Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 12:00PM-12:50PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an expensive disease which untreated can lead to disability and socioeconomic burden. This high cost of treatment impacts the use of limited medical resources. Subcutaneous (SC) methotrexate (MTX) has higher bioavailability, greater efficacy and better tolerability when compared with oral MTX. Furthermore, it is a less costly treatment prior to starting biologics. In our study, we aimed to provide Treat-to-Target and value concordant care by increasing the use of SC MTX.
Methods: Baseline and prospective data on RA patients treated with MTX were obtained from the EHR (Epic) 2/1/2017 -4/2020 with intervention starting 11/2018. Prior to testing, a Treat-to-Target plan for increasing the use of SC MTX was discussed with the rheumatologists. A value concordant DMARD table was built and available in the EHR during each visit. Patients received medication education via the physician or rheumatology pharmacist. Data on value concordant MTX use, Clinical Disease Active Index (CDAI) and financial costs was collected and analyzed quarterly pre and post intervention. SC MTX was designated as value concordant while oral MTX was designated as non-value concordant. The percentage of value concordant MTX use was calculated by dividing SC MTX by total MTX use. The mean uncontrolled CDAI was calculated by dividing the number of RA patients with CDAI >10 by the total RA population with a CDAI. The MTX cost was determined by calculating the average cost per MTX script per month (both oral and SC methotrexate). Shewhart charts were used to analyze data. The SC MTX use per individual physician pre and post intervention was determined by finding the absolute and relative increase for each.
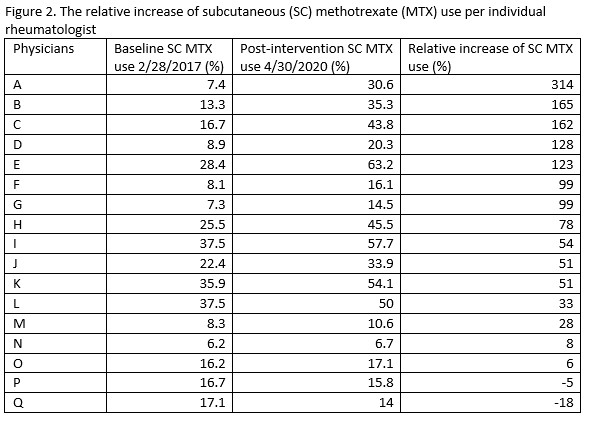
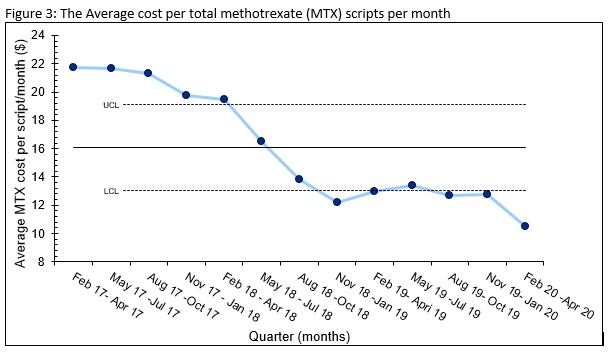
Results: The use of total SC MTX among RA patients showed an absolute and relative increase of 8% and 50% respectively between 2/2017 at baseline to 4/30/2020 post intervention (Figure 1). The Shewhart P-Chart analysis met statistical significance for increased SC MTX use. 88% of individual physicians prescribing MTX had a relative increase of 93% SC use with high to low range varying between (+)315% to (-)18% (Figure 2). The % of RA patients with CDAI > 10 remained stable during the study. The average cost per MTX script per month within our health care plan steadily decreased from $21.73 (2/1/17- 4/30/17) pre intervention to $10.53 (2/1/20 – 4/30/20) post intervention for an absolute cost decrease of 49% meeting statistical significance per Shewhart I-chart (Figure 3).
Conclusion: The healthcare cost associated with RA treatment is substantial, and it creates a financial and economic burden. Patients and rheumatologists can work together to create individualized treatment plans to control the disease without causing excessive financial strain. Our study showed that the increased use of SC methotrexate provided a more cost-effective treatment plan for our RA population by reducing the average methotrexate cost per script per month by 49% without compromising the quality of care. It also suggested that the intervention we used was successful in modifying our rheumatologists’ decision making to provide greater value concordant care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bankert J, Cote J, Chronowski J, Newman E. Improving Value Concordant Care Through Increased Use of Subcutaneous Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-value-concordant-care-through-increased-use-of-subcutaneous-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improving-value-concordant-care-through-increased-use-of-subcutaneous-methotrexate-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/