Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:15AM
Background/Purpose: There exists a need to identify informative peripheral blood biomarkers for RA-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) and elucidate the pathophysiological processes driving RA-ILD onset. Several inflammatory- and fibrosis-related mediators have been identified in diseases characterized by tissue fibrosis such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and heart failure, but few have been evaluated specifically in RA-ILD. We investigated the association of inflammatory- and fibrosis-related biomarkers with RA-ILD risk in a large, prospective RA cohort.
Methods: Using a multicenter, prospective cohort of U.S. Veterans with RA, we performed a cross-sectional study of prevalent RA-ILD and cohort study of incident RA-ILD. Inflammatory- and fibrosis-related biomarkers discovered in IPF and heart failure: growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), interleukin-18, interferon-gamma inducible protein-10, interferon-inducible T-cell alpha chemoattractant, monokine induced by gamma interferon, pentraxin-3, and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule, were measured from serum at enrollment using the MesoScale Discovery platform. Biomarker concentrations were log-transformed and standardized, as well as categorized into quartiles to assess non-linear associations. RA-ILD was identified through informatics-based screening and validation by a board-certified rheumatologist requiring a clinical diagnosis plus imaging or biopsy findings. The associations of candidate biomarkers with RA-ILD were assessed separately in multivariable logistic (prevalent RA-ILD) and Cox (incident RA-ILD) regression models adjusted for age, sex, race, smoking status, body mass index category, anti-CCP antibody positivity, DAS28, and comorbidity burden.
Results: Cross-sectional analyses were conducted among 2,737 RA participants (87% male, mean age 64 years), with 124 having prevalent RA-ILD. Higher concentrations of GDF-15 (per 1 SD aOR 1.42 [1.08, 1.87]) and pentraxin-3 (aOR 1.30 [1.07, 1.58]) were significantly associated with prevalent RA-ILD (Table 1). Referent to the lowest quartile, higher quartiles of GDF-15 (Q3 aOR 3.76 [1.68, 8.41]; Q4 4.10 [1.80, 9.31]) and the highest quartile of Pentraxin-3 (aOR 2.18 [1.30, 3.65]) were associated with prevalent ILD (Figure 1). Concentrations of other biomarkers were not associated with prevalent RA-ILD. After excluding those with prevalent RA-ILD, 174 participants developed incident RA-ILD over 20,957 patient-years of follow-up. None of the analyte concentrations were significantly associated with incident RA-ILD risk (Table 1). However, the highest quartile of GDF-15 was associated with a >3-fold higher risk of incident RA-ILD (adjusted HR 3.21 [1.94, 5.32]) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: GDF-15, a member of the transforming growth factor-β family, was independently associated with both prevalent and incident RA-ILD in a large RA cohort. Other inflammatory- and fibrosis-related mediators seen in other fibrotic diseases, such as IPF and heart failure, were not associated with RA-ILD risk, suggesting there may be unique disease specific inflammatory and fibrotic pathophysiologic pathways in RA-ILD.
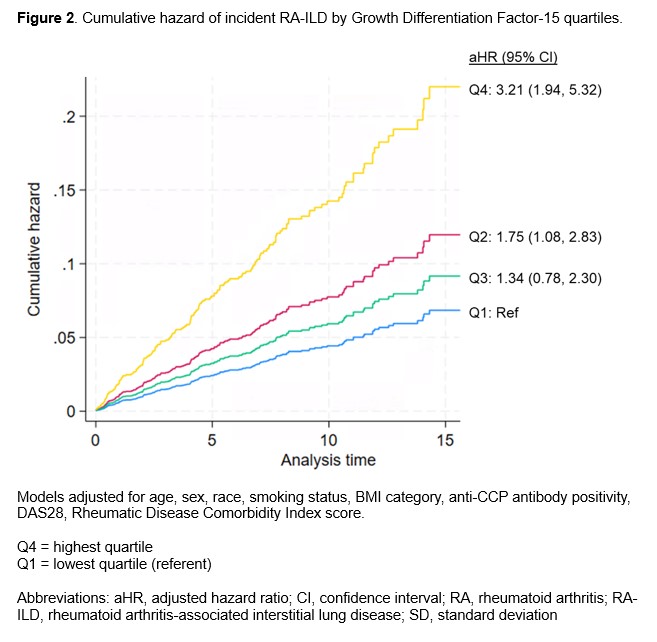 Table 1. Associations of selected inflammatory- and fibrosis-related mediators with prevalent and incident RA-ILD.
Table 1. Associations of selected inflammatory- and fibrosis-related mediators with prevalent and incident RA-ILD.
.jpg) Figure 1. Associations of Growth Differentiation Factor-15 and Pentraxin-3 quartiles with prevalent RA-ILD.
Figure 1. Associations of Growth Differentiation Factor-15 and Pentraxin-3 quartiles with prevalent RA-ILD.
.jpg) Figure 2. Cumulative hazard of incident RA-ILD by Growth Differentiation Factor-15 quartiles.
Figure 2. Cumulative hazard of incident RA-ILD by Growth Differentiation Factor-15 quartiles.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
England B, Johnson T, Duryee M, Frideres H, Wysham K, Cannon G, Kunkel G, Ascherman D, Richards J, Monach P, Kerr G, Reimold A, Baker J, Thiele G, Mikuls T. Inflammatory- and Fibrosis-Related Biomarkers and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Risk [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammatory-and-fibrosis-related-biomarkers-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-risk/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammatory-and-fibrosis-related-biomarkers-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-risk/
