Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Comorbidities
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: In 2021, the European and US-American regulatory agencies EMA and FDA issued warnings about malignancy risk associated with the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) tofacitinib and required changes in labelling. These actions were based on results of the post-authorisation safety trial Oral Surveillance (OST)[1]. We aimed to analyse incident malignancies under treatment with JAKi, tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), abatacept (ABA), rituximab (RTX), interleukin 6 inhibitors (IL6i) or conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs – bionaive) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) observed in daily rheumatological care.
Methods: Data from patients without cancer history enrolled in the biologics register RABBIT and initiating any DMARD treatment between 01/2017 – 04/2022 were included. Incidence rates (IR) of malignancies (without non melanoma skin cancer) per 1000 patient-years (PY) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and adjusted hazard ratios (HR) were calculated for all and for selected patients according to OST inclusion criteria (age ≥ 50 years and ≥ 1 cardiovascular (CV) risk factor) to compare treatment groups to the reference (TNFi). Andersen-Gill regression analysis was used with a 6-months risk window, adjusted via stabilized and winsorized inverse probability of treatment weights taking into account age, sex, smoking, disease activity, prior therapies, comorbidities, and type of enrolling institution (clinic vs. private practice) as covariates. Multiple imputation of missing data was applied.
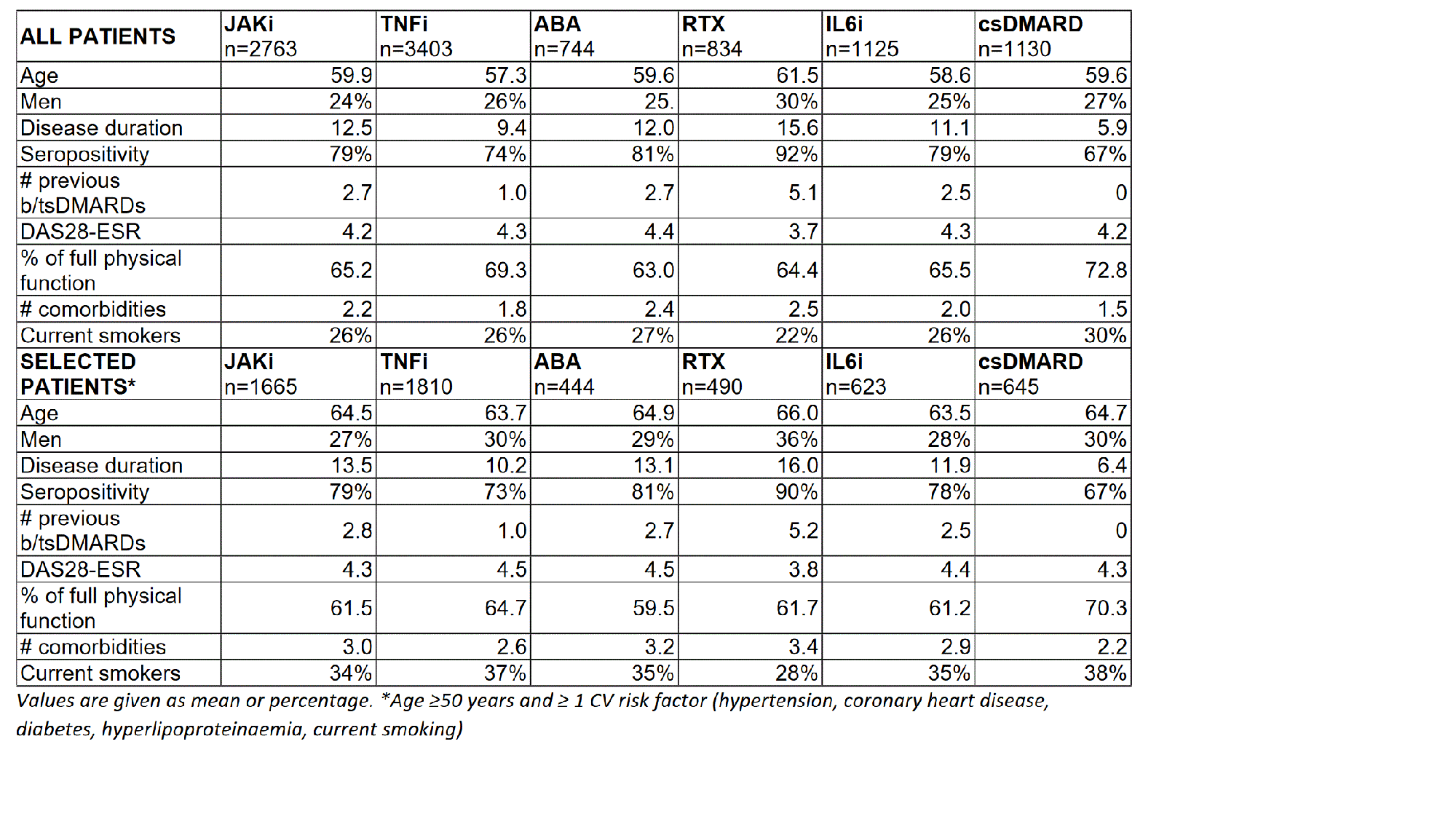
Results: 2763 JAKi, 3403 TNFi, 744 ABA, 834 RTX, 1125 IL6i and 1130 csDMARD initiations were documented. Patients with a JAKi start were less often men and (with exception of RTX) slightly older and had a longer RA disease duration (table). The proportion with positive autoantibodies and the number of previous treatments with biological (b) or targeted (ts) synthetic DMARDs was higher than in the TNFi and csDMARD group, but lower than in the ABA and RTX groups.
