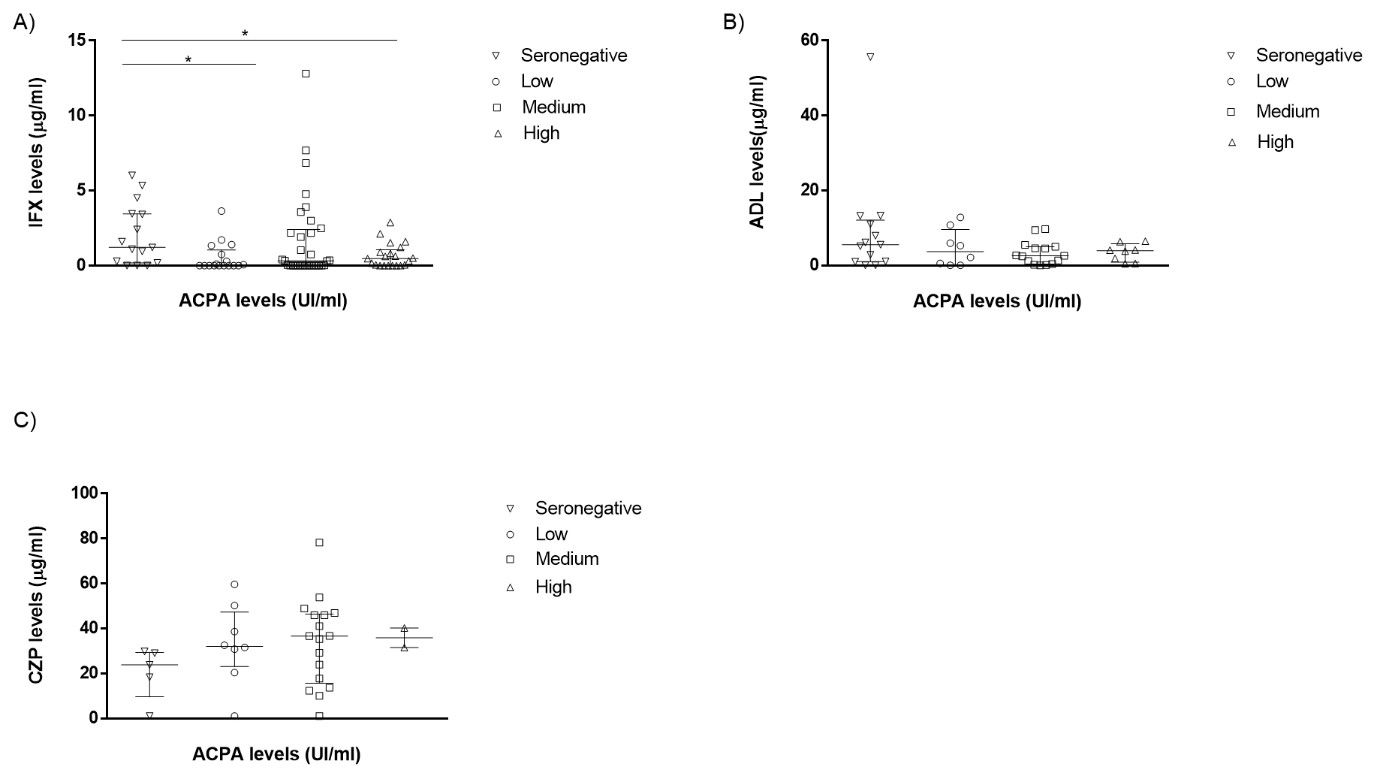
Results: A total of 170 patients from a tertiary hospital were evaluated: 90 (66%) received IFX, 48 (35%) ADL and 32 (22%) CZP. Demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. RF and ACPA were positive in 76% and 80 % of patients, respectively. A higher proportion of patients in the IFX group (77%) had both RF+ and ACPA+ status followed by CZP (75%) and ADL (54%) groups. Serum IFX and ADL levels at T6 were significantly lower in patients with higher basal RF titers (Fig 1). In contrast, no differences between drug levels at T6 across baseline RF titers were observed in the CZP group (Fig. 1).For ACPA status, only IFX levels at T6 were statistically higher in basal ACPA negative patients (Fig.2).Most patients with high ACPA levels had also medium or high RF levels: 11/22 (50%) patients and 1/22 (32%), respectively. Anti-Drug Antibodies (ADA) were detected in 26 patients with IFX, 2 with ADL and 2 with CZP.In the case of IFX, the major percentage of patients with ADA positive had medium or high RF levels patients (39% and 38%, respectively) compared to patients with seronegative andlow RF levels (4% and 19% respectively).
Conclusion: Baseline RF titers do not impact serum drug levels of CZP (a Fc-free anti-TNF ) whereas they are significantly linked to low serum drug levels of complete monoclonal antibodies (IFX and ADL) in clinical settings in RA patients. These differences might aid physicians to select suitable treatment for the management of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinez Feito A, Plasencia-Rodríguez C, Novella-Navarro M, Gehin J, Hernandez-Breijo B, M.Brenis C, Villalba A, Fernandez-Fernandez E, Monjo I, Pascual-Salcedo D, Nozal P, Balsa A. Influence of Rheumatoid Factor on Serum Drug Levels of TNF Inhibitors with Different Structures in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-rheumatoid-factor-on-serum-drug-levels-of-tnf-inhibitors-with-different-structures-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-rheumatoid-factor-on-serum-drug-levels-of-tnf-inhibitors-with-different-structures-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/