Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Presence of citrullinated protein fragments in the circulation of patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a highly disease-specific phenomenon. Vimentin is often a target for citrullination and MMP-mediated degradation as a consequence of disease initiation and progression. Generation of citrullinated or non-citrullinated vimentin fragments (VICM and VIM) are associated with chronic inflammation and can be of high biomarker potential for disease and treatment monitoring. In this study, we aimed to investigate if two different monotherapies, Tocilizumab (TCZ) and Methotrexate (MTX) can differently modulate serum levels of VIM and VICM in RA patients at the early therapy time-point.
Methods: Patients with moderate to severe RA in phase III randomized controlled clinical trial were exposed to either TCZ monotherapy (8 mg/kg every 4 weeks) or MTX monotherapy (starting at 7.5 mg/kg and titrated to 20 mg/kg) over 24 weeks. Serum levels of VIM and VICM were measured at baseline and 8-weeks sera from 304 RA patients and 64 healthy controls by validated ELISA assays. We investigated the comparison between treatment and response groups using ANCOVA and correlations using Spearman’s rho adjusted for patient demographic characteristics (gender, age, BMI and disease duration).
Results: Serum levels of VIM and VICM were significantly higher in RA patients than in healthy controls (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 1). RA patients with the greatest disease activity had the highest serum levels of VICM (P < 0.01). VIM and VICM biomarkers were significantly inhibited at week 8 by TCZ compared to placebo patients (P < 0.001 and P < 0.0001, respectively) (Fig. 2). The inhibition of VIM and VICM levels with TCZ was respectively 33% and 34% greater than that of MTX (both P < 0.0001). Biomarker profiles of VIM and VICM revealed a significant inhibition difference in MTX ACR50 treatment responding and non-responding patients (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01), whereas no statistically significant difference was observed in TCZ ACR50 patients. Change in serum levels of VICM to week 8 in MTX patients correlated significantly with change in disease activity score-28 (DAS28) at week 8, 16 and 24 (rho 0.31 to 0.23, P = 0.0006 to 0.01).
Conclusion: Present findings show that patients treated with TCZ for 8 weeks have clearly higher suppression of VIM and VICM biomarkers over patients treated with MTX. The differences in biomarker profiles of ACR50 patients enable for their stratification and identification of those who benefit from the treatment at the early time-point. The correlation of serum VICM with DAS28 at different time-points may suggest its treatment prognostic value in RA.
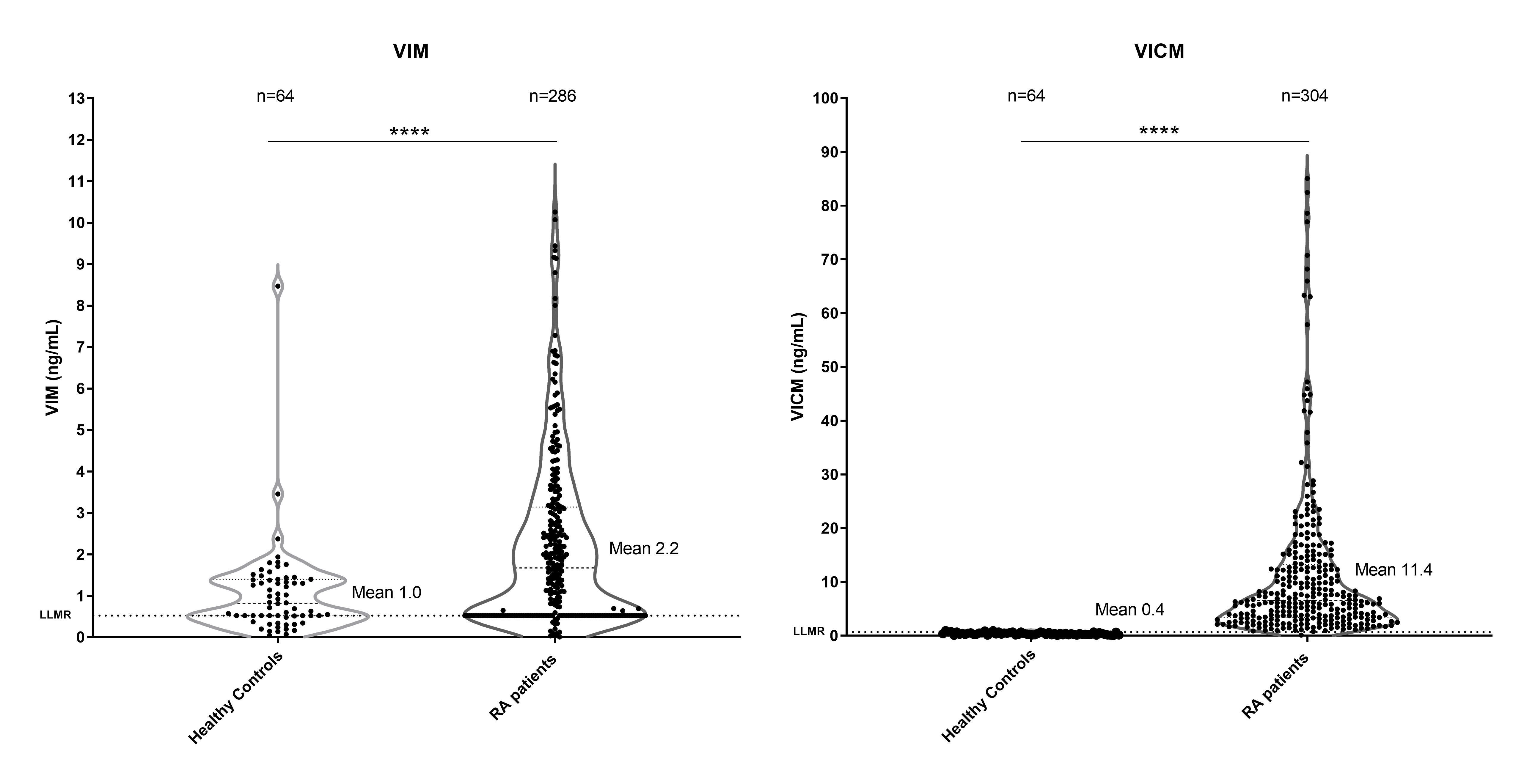 Figure 1. Figures represent differences in serum levels of VIM and VICM biomarker between healthy controls and RA patients at baseline.
Figure 1. Figures represent differences in serum levels of VIM and VICM biomarker between healthy controls and RA patients at baseline.
 Figure 2. Figures represent differences in modulation of VIM and VICM biomarker levels according to treatment group from baseline to week 8. Data are shown as mean with confidence interval CI-95%.
Figure 2. Figures represent differences in modulation of VIM and VICM biomarker levels according to treatment group from baseline to week 8. Data are shown as mean with confidence interval CI-95%.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Drobinski P, Bay-Jensen A, Siebuhr A, Karsdal M. Increased Serum Levels of Circulating Vimentin and Citrullinated Vimentin Are Differently Regulated by Tocilizumab and Methotrexate Monotherapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-serum-levels-of-circulating-vimentin-and-citrullinated-vimentin-are-differently-regulated-by-tocilizumab-and-methotrexate-monotherapies-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-serum-levels-of-circulating-vimentin-and-citrullinated-vimentin-are-differently-regulated-by-tocilizumab-and-methotrexate-monotherapies-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