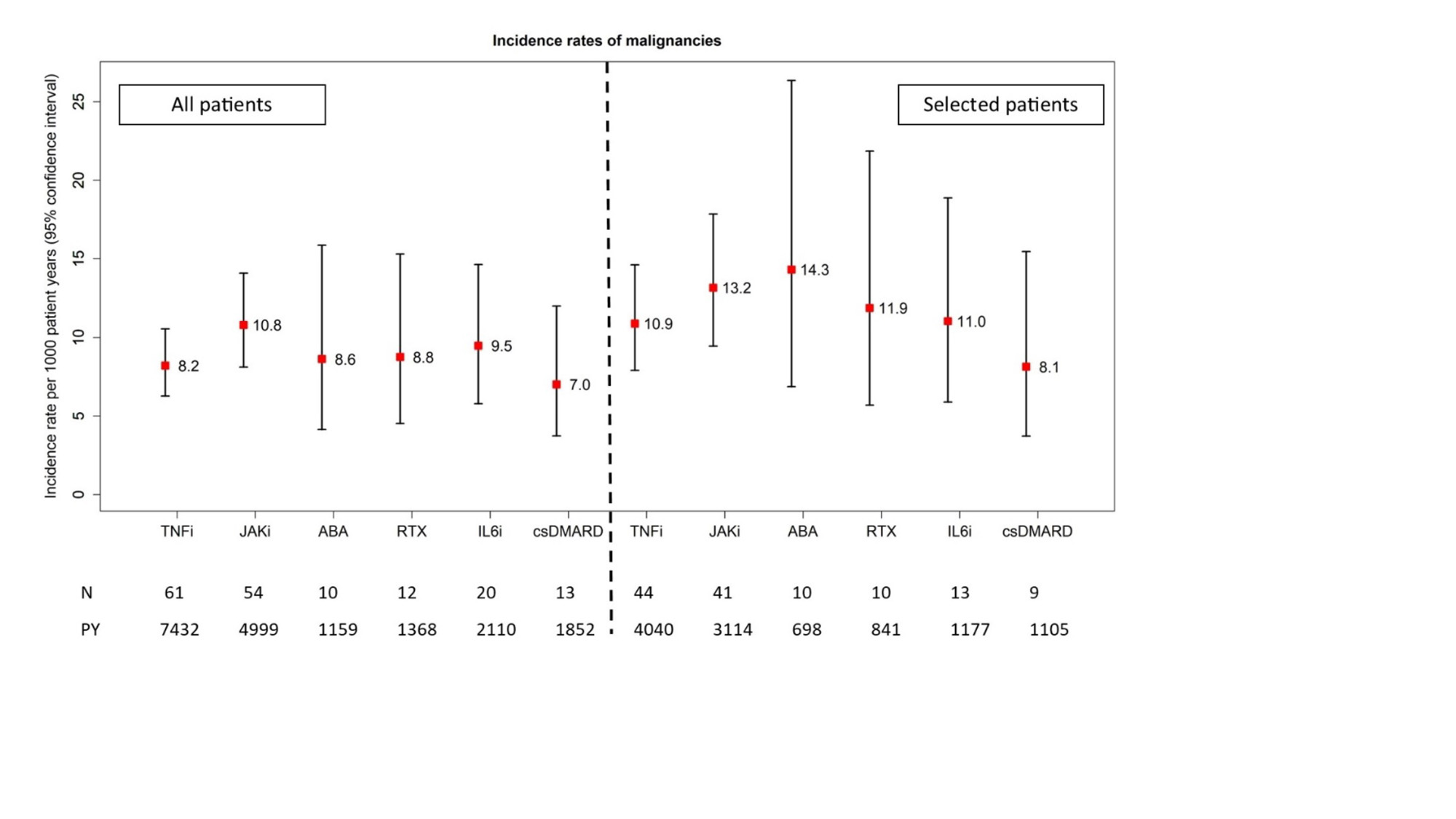
151 incident malignancies were reported. Across treatments, patients showed comparable IRs between 7 and 11 events per 1000 PY (10.8 events per 1000 PY in JAKi patients, 95% CI: 8.1 – 14.1, see figure). Among selected patients IRs were higher (13.2 events per 1000 PY in JAKi patients, 95% CI: 9.5 – 17.9). In adjusted analyses, neither JAKi (HR 1.07, 95% CI: 0.71 – 1.62), ABA (HR 0.73, 0.38 – 1.40), RTX (HR 0.86, 0.42 – 1.75), IL6i (HR 0.79, 0.44 – 1.40) nor csDMARDs (HR 2.07, 0.87 – 4.94) showed a significantly altered risk for malignancies compared with TNFi in unselected patients, with similar results in selected patients.
Conclusion: IR of malignancies in selected patients receiving JAKi in a real-world setting was numerically higher than the IR reported for tofacitinib in the Oral Surveillance study. However, we found no statistical evidence of an increased risk of malignancies with JAKi compared to TNFi, although patients on JAKi were older and had longer disease duration and more previous b/tsDMARDs treatments. Further analyses assessing exposure in terms of treatment duration are needed.
References:
[1] PMID: 35081280
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schaefer M, Meissner Y, Manger B, Berger S, Rockwitz K, Regierer A, Strangfeld A. Incident Malignancies in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Daily Rheumatological Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incident-malignancies-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-daily-rheumatological-care/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incident-malignancies-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-daily-rheumatological-care/