Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: MAIT (mucosal associated invariant T) cells are involved in mucosa defense against bacteria. This cellular subset is characterized by a semi-invariant αβ TCR and the expression of CD161. In patients with axial spondyloarthritis (ax SpA), previous works reported a decreased frequency of circulating MAIT cells compared to normal subjects. IL-17A is a relevant cytokine involved in SpA pathophysiology. MAIT cells are a cellular source of IL-17 and IL-17+ MAIT cells were found increased in ax SpA. We have previously reported an increased frequency of IFNγ+/IL-17+ MAIT cells as well as IL-22+ MAIT cells in ax SpA.
In this study, we aimed to complete our previous results by evaluating activation markers and chemokine receptor/integrin expression, especially those for gut homing, in MAIT cells.
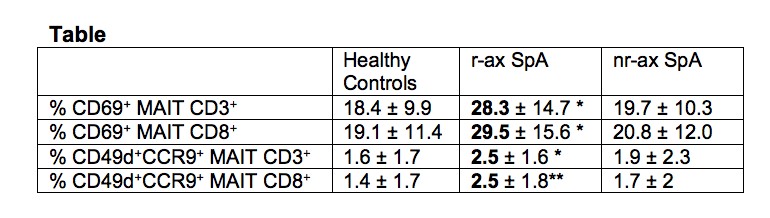
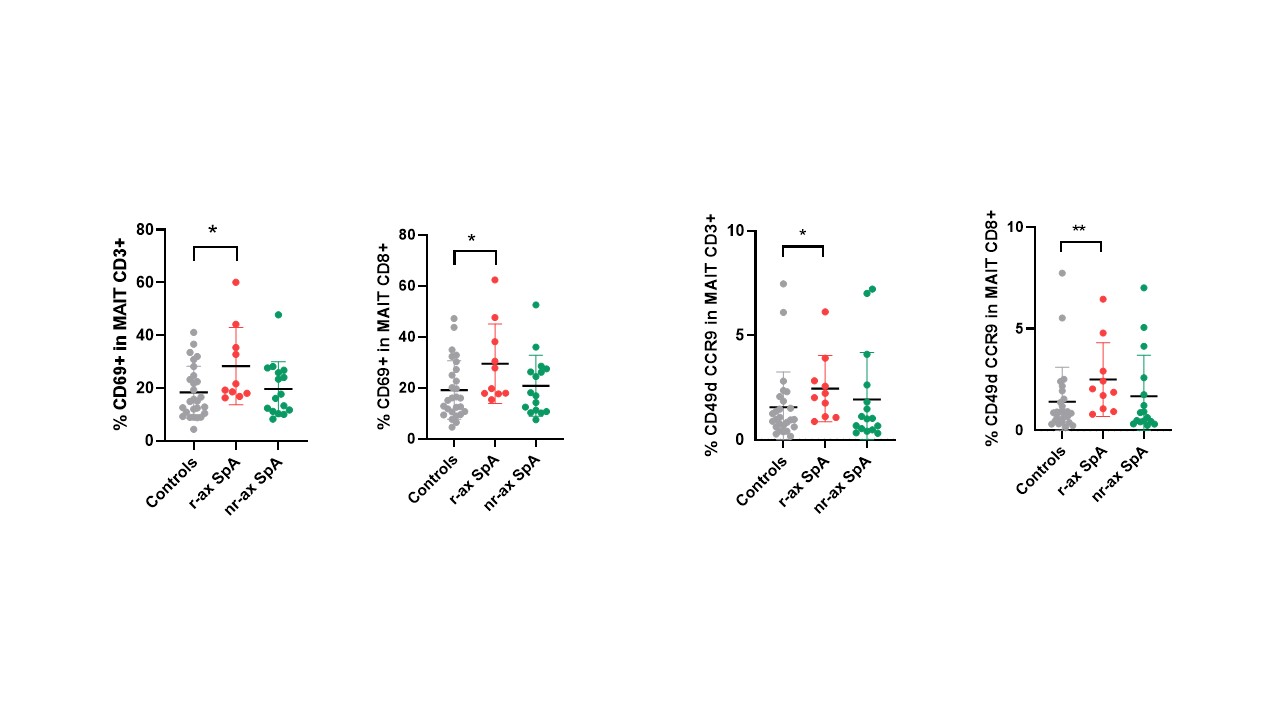
Methods: patients exhibited ax SpA (ASAS criteria) with a radiographic (r-ax SpA) or non-radiographic (nr-ax SpA) form. They all were under NSAIDs and biologic naïve. Healthy subjects were recruited as controls (HC). Circulating CD4+and CD8+T cells and MAIT cells were determined on blood samples by single platform flow cytometry (Cytoflex, Beckman Coulter). MAIT cells were identified by the co-expression of CD3, CD161 and TCRα7.2. In each subpopulation, we examined the expression of CD26, CD69, CCR9 and CD49d integrin.
Results: 26 patients were included (11 r-ax SpA: 9 males [M]; mean age 54.1 ± 19.6 years; disease duration: 16.2 years; ASDAS score: 4.1; and 15 nr-ax SpA: 7 M; age: 36.4 ± 1.3; ASDAS: 5.6) and 27 HC (16 M; age: 43 ± 12.7). In patients with r-ax SpA, we observed an increased frequency of activated CD3+ CD69+ MAIT cells and CD3+ MAIT cells expressing the gut homing markers CCR9 and CD49d, as compared to HC (p < 0.05). These higher frequencies were not observed in patients with nr-ax SpA. In addition, when examining the CD8+ MAIT population, similar higher frequencies of cells positive for CD69, CCR9 and CD49d were observed in patients with r-ax SpA compared to HC and patients with nr-ax SpA (p< 0.01 and p< 0.05, respectively).These modifications were specific for MAIT cells and were not observed in conventional CD4+ or CD8+ T lymphocytes.
Conclusion: patients with r-ax SpA are characterized by an increased frequency of activated MAIT cells that expressed homing receptors (chemokine and integrin) for the gut. These results suggest an involvement of this cellular population in the gut-joint axis that is well described in the pathophysiology of SpA.
these results confirm that MAIT cells are altered in ax SpA and highlight the relationships between ax SpA and gut inflammation, especially for the radiographic form.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Toussirot E, Laheurte C, Gravelin E, Vauchy C, Puyraveau M, Saas P. Increased Frequency of Activated MAIT Cells Expressing the Gut Homing Receptor CCR9 in Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-frequency-of-activated-mait-cells-expressing-the-gut-homing-receptor-ccr9-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-frequency-of-activated-mait-cells-expressing-the-gut-homing-receptor-ccr9-in-patients-with-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/