Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High-density lipoprotein (HDL) eliminates cholesterol from atherosclerotic lesions, a function known as cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC). ATP-binding-cassette A1 (ABCA1) membrane transporter initiates cholesterol transfer from plaque macrophages to pre-b HDL particles. Methotrexate and biologic disease modifying drugs (bDMARDs) are atheroprotective whereas corticosteroids are proatherogenic. We here evaluated the influence of inflammation and these treatments on ABCA1-CEC and its relationship with coronary atherosclerosis burden, progression and cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Coronary atherosclerosis (noncalcified, partially or fully calcified plaque) was evaluated with computed tomography angiography in 140 patients without cardiovascular disease and reassessed in 99 after 6.9±0.4 years. Incident cardiovascular events were recorded. ABCA1-CEC was measured in J774 macrophages. Multivariable negative binomial and robust logistic regression evaluated associations of ABCA1-CEC with baseline plaque numbers and their progression at follow-up respectively. The moderating role of baseline inflammation, prednisone, methotrexate and bDMARD use on the relationship between ABCA1-CEC and cardiovascular risk was examined in multivariable Cox models including the respective moderators and their interaction term with ABCA1-CEC.
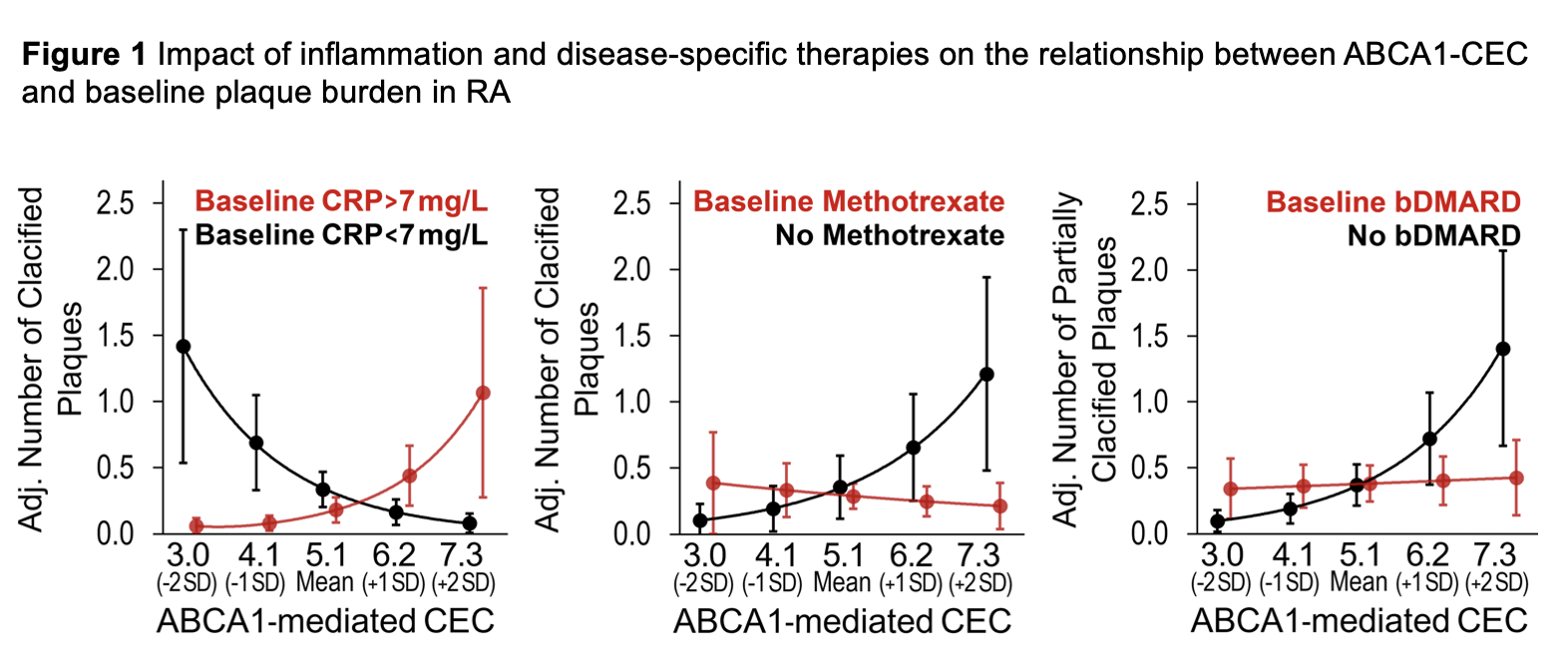
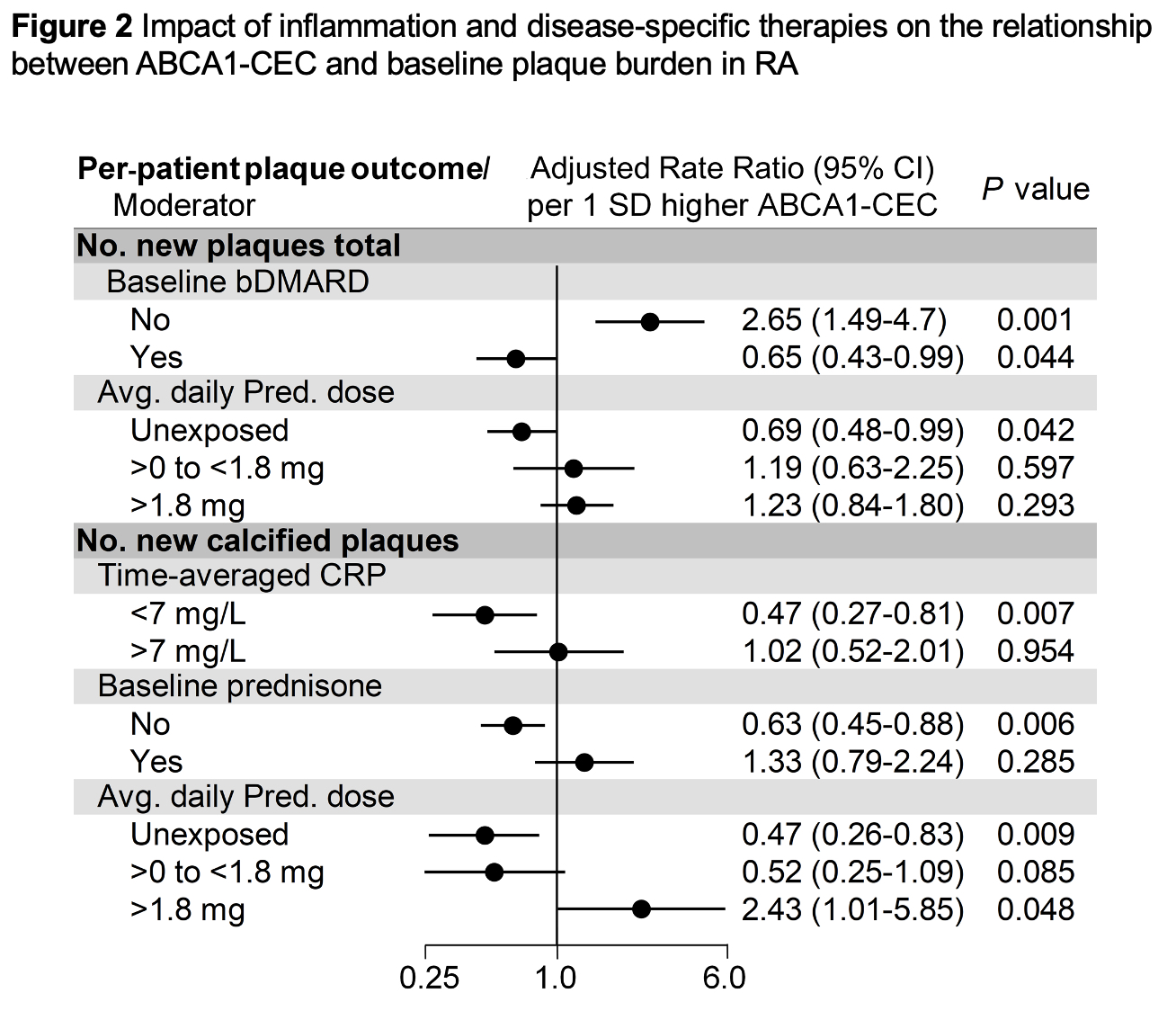
Results: ABCA1-CEC had no main effect on baseline atherosclerosis; prednisone use did not influence this relationship. Higher ABCA1-CEC (per standard deviation increment) associated with (i) more calcified plaques at baseline only in patients with CRP > 7mg/L (median) (p for interaction = 0.001), more calcified plaques only in methotrexate nonusers (p for interaction = 0.037), and more partially-calcified plaques only in bDMARD nonusers (p for interaction = 0.029, Figure 1); (ii) fewer new calcified plaques in patients with time-averaged CRP < 7mg/L (median) (p for interaction = 0.028, Figure 2); (iii) fewer new calcified plaques in baseline prednisone nonusers but not users (p for interaction = 0.021); (iv) fewer new total plaques in prednisone unexposed but not those exposed to prednisone during follow-up (p for interaction = 0.034), and fewer new calcified plaques in prednisone unexposed and more in those with high time-weighted average dose (p for interaction = 0.004); (v) more new plaques in baseline bDMARD nonusers and fewer in bDMARD users (p for interaction≤0.001); (vi) greater cardiovascular risk in baseline prednisone users but not nonusers (p for interaction = 0.027).
Conclusion: ABCA1-CEC attenuated coronary atherosclerosis burden and progression in patients with low baseline and cumulative inflammation and baseline methotrexate and bDMARD use. In contrast, ABCA1-CEC associated with plaque increase in corticosteroid users, methotrexate and bDMARD nonusers. While in well-treated, controlled disease ABCA1-CEC is atheroprotective, in uncontrolled RA its action may be masked or fails to counteract the proatherogenic state promoted by inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Papotti B, Ormseth S, Palumbo M, Hernandez E, Adorni M, Zimetti F, Budoff M, Ronda N. Inflammation and Immunomodulatory Therapies Influence the Relationship Between ATP-binding Cassette Transporter A1 (ABCA1)-mediated Cholesterol Efflux and Coronary Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammation-and-immunomodulatory-therapies-influence-the-relationship-between-atp-binding-cassette-transporter-a1-abca1-mediated-cholesterol-efflux-and-coronary-atherosclerosis-in-rheumatoid-arthri/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inflammation-and-immunomodulatory-therapies-influence-the-relationship-between-atp-binding-cassette-transporter-a1-abca1-mediated-cholesterol-efflux-and-coronary-atherosclerosis-in-rheumatoid-arthri/