Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1082–1099) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The 2022 ACR guidelines for vaccination strongly recommend recombinant VZV vaccination for all patients > 18 years old who are taking immunosuppressive medication. Studies have shown that there is a higher risk of shingles in patients on JAK inhibitors. To assess the Shingrix vaccination rate at the rheumatology outpatient practice of an urban academic institution and improve adherence, we initiated a quality improvement project in patients who are on JAK inhibitors.
Methods: The primary aim of our QI project was to increase the Shingrix vaccination rate by 10%. We also attempted to identify the risk factors for eligible patients not receiving Shingrix despite guideline recommendations. We acquired data quarterly from electronic health records, including patients’ MRN, age, sex, race, Shingrix vaccination status, and last visit dates. Vaccination status was further validated with manual chart review. Data obtained from 4/1/2022 to 6/30/2022 were considered the baseline. We implemented interventions via Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) method: 1) provide posters at clinics to improve awareness, 2) remind eligible patients during the encounter 3) notify patients’ primary rheumatologists quarterly. Data were obtained from 9/1/2022-11/30/2022 and 12/1/2022-2/28/2023 respectively. We used descriptive statistics and analyzed the data via Stata/SE 17.0, stratified by Shingrix vaccination status. We also studied the trend of the Shingrix vaccination rate.
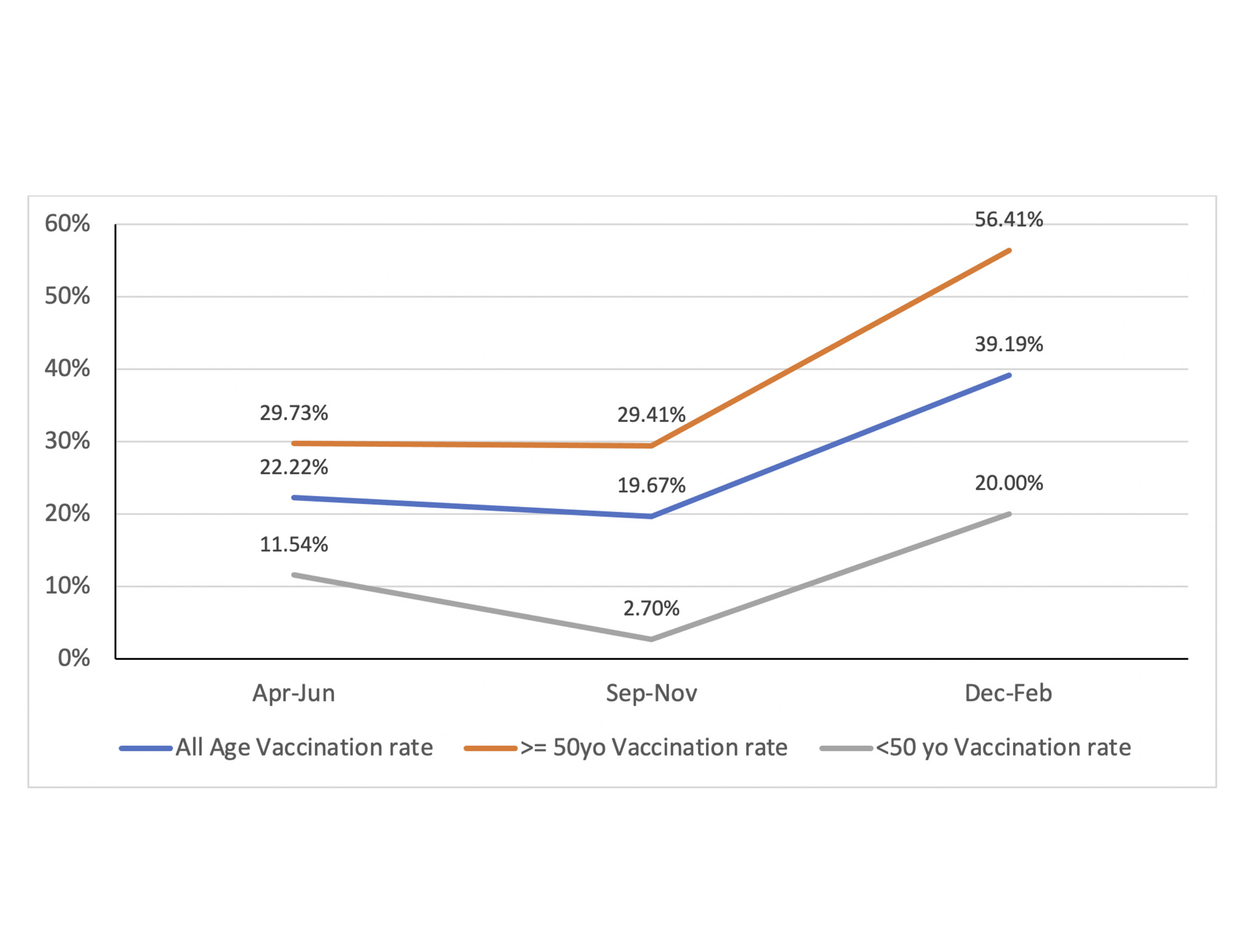
Results: From 4/1/2022 to 2/28/2023, the Shingrix vaccination rate raised from 22.22% (14/63) to 39.19% (29/74) after two cycles of PDSA, meeting our goal of a 10% increase. (Figure 1) After PDSA #1 in 9/2022, the overall vaccination rate slightly declined to 19.67%. After PDSA #2 in 12/2022, it significantly improved. Among all the patients (N = 198) seen from 4/1/2022 – 2/28/2023, 55.56% (110) of them were ≥ 50 years old while 44.44% (88) were < 50 years old. 14.14% (28) were male, while 85.86% (170) were female. 41.41% (82) of the patients were Caucasian, 10.61% (21) were African American, and 9.09% (18) of the patients identified as AAPI.
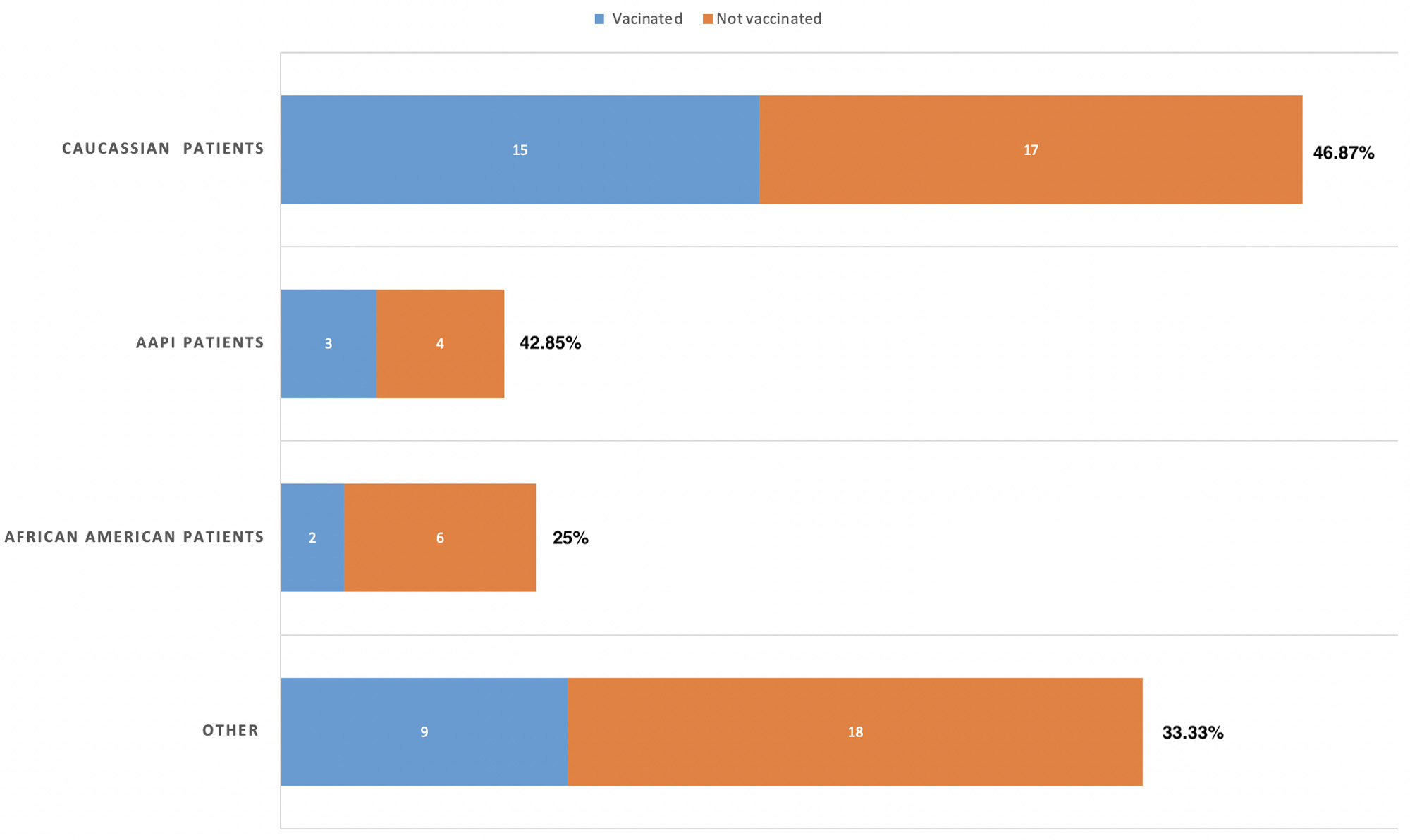
Patients ≥ 50 years old had higher vaccination rate than patients < 50 years old. (Figure 1) From 4/1/2022 to 2/28/2023, patients ≥ 50 years old had a significant increase in vaccination rate from 29.73% to 56.41%. Male and female patients had similar vaccination rates, with 41.67% male and 38.71% female vaccinated. Despite the improvement in the 12/2022 – 2/2023 period, patients who identified as African American had a lower vaccination rate than their Caucasian counterparts. 25% (2/8) African American patients were vaccinated compared to 46.97% (15/32) Caucasian patients. (Figure 2)
Conclusion: Our interventions improved the Shingrix vaccination rate. Congress’s new bill eliminating the cost of vaccines covered by Medicare Part D may have also played a role. Besides achieving our goal of a 10% increase, we identified the risk factors for lower vaccination rates: patients < 50 years old and African American patients. As the PDSA cycle continues, targeted interventions will be implemented to address disparities and improve adherence to Shingrix vaccination.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Feng J, Koci K. Increase Shingrix Vaccination Rate in Patients on JAK Inhibitors: A Quality Improvement Project at the Rheumatology Practice of an Urban Institution [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increase-shingrix-vaccination-rate-in-patients-on-jak-inhibitors-a-quality-improvement-project-at-the-rheumatology-practice-of-an-urban-institution/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increase-shingrix-vaccination-rate-in-patients-on-jak-inhibitors-a-quality-improvement-project-at-the-rheumatology-practice-of-an-urban-institution/