Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Depression occurs with a prevalence of about 17% (95% confidence interval (CI): 10-24) in patients with RA (1) and both disorders may share common proinflammatory pathways affecting neural and extra-neural tissues (2). Recently, in an incident RA single center cohort, we have shown that the main indication for dispensing antidepressants is depression and the frequency of dispensing coincides with the occurrence of depression reported in the medical literature (3). In the present study, we used the first dispensing of antidepressants as proxy for clinical depression with the aim to describe the mortality risk associated with depression in patients with incident RA.
Methods: In DANBIO (4), we identified 18,085 patients diagnosed with RA (index date) from January 1, 2008 to September 30, 2018 by their unique personal registration numbers. We excluded patients with a recorded dispensing of MTX (Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical code L01BA01) and/or antidepressants (N06A) in the Danish National Prescription Register or recorded hospital contacts with RA (International Classification of Diseases (version 10) codes M05 or M06) in the Danish National Patient Register, 3 years prior to the index date. From the index date, we defined depression as first dispensing of antidepressants and collected death dates from the Danish Civil Registration System. The patients were followed until December 31, 2018 and all-cause mortality was estimated in two dynamic risk periods: the period from the index date until first dispensing of antidepressants (if it occurred) and the period after dispensing of antidepressants. We calculated hazard rate ratios (HRR) by modelling dispensing of antidepressants as time-varying exposure and adjusted for potential confounders: age, gender, comorbidity, cohabitation, employment status, highest attained education, and income.
Results: We included 11,187 incident RA patients of which 1,111 (10%) were initiators of antidepressants (Table 1). Initiation of antidepressants was a strong predictor of both 2-year mortality (adjusted HRR 3.53) and mortality during the total follow-up period (adjusted HRR 3.23) (Table 2).
Conclusion: Depression, defined as first dispensing of antidepressants, was associated with more than 3-fold increased mortality risk in patients with incident RA.
1. Matcham F, et al. The prevalence of depression in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2013;52:2136-48.
2. Nerurkar L, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and depression: an inflammatory perspective. Lancet Psychiatry 2019;6:164-73.
3. Pedersen JK, et al. No difference in antidepressant prescription in rheumatoid arthritis and controls. Results from a population-based, matched inception cohort. (Accepted, Scand J Rheumatol 2021).
4. Ibfelt EH, et al. The Danish nationwide clinical register for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: DANBIO. Clin Epidemiol 2016;8:737-42.
 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of RA patients by depression status defined as first dispensing of antidepressants (no missing observations unless otherwise stated)
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of RA patients by depression status defined as first dispensing of antidepressants (no missing observations unless otherwise stated)
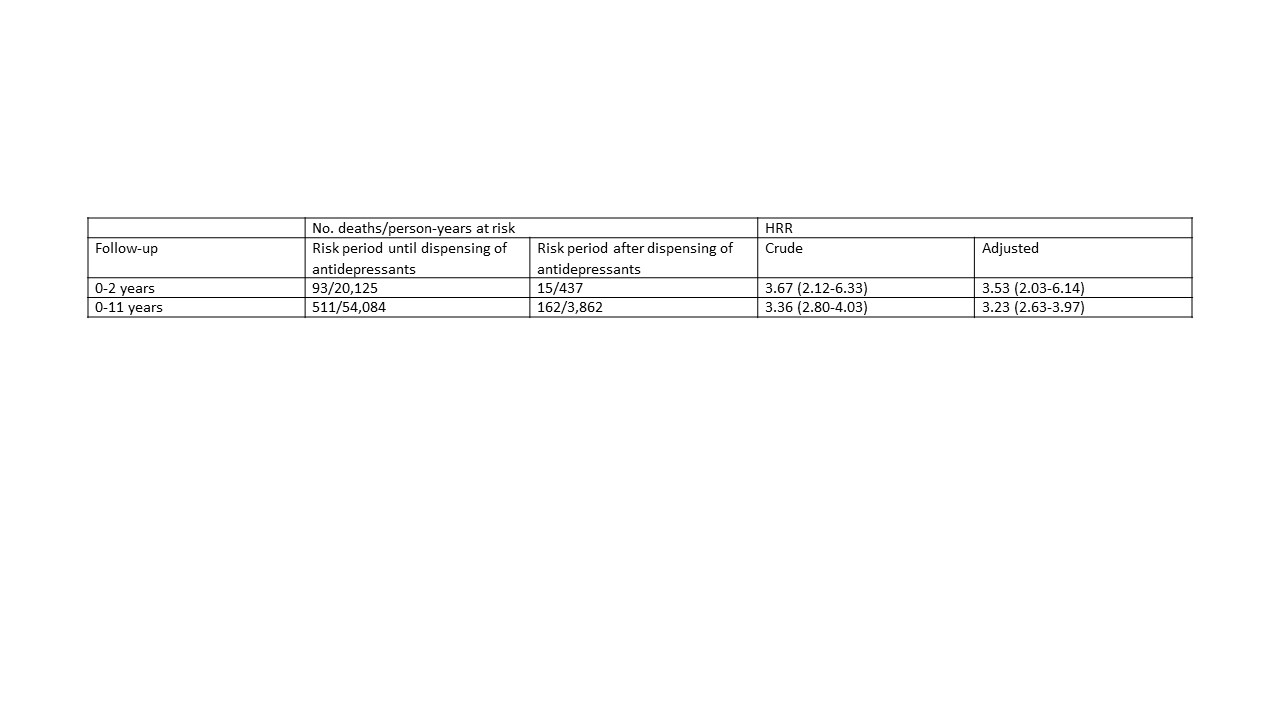 Table 2. Crude and adjusted HRR (95% CI) for death, comparing mortality in the risk period until and after dispensing of antidepressants.
Table 2. Crude and adjusted HRR (95% CI) for death, comparing mortality in the risk period until and after dispensing of antidepressants.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pedersen j, Wang L, Pedersen A, Andersen K, Sørensen C, Ellingsen T. Increased All-Cause Mortality Risk in Patients with Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis After First Antidepressant Dispensing: Results from the Nationwide DANBIO Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-all-cause-mortality-risk-in-patients-with-incident-rheumatoid-arthritis-after-first-antidepressant-dispensing-results-from-the-nationwide-danbio-database/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-all-cause-mortality-risk-in-patients-with-incident-rheumatoid-arthritis-after-first-antidepressant-dispensing-results-from-the-nationwide-danbio-database/
