Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2015–2051) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a progressive, systemic, fibroinflammatory disease characterized by unpredictable and recurring flares, leading to organ damage and decreased quality of life. Inebilizumab (INEB) is a humanized, glycoengineered, CD19-directed, monoclonal antibody that depletes CD19+ B cells, including plasmablasts and some plasma cells, effectively in a targeted manner. MITIGATE (NCT04540497) is an international, randomized, blinded, placebo (PBO)-controlled Phase 3 trial that evaluated the safety and efficacy of INEB as treatment for IgG4-RD, and met its primary endpoint (reduction in flare risk, INEB vs. PBO) and all key secondary endpoints. Here, we evaluate the safety and efficacy of INEB across MITIGATE subgroups defined by baseline organ involvement, with a focus on organs most commonly affected in the study population, organs with potentially urgent manifestations, and organs characteristic of the fibrotic phenotype of IgG4-RD.
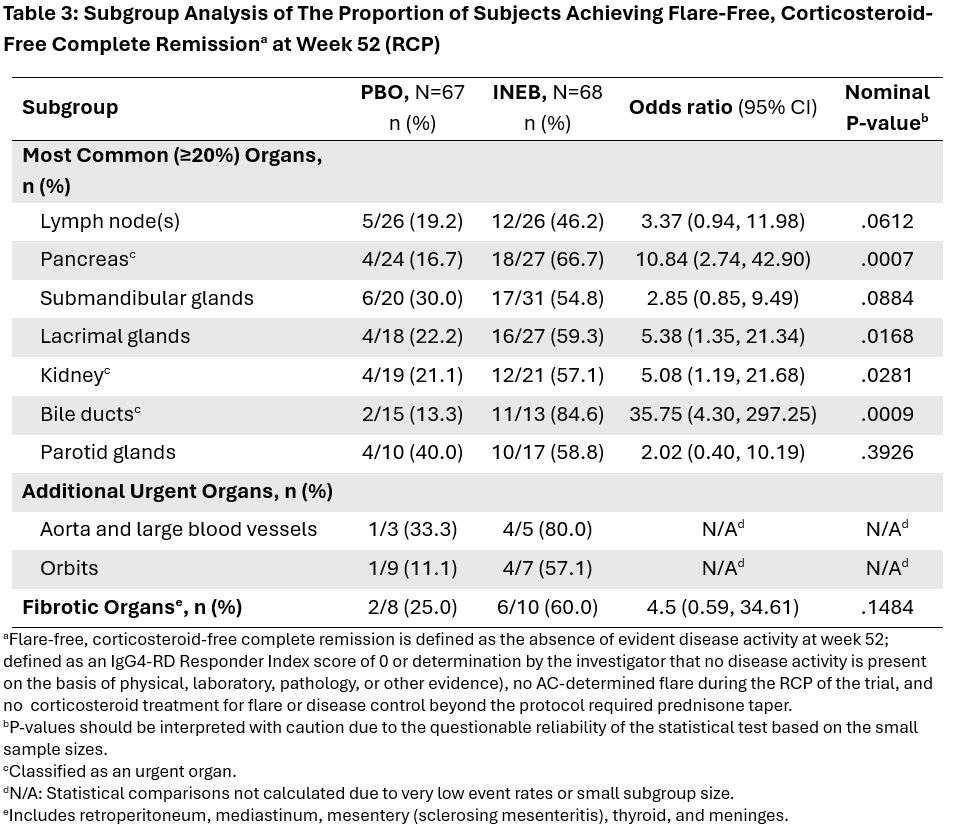
Methods: MITIGATE study design and results have been previously reported (Stone et al, NEJM 2024). All participants had experienced a recent flare (prior to screening) that required glucocorticoid (GC) treatment. Post hoc subgroup analyses of efficacy and safety were conducted in participants on the basis of the organs involved in this recent flare. Subgroups were defined by the most common organs (affecting at least 20% of participants), those with urgent or severe manifestations: pancreas, kidney, bile ducts, aorta and large blood vessels, and orbits; and those associated with the fibrotic phenotype of IgG4-RD: retroperitoneum, mediastinum, mesentery, thyroid, and meninges (Lanzillotta et al., 2023).
Results: 135 participants were randomized and received at least one dose of INEB (n=68) or PBO (n=67). The spectrum of organ involvement at baseline was generally well balanced between the 2 treatment groups (Table 1). INEB treatment reduced the risk of flare relative to PBO in all organ subgroups, with HR values similar to that of the overall population (HR 0.13) (Table 2). The greatest treatment effect was observed in participants with pancreatic (HR 0.03), bile duct (HR 0.00), and kidney (HR 0.08) involvement. The orbital and fibrotic organ groups also experienced clear benefit of INEB on flare risk reduction.Proportions of participants achieving flare-free, corticosteroid-free complete remission at Week 52 were increased by INEB in all organ subgroups with sufficient representation to permit analysis (Table 3). Proportion of subjects requiring on-study GCs for IgG4-RD control and mean daily dose of GCs per subject were substantially reduced with INEB vs. PBO in all organ subgroups with sufficient representation to permit analysis. Safety outcomes will be presented.
Conclusion: The MITIGATE trial demonstrates consistent safety and efficacy of INEB across all IgG4-RD subgroups defined on the basis of organ involvement at study baseline, including the most common organs, urgent organs, and organs characteristic of the fibrotic disease phenotype.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khosroshahi A, Culver E, Zhang W, Okazaki K, Tanaka Y, Lohr M, schleinitz n, Dong X, Cheng S, Cimbora D, Stone J. Inebilizumab Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Common, Urgent, and Fibrotic Organ Manifestations of IgG4-RD: Subgroup Analyses from the MITIGATE Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inebilizumab-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-common-urgent-and-fibrotic-organ-manifestations-of-igg4-rd-subgroup-analyses-from-the-mitigate-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/inebilizumab-efficacy-and-safety-in-patients-with-common-urgent-and-fibrotic-organ-manifestations-of-igg4-rd-subgroup-analyses-from-the-mitigate-trial/

.jpg)
.jpg)